Testing Process
Improvement
�Goal with this Presentation
Need for process improvement.
Present an idea, TMM and TPI.
Describe the process which build up TMM
Difference between the TMM and TPI
2
�Test Process Improvement: Why?
Increasing importance and size of software in society as a
whole
Testing often takes 30 - 40% of project costs.
How do we improve the efficiency of software testing, and
at the same time reduce the cost of testing? In other words,
how do we make software testing both better and cheaper?
The answer of course is process improvement.
3
�Purpose of TMM
The purpose of the TMM is to assist software organizations
with assessing and improving their software testing
processes.
4
�TMM’s development History
Developed by IIT (Illinois Institute of Technology).
Component CMM on areas of interest.
Any organization that wishes to improve its testing process
by use of the TMM first commit to improving its overall
software development process by application of the CMM.
(Testing process is a subset of the overall software
development process; therefore, its maturity growth needs
support from the KPAs associated with general process
growth )
5
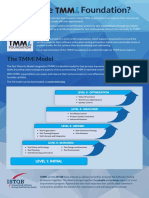
�What is TMM
A maturity model with focus on following points
Describes the processes, which are the basic in order to
ensure a well planned and controlled test part of a project.
5 level of maturity in testing.
Inspired by CMM
The model aims at raising through the 5 levels of maturity.
The higher the level of maturity, higher is the quality of
software being developed.
6
�TMM – usability
The TMM can be used by:
. Internal teams to evaluate the current testing maturity
. Management to launch specific improvement initiatives
. Development projects to improve a specific test
. Users and contractors to define their roles in testing
7
�Process Flow of Test Process
Improvement.
8
�TMM’s 2 Main Component
A Set of Levels
TMM consist of 5 levels each level represents a stage in evaluation to a
mature testing process.
A set of maturity goals for each level and activities, task and
responsibilities needed to support them.
For each maturity level, a number of process areas are defined. A
process area is a cluster of related activities within the test process, e.g.
test planning or test training.
An Assessment Models
A set of maturity related goal questions. They will help determine to
what extent the organization has mechanisms in place to achieve those
goals and for resolving the maturity issues.
An assessment method
A training program design to select and instruct the evaluation team.
9
�TMM Maturity Goals By Level
10
�Maturity Goals Level 1- Initial
There are no maturity goals at this level.
Tests are developed in an ad hoc way after coding is done.
Testing and debugging activities go hand-in-hand to get the
defects out of the software.
The objective of testing is to show that the software works/
runs.
11
�Maturity Goals Level 2-Phase
Definition
Develop Testing and Debugging goals
A life cycle phase that follows coding
Initiate a Test planning process
Basic testing techniques and methods are used during
testing.
No reviews to address early defects
The objective of testing is to show that the software meets
its specification
12
�Maturity Goals Level 3- Integration
Software Test Organization
Technical Training Program
Integrate Testing into Software Lifecycle
Control and Monitor Testing Process.
Objective : to provide insight into the quality of the product,
13
� Monitoring and Control
Risk Project Data
Control de
via
Schedule g es tio
h an ns
c
Effort
Cost Plan Monitor
plan
Deliverables
Product quality
Exit criteria Test Project
14
�Maturity Goals Level 4- Management
& Measurement
Establish Review Program
Establish a Test Measurement Program.
Software Quality Evaluation
15
�Level 5- Optimization, Defect
Prevention and Quality Control
Application of process data for defect prevention.
Quality Control
Test Process Optimization
The objective of testing is to prevent defects from re-
occurring in the future
16
�Support for TMM maturity levels
TMM CMM
Supporting Key Process Areas
2 2 Requirements management, project planning and
software configuration management
3 2 Project tracking SQA
3 3 Organization process focus, organization process definition and training
programs
4 3 Intergroup coordination, Peer reviews
4 4 Software quality management and Quantitative process management
5 5 Process change management, technology change
management and defect prevention
17
�TMM Summary
Baseline the current testing process level of maturity
Identify areas that can be improved identify testing
processes that can be adopted organization-wide
Provide a road map for implementing the improvements
Provide a method for measuring the improvement results
18
�TPI (Test Process Improvement)
The Test Process Improvement (TPI®)-model offers insight
in the 'maturity' of test processes within your organization.
The TPI has been developed by Sogeti, a wholly owned
subsidiary of the international Capgemini organization. It
goes hand in hand with the Test Management Approach
(TMap) which is also a testing methodology from Sogeti.
This model has four basic components -
1. Key Areas
2. Levels
3. Checkpoints
4. Improvement Suggestions
19
�Model Description
Each of the above key areas is assessed at various levels
like A, B, C and D.
The number of levels for all the key areas is not the same.
For e.g. ‘Static Testing Techniques’ key area has only two
levels – A and B. However, ‘Test Strategy’ has 4 levels – A,
B, C and D.
Each level has certain checkpoints for each of the key
areas.
The test process under assessment should satisfy these
checkpoints to be certified for that level.
The model also includes improvement suggestions to assist
the organizations in achieving higher levels of maturity.
20
�TPI Model
21
�Key Areas
Life cycle
1. Test Strategy
2. Lifecycle Model
3. Moment of involvement
Techniques
4. Estimating and Planning
5. Test Specification Techniques
6. Static Test Techniques
7. Metrics
Infrastructure
8. Test Automation
9. Test Environment
10. Office Environment
Organization
11. Commitment and Motivation
12. Testing Functions and Trainings
13. Scope of Methodology
14. Communication
15. Reporting
16. Defect Management
17. Test ware Management
18. Test Process Management
All Cornerstones
19. Evaluation
20. Low-level Testing
22
�23
�24
�Test Maturity Matrix
The Test Maturity Matrix relates Levels to Key Areas.
It does so by expressing the internal priorities and
dependencies between Levels and Key Areas.
It illustrates the strong and weak points of the current test
process. This aids the prioritizing of actions for
improvement.
In the matrix each level is related to a certain scale of test
maturity. This results in 13 scales of test maturity.
The open cells between different levels have no meaning in
themselves, but indicate that achieving a higher maturity for
a key area is related to the maturity of other key areas
25
�Test Maturity Matrix
26
�Test Maturity Matrix
Indicates the level of maturity of each key area .
As we go from left to right in the matrix, our testing process
becomes more and more sophisticated from Controlled to
Efficient to Optimizing.
For example, to start with static testing techniques (at level
A), the moment of involvement must be at level A also. Due
to this dependency, the level A of moment of involvement is
earlier than level A of the Static testing techniques.
The blanks in the test matrix essentially mean nothing and
are present to take care of the dependencies.
Level 0 indicates that the key area does not exist in the
current testing process.
27
�TPI Summary
The TPI model offers objective procedures for classifying
the current situation of the test process. Additionally, the
model offers assistance for test process improvement in the
form of key areas, levels and improvement suggestions.
means of checkpoints it is possible to determine the levels
of key areas that a test process is on.
The different maturity levels and key areas and their
dependencies are presented in the Test Maturity Matrix.
28
�Comparison of TMM and TPI
TMM TPI
Complements CMMi Associated closely with
TMap
Includes all levels of testing Focus on high level tests
Research Product Commercial Product
Contains 5 levels Contains 13 scales of
maturity
Follows staged progress Follows continuous process
29