0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views14 pagesSpoken Tutorial Python - English
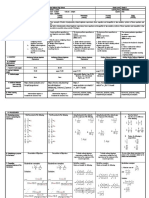
The document provides an introduction and overview of the Python programming language. It discusses some key pluses of Python including its ease of use as an object-oriented language, its interpretive nature, and cross-platform capabilities. It also notes some minuses like slower speed compared to other languages. The document then provides examples of basic Python concepts like data types, operators, and control flow statements. It includes code samples for tasks like swapping values, calculating a sum, finding the largest of three numbers, and printing a multiplication table.
Uploaded by
atul211988Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views14 pagesSpoken Tutorial Python - English
The document provides an introduction and overview of the Python programming language. It discusses some key pluses of Python including its ease of use as an object-oriented language, its interpretive nature, and cross-platform capabilities. It also notes some minuses like slower speed compared to other languages. The document then provides examples of basic Python concepts like data types, operators, and control flow statements. It includes code samples for tasks like swapping values, calculating a sum, finding the largest of three numbers, and printing a multiplication table.
Uploaded by
atul211988Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 14