100% found this document useful (1 vote)
1K views47 pagesCardiovascular System
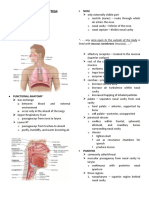
The cardiovascular system transports blood, nutrients, gases, hormones, and waste products around the body. It consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. The heart pumps blood through two circuits - the pulmonary circuit, which circulates blood to and from the lungs, and the systemic circuit, which pumps blood to and from the entire body via arteries, veins, and capillaries. Blood flows through the heart's four chambers and is routed via valves between the atria and ventricles and from the ventricles to the arteries.
Uploaded by
Atnasiya GadisaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
1K views47 pagesCardiovascular System
The cardiovascular system transports blood, nutrients, gases, hormones, and waste products around the body. It consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. The heart pumps blood through two circuits - the pulmonary circuit, which circulates blood to and from the lungs, and the systemic circuit, which pumps blood to and from the entire body via arteries, veins, and capillaries. Blood flows through the heart's four chambers and is routed via valves between the atria and ventricles and from the ventricles to the arteries.
Uploaded by
Atnasiya GadisaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 47