0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views22 pagesWifi
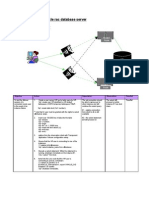
This document provides an overview of Wi-Fi technology, including its history, components, how it works, applications, and security measures. It discusses how Wi-Fi networks connect devices wirelessly using radio frequencies and standards like 802.11b, 802.11a, and 802.11g. In conclusion, Wi-Fi allows for mobility and flexibility by providing wireless internet access within a local range.
Uploaded by
chandan kumarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views22 pagesWifi
This document provides an overview of Wi-Fi technology, including its history, components, how it works, applications, and security measures. It discusses how Wi-Fi networks connect devices wirelessly using radio frequencies and standards like 802.11b, 802.11a, and 802.11g. In conclusion, Wi-Fi allows for mobility and flexibility by providing wireless internet access within a local range.
Uploaded by
chandan kumarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 22