0% found this document useful (0 votes)
362 views18 pagesModule 6: Flow Control Valves: Basic Pneumatics
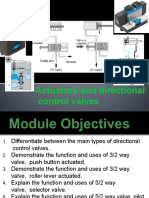
This document discusses flow control valves in pneumatic systems. It covers one-way flow control valves and quick exhaust valves.
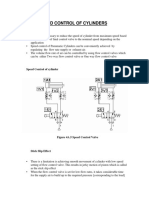
It explains that one-way flow control valves control air flow in one direction only and are used to adjust cylinder speed. Quick exhaust valves are used to rapidly exhaust air from cylinders during retraction to increase cycle speed.
The document provides examples of using these valves to control single-acting cylinders, including adjusting advancing and retracting speeds. It includes objectives, descriptions of components, and instructions for practical tasks to simulate circuits using these valves.
Uploaded by
John Fernand RacelisCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
362 views18 pagesModule 6: Flow Control Valves: Basic Pneumatics
This document discusses flow control valves in pneumatic systems. It covers one-way flow control valves and quick exhaust valves.
It explains that one-way flow control valves control air flow in one direction only and are used to adjust cylinder speed. Quick exhaust valves are used to rapidly exhaust air from cylinders during retraction to increase cycle speed.
The document provides examples of using these valves to control single-acting cylinders, including adjusting advancing and retracting speeds. It includes objectives, descriptions of components, and instructions for practical tasks to simulate circuits using these valves.
Uploaded by
John Fernand RacelisCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 18