0% found this document useful (0 votes)
620 views22 pagesEvolution of Operating System
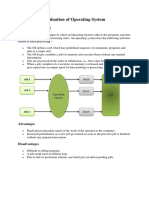
1. Operating systems have evolved from batch processing to support multiprogramming, multitasking, and distributed systems.
2. Batch processing collects programs and data into batches that are processed sequentially without user interaction.
3. Multiprogramming allows multiple programs to reside in memory simultaneously by switching between them, improving CPU utilization.
4. Multitasking provides even faster switching between programs, allowing users to interact with each program while it runs.
Uploaded by
Rishi JainCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
620 views22 pagesEvolution of Operating System
1. Operating systems have evolved from batch processing to support multiprogramming, multitasking, and distributed systems.
2. Batch processing collects programs and data into batches that are processed sequentially without user interaction.
3. Multiprogramming allows multiple programs to reside in memory simultaneously by switching between them, improving CPU utilization.
4. Multitasking provides even faster switching between programs, allowing users to interact with each program while it runs.
Uploaded by
Rishi JainCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 22