0% found this document useful (0 votes)
144 views4 pagesData Dependency Graph
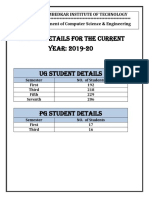
This document discusses data dependency graphs (DDG), which represent data dependencies using acyclic graphs with instructions as nodes. DDGs differ from data flow graphs in that they do not include control structures. DDGs are normally represented using tree data structures that examine instruction pairs for dependencies and construct the graph accordingly. An example DDG is given for 5 instructions showing their dependencies.
Uploaded by
Vishal SindhnoorCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
144 views4 pagesData Dependency Graph
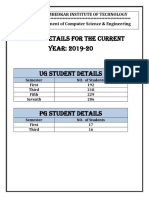
This document discusses data dependency graphs (DDG), which represent data dependencies using acyclic graphs with instructions as nodes. DDGs differ from data flow graphs in that they do not include control structures. DDGs are normally represented using tree data structures that examine instruction pairs for dependencies and construct the graph accordingly. An example DDG is given for 5 instructions showing their dependencies.
Uploaded by
Vishal SindhnoorCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 4