0% found this document useful (0 votes)
310 views15 pagesPPT1 - Data Link Layer HDLC Protocol-Part I
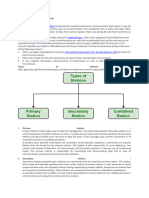
This document provides an overview of the High-Level Data Link Control (HDLC) protocol. HDLC is a bit-oriented protocol used at the data link layer for point-to-point and multipoint communication. It supports both half-duplex and full-duplex modes. The document describes the different types of HDLC stations, including primary, secondary, and combined stations. It also outlines the balanced and unbalanced link configurations and various transfer modes of HDLC, such as normal response mode, asynchronous balanced mode, and asynchronous response mode. Finally, it discusses the non-operational modes of HDLC, including normal disconnected mode, asynchronous disconnected mode, and initialization mode.
Uploaded by
vipulkondekarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
310 views15 pagesPPT1 - Data Link Layer HDLC Protocol-Part I
This document provides an overview of the High-Level Data Link Control (HDLC) protocol. HDLC is a bit-oriented protocol used at the data link layer for point-to-point and multipoint communication. It supports both half-duplex and full-duplex modes. The document describes the different types of HDLC stations, including primary, secondary, and combined stations. It also outlines the balanced and unbalanced link configurations and various transfer modes of HDLC, such as normal response mode, asynchronous balanced mode, and asynchronous response mode. Finally, it discusses the non-operational modes of HDLC, including normal disconnected mode, asynchronous disconnected mode, and initialization mode.
Uploaded by
vipulkondekarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 15