0% found this document useful (0 votes)
125 views28 pagesArya College of Engineering and Research Centre: Industrial Training
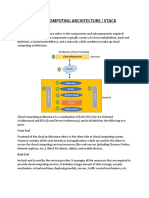
Cloud computing provides on-demand access to shared computing resources like servers, storage, databases, and software over the Internet. It has evolved since the 1950s from mainframe computing to virtual machines and public cloud services from Amazon, Google, and Microsoft. Key benefits include cost reduction, accessibility, scalability, automatic updates, and business continuity. Common cloud characteristics include on-demand self-service, broad network access, resource pooling, and rapid elasticity. There are different deployment models like public, private, hybrid and community clouds as well as service models including Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).
Uploaded by
riya ahujaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
125 views28 pagesArya College of Engineering and Research Centre: Industrial Training
Cloud computing provides on-demand access to shared computing resources like servers, storage, databases, and software over the Internet. It has evolved since the 1950s from mainframe computing to virtual machines and public cloud services from Amazon, Google, and Microsoft. Key benefits include cost reduction, accessibility, scalability, automatic updates, and business continuity. Common cloud characteristics include on-demand self-service, broad network access, resource pooling, and rapid elasticity. There are different deployment models like public, private, hybrid and community clouds as well as service models including Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).
Uploaded by
riya ahujaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 28