0% found this document useful (0 votes)
62 views40 pagesLecture 1: Introduction To Java Programming: Dr. Kyung Eun Park Summer 2017
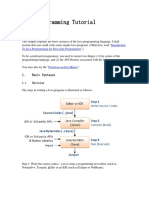
This document provides an introduction to a lecture on Java programming. It discusses how computers communicate using binary digits (bits) represented as 0s and 1s. It introduces basic Java concepts like primitive data types, operators, and the structure of a Java program. It also presents a simple "Hello World" Java program as an example and discusses naming conventions, comments, and static methods in Java.
Uploaded by
chibssa alemayehuCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
62 views40 pagesLecture 1: Introduction To Java Programming: Dr. Kyung Eun Park Summer 2017
This document provides an introduction to a lecture on Java programming. It discusses how computers communicate using binary digits (bits) represented as 0s and 1s. It introduces basic Java concepts like primitive data types, operators, and the structure of a Java program. It also presents a simple "Hello World" Java program as an example and discusses naming conventions, comments, and static methods in Java.
Uploaded by
chibssa alemayehuCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 40