0% found this document useful (0 votes)
233 views21 pagesITC Tobacco Strategy & Market Analysis
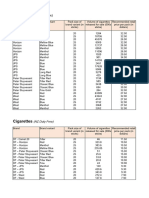
ITC has a 70% market share in the Indian cigarette market, marketing 14 brands. A SWOT analysis found strengths in research and supply chain but weaknesses in price increases and ethical concerns. PEST analysis showed political restrictions on advertising and excise taxes while economic factors include tobacco's role in employment. Porter's Five Forces found high competitive rivalry but low threat of new entrants. Consumer behavior analysis showed preferences for taste over price and brands like Goldflake and Classic. Positioning strategies focus on availability, quality, and flavors. Future recommendations include more flavors, improving brand value, and reducing packaging focus.
Uploaded by
Aditya AnandCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
233 views21 pagesITC Tobacco Strategy & Market Analysis
ITC has a 70% market share in the Indian cigarette market, marketing 14 brands. A SWOT analysis found strengths in research and supply chain but weaknesses in price increases and ethical concerns. PEST analysis showed political restrictions on advertising and excise taxes while economic factors include tobacco's role in employment. Porter's Five Forces found high competitive rivalry but low threat of new entrants. Consumer behavior analysis showed preferences for taste over price and brands like Goldflake and Classic. Positioning strategies focus on availability, quality, and flavors. Future recommendations include more flavors, improving brand value, and reducing packaging focus.
Uploaded by
Aditya AnandCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 21