100% found this document useful (1 vote)
491 views12 pagesROHC in LTE: Compression Techniques
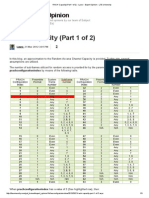
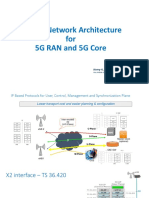
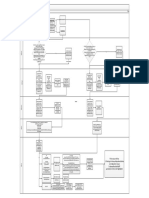
This document discusses Robust Header Compression (ROHC) in LTE networks. ROHC is used to compress headers of IP packets like IPv4, IPv6, UDP, and RTP to reduce their size from 40-60 bytes down to 2-3 bytes. This compression saves bandwidth and is useful for real-time applications like voice calls, texting, and gaming that generate many small packets. The document describes the basics of ROHC including its implementation in the PDCP layer and use of compressor and decompressor state machines. It also covers ROHC modes of operation, profiles, logs, and calculations for VoLTE packet size and scheduling blocks with and without ROHC enabled.
Uploaded by
rahulCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
491 views12 pagesROHC in LTE: Compression Techniques
This document discusses Robust Header Compression (ROHC) in LTE networks. ROHC is used to compress headers of IP packets like IPv4, IPv6, UDP, and RTP to reduce their size from 40-60 bytes down to 2-3 bytes. This compression saves bandwidth and is useful for real-time applications like voice calls, texting, and gaming that generate many small packets. The document describes the basics of ROHC including its implementation in the PDCP layer and use of compressor and decompressor state machines. It also covers ROHC modes of operation, profiles, logs, and calculations for VoLTE packet size and scheduling blocks with and without ROHC enabled.
Uploaded by
rahulCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 12