0% found this document useful (0 votes)
58 views22 pagesUnit 1 - Introduction
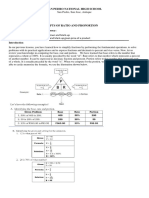
This document provides an introduction to marketing. It defines marketing as the process of planning and executing the conception, pricing, promotion, and distribution of ideas, goods and services to create exchanges that satisfy individual and organizational goals. The core concepts of marketing are identified as the business enterprise, environmental scanning, product/services development, value and customer satisfaction, the exchange process, and customer relationship management. The evolution of marketing philosophies from the production, product, and selling concepts to today's customer-centric marketing concept and societal marketing concept are outlined. The importance of marketing and the 4P's of the marketing mix - product, price, place, and promotion - are also summarized.
Uploaded by
Mohammed TauheedCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
58 views22 pagesUnit 1 - Introduction
This document provides an introduction to marketing. It defines marketing as the process of planning and executing the conception, pricing, promotion, and distribution of ideas, goods and services to create exchanges that satisfy individual and organizational goals. The core concepts of marketing are identified as the business enterprise, environmental scanning, product/services development, value and customer satisfaction, the exchange process, and customer relationship management. The evolution of marketing philosophies from the production, product, and selling concepts to today's customer-centric marketing concept and societal marketing concept are outlined. The importance of marketing and the 4P's of the marketing mix - product, price, place, and promotion - are also summarized.
Uploaded by
Mohammed TauheedCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 22