0% found this document useful (0 votes)
62 views28 pagesBAPI
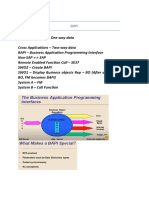
The document discusses Business Application Programming Interfaces (BAPIs), which allow integration at the business level rather than the technical level. BAPIs provide standardized interfaces to read, create, change, and process data in SAP systems. They allow accessing and exchanging business data between SAP and non-SAP applications in a distributed environment.
Uploaded by
PRASHANT KUMARCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
62 views28 pagesBAPI
The document discusses Business Application Programming Interfaces (BAPIs), which allow integration at the business level rather than the technical level. BAPIs provide standardized interfaces to read, create, change, and process data in SAP systems. They allow accessing and exchanging business data between SAP and non-SAP applications in a distributed environment.
Uploaded by
PRASHANT KUMARCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 28