0% found this document useful (0 votes)
119 views20 pagesUnreadable Document Analysis
The document discusses key aspects of contract formation and terms under the Uniform Commercial Code (UCC).
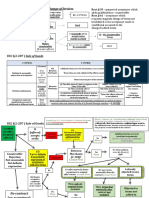
The UCC governs contracts for the sale of goods between merchants. It aims to promote uniformity and ease of commerce. The UCC covers acceptance of offers, open terms, acceptance of goods, additional terms in acceptance, contract modifications, and the statute of frauds. It also addresses interpretation of agreements using course of performance, course of dealing, and trade usage evidence.
Uploaded by
Tushar MehtaCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
119 views20 pagesUnreadable Document Analysis
The document discusses key aspects of contract formation and terms under the Uniform Commercial Code (UCC).
The UCC governs contracts for the sale of goods between merchants. It aims to promote uniformity and ease of commerce. The UCC covers acceptance of offers, open terms, acceptance of goods, additional terms in acceptance, contract modifications, and the statute of frauds. It also addresses interpretation of agreements using course of performance, course of dealing, and trade usage evidence.
Uploaded by
Tushar MehtaCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 20