0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views26 pagesRapid Prototyping
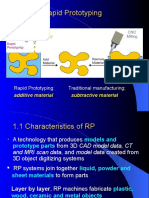
Rapid Prototyping (RP) techniques are methods that allow designers to produce physical prototypes quickly.
It consists of various manufacturing processes by which a solid physical model of part is made directly from 3D CAD model data without any special tooling.
The first commercial rapid prototyping process was brought on the market in 1987.
Nowadays, more than 30 different processes (not all commercialized) with high accuracy and a large choice of materials exist.
These processes are cla
Uploaded by
DIGITAL SEVACopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views26 pagesRapid Prototyping
Rapid Prototyping (RP) techniques are methods that allow designers to produce physical prototypes quickly.
It consists of various manufacturing processes by which a solid physical model of part is made directly from 3D CAD model data without any special tooling.
The first commercial rapid prototyping process was brought on the market in 1987.
Nowadays, more than 30 different processes (not all commercialized) with high accuracy and a large choice of materials exist.
These processes are cla
Uploaded by
DIGITAL SEVACopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 26