0% found this document useful (0 votes)
74 views19 pagesCSVTU Syllabus Unit 3 Routing Protocols (INTRODUCTION)
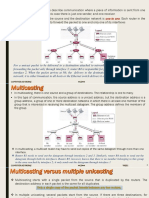
An Automated Teller Machine (ATM) is an electronic telecommunications device that enables customers of financial institutions to perform financial transaction , such as cash withdrawals , deposits , transfer funds , or obtaining account information , at any time and without the need for direct interaction with bank staff.
Uploaded by
Eshita ShuklaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
74 views19 pagesCSVTU Syllabus Unit 3 Routing Protocols (INTRODUCTION)
An Automated Teller Machine (ATM) is an electronic telecommunications device that enables customers of financial institutions to perform financial transaction , such as cash withdrawals , deposits , transfer funds , or obtaining account information , at any time and without the need for direct interaction with bank staff.
Uploaded by
Eshita ShuklaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 19