Introduction to Google MapReduce
WING Group Meeting 13 Oct 2006 Hendra Setiawan
�What is MapReduce?
A programming model (& its associated
implementation) For processing large data set Exploits large set of commodity computers Executes process in distributed manner Offers high degree of transparencies In other words:
simple and maybe suitable for your tasks !!!
�Distributed Grep
Split data
Very big data
Split data Split data
grep grep grep grep
matches matches
matches
cat
All matches
Split data
matches
�Distributed Word Count
Split data
Very big data
Split data Split data
count count count count
count count
count
merge
merged count
Split data
count
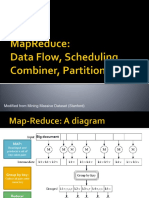
�Map Reduce
Very big data M A P Partitioning Function R E D U C E Result
Map:
Accepts input key/value pair Emits intermediate key/value pair
Reduce :
Accepts intermediate key/value* pair Emits output key/value pair
�Partitioning Function
�Partitioning Function (2)
Default : hash(key) Guarantee:
mod R
Relatively well-balanced partitions Ordering guarantee within partition
Distributed Sort
Map:
emit(key,value)
Reduce (with R=1):
emit(key,value)
�MapReduce
Distributed Grep
Map:
if match(value,pattern) emit(value,1)
Reduce:
emit(key,sum(value*))
Distributed Word Count
Map:
for all w in value do emit(w,1)
Reduce:
emit(key,sum(value*))
�MapReduce Transparencies
Plus Google Distributed File System : Parallelization Fault-tolerance Locality optimization Load balancing
�Suitable for your task if
Have a cluster Working with large dataset Working with independent data (or
assumed) Can be cast into map and reduce
�MapReduce outside Google
Hadoop (Java)
Emulates MapReduce and GFS
The architecture of Hadoop MapReduce
and DFS is master/slave
Master Slave MapReduce jobtracker tasktracker DFS namenode datanode
�Example Word Count (1)
Map
public static class MapClass extends MapReduceBase implements Mapper { private final static IntWritable one = new IntWritable(1); private Text word = new Text(); public void map(WritableComparable key, Writable value, OutputCollector output, Reporter reporter) throws IOException { String line = ((Text)value).toString(); StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(line); while (itr.hasMoreTokens()) { word.set(itr.nextToken()); output.collect(word, one); } } }
�Example Word Count (2)
Reduce
public static class Reduce extends MapReduceBase implements Reducer { public void reduce(WritableComparable key, Iterator values, OutputCollector output, Reporter reporter) throws IOException { int sum = 0; while (values.hasNext()) { sum += ((IntWritable) values.next()).get(); } output.collect(key, new IntWritable(sum)); } }
�Example Word Count (3)
Main
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //checking goes here JobConf conf = new JobConf();
conf.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); conf.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class); conf.setMapperClass(MapClass.class); conf.setCombinerClass(Reduce.class); conf.setReducerClass(Reduce.class); conf.setInputPath(new Path(args[0])); conf.setOutputPath(new Path(args[1])); JobClient.runJob(conf); }
�One time setup
set hadoop-site.xml and slaves Initiate namenode Run Hadoop MapReduce and DFS Upload your data to DFS Run your process Download your data from DFS
�Summary
A simple programming model for
processing large dataset on large set of computer cluster Fun to use, focus on problem, and let the library deal with the messy detail
�References
Original paper
(http://labs.google.com/papers/mapreduce .html) On wikipedia (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MapReduce) Hadoop MapReduce in Java (http://lucene.apache.org/hadoop/) Starfish - MapReduce in Ruby (http://rufy.com/starfish/)