100% found this document useful (1 vote)
211 views5 pages2-Example Hierarchy of Control
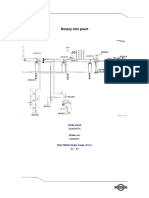
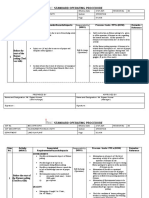
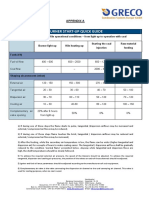
The document discusses the hierarchy of risk control options in occupational health and safety, emphasizing that some controls are more effective than others. It presents a scenario involving noise exposure in a control room and outlines various control options such as elimination, substitution, engineering, administrative, and personal protective equipment. The document concludes with a comparison of these options, highlighting the best long-term solutions and practical implementations.
Uploaded by
Anonymous iI88LtCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
211 views5 pages2-Example Hierarchy of Control
The document discusses the hierarchy of risk control options in occupational health and safety, emphasizing that some controls are more effective than others. It presents a scenario involving noise exposure in a control room and outlines various control options such as elimination, substitution, engineering, administrative, and personal protective equipment. The document concludes with a comparison of these options, highlighting the best long-term solutions and practical implementations.
Uploaded by
Anonymous iI88LtCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 5