0% found this document useful (0 votes)
441 views12 pagesUnit-4-STL File Problems
The document discusses common problems that can occur with STL files generated from CAD models, including:
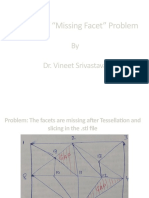
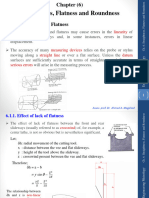
1. Gaps or holes in the tessellated model known as shell punctures, which occur when facets are missing.
2. Degenerate or invalid facets, which have collinear vertices or all vertices lying in the same plane.
3. Inconsistent or incorrectly oriented facet normals, which can result in the model material appearing on the wrong side of facets. This is a common issue with finite element mesh generation.
4. Overlapping facets caused by numerical rounding errors during the tessellation process setting tolerances too loosely.
Uploaded by
Kushal GortiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
441 views12 pagesUnit-4-STL File Problems
The document discusses common problems that can occur with STL files generated from CAD models, including:
1. Gaps or holes in the tessellated model known as shell punctures, which occur when facets are missing.
2. Degenerate or invalid facets, which have collinear vertices or all vertices lying in the same plane.
3. Inconsistent or incorrectly oriented facet normals, which can result in the model material appearing on the wrong side of facets. This is a common issue with finite element mesh generation.
4. Overlapping facets caused by numerical rounding errors during the tessellation process setting tolerances too loosely.
Uploaded by
Kushal GortiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 12