100% found this document useful (1 vote)
780 views39 pagesSwitch Yard REVISE
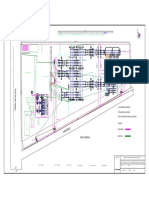
The document discusses switchyard layouts and equipment. It defines a switchyard as a switching station that links generating stations to transmission systems and allows for voltage step-up/step-down depending on network requirements. It classifies substations based on service, mounting, function and apparatus type. Various switching schemes are described including single bus, main and transfer bus, ring bus, and double bus double breaker schemes. Insulation levels and clearance requirements are provided for different voltage levels. The document concludes with details about equipment used at RSTPS including transformers, circuit breakers, transmission lines and switchyard components.
Uploaded by
Prashanth PittaCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
780 views39 pagesSwitch Yard REVISE
The document discusses switchyard layouts and equipment. It defines a switchyard as a switching station that links generating stations to transmission systems and allows for voltage step-up/step-down depending on network requirements. It classifies substations based on service, mounting, function and apparatus type. Various switching schemes are described including single bus, main and transfer bus, ring bus, and double bus double breaker schemes. Insulation levels and clearance requirements are provided for different voltage levels. The document concludes with details about equipment used at RSTPS including transformers, circuit breakers, transmission lines and switchyard components.
Uploaded by
Prashanth PittaCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 39