0% found this document useful (0 votes)
70 views29 pagesIntroduction To Program Logic Formulation
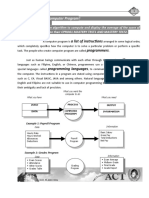
1. The document introduces the concepts of data, information, procedures, computer programs, and the programming process.
2. It explains that data becomes information when it is organized and processed, and that a computer program consists of a set of instructions that direct a computer to perform a specific task.
3. The programming process involves problem analysis, program design, coding, testing and debugging, documentation, and implementation and maintenance.
Uploaded by
Rovell AsideraCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
70 views29 pagesIntroduction To Program Logic Formulation
1. The document introduces the concepts of data, information, procedures, computer programs, and the programming process.
2. It explains that data becomes information when it is organized and processed, and that a computer program consists of a set of instructions that direct a computer to perform a specific task.
3. The programming process involves problem analysis, program design, coding, testing and debugging, documentation, and implementation and maintenance.
Uploaded by
Rovell AsideraCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 29