0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views23 pages1 Arduino PPT Intro
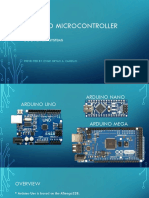
The document provides an overview of Arduino, an open-source platform that simplifies the use of microcontrollers through easy-to-use hardware and software. It details the features of various Arduino boards, particularly the Arduino Uno, and explains the programming structure, including key functions like setup() and loop(). Additionally, it includes practical examples such as blinking an LED and outlines the steps for creating and uploading projects using the Arduino IDE.
Uploaded by
sangu vadgaveCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views23 pages1 Arduino PPT Intro
The document provides an overview of Arduino, an open-source platform that simplifies the use of microcontrollers through easy-to-use hardware and software. It details the features of various Arduino boards, particularly the Arduino Uno, and explains the programming structure, including key functions like setup() and loop(). Additionally, it includes practical examples such as blinking an LED and outlines the steps for creating and uploading projects using the Arduino IDE.
Uploaded by
sangu vadgaveCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 23