CS-107
COMPUTER
PROGRAMMING
MEHREEN TAHIR
� GRADING
Assessments Details
•Theory: 75%
•Quizzes: 10%
•Assignments: 10%
•MSE: 30%
•ESE: 50%
•Labs: 25% •Lab Tasks and Viva: 70%
•Project: 30%
•Total: 100%
� GRADING
• Attendance • 75%
� Introduction
• Introduction to Computer Programming,
Course Outline and Objectives
– CourseOutline.doc
�Computer programming course for an Electrical
Engineer
�Computer programming course for an
Electrical Engineer
• Primary focus: Hardware
HW Computer Programming SW
Smarter+Efficient System
�Computer programming course for an
Electrical Engineer
• Embedded Systems
• Simulation and Modeling
• Signal Processing
• Design and Testing
• Automation and Control Systems
�Computer programming course for an
Electrical Engineer
• Interdisciplinary Collaboration
– collaborate effectively with software engineers,
ensuring seamless integration of hardware and
software
�Computer programming course for an
Electrical Engineer
• Innovation in Emerging Fields
– Cutting-edge technologies like renewable energy
systems, electric vehicles, and smart grids. Many
of these fields require programming for system
optimization, monitoring, and control
�Computer programming course for an
Electrical Engineer
• Improved Career Opportunities
– Employers value electrical engineers with
programming skills because they are versatile and
can contribute to both hardware and software
development. This makes engineers more
competitive and adaptable in the job market.
�Computer programming course for an
Electrical Engineer
• Computer Programming is a crucial skill that
enhances an electrical engineer's capabilities
and expands their career potential.
� IDE
• Integrated Development Environment
– develop software code efficiently
– increases developer productivity
• Combining software editing, building, testing, and
packaging in user friendly application
– Just as writers use text editors and accountants use
spreadsheets, software developers use IDEs to make
their job easier.
• Choose based on programming language, OS
and features of IDE.
� IDEs
• VS Code
• Visual Studio
• Code Blocks
• CLion
�Introduction to Computer
Programming
LECTURE-1
� Programming
• Logical sequence of steps for solving a
problem
– Computer and Humans
• Install and IDE on a computer
• Organize an event
� Computer Programming
• The process of planning a sequence of steps
for a computer to follow
– A computer is not intelligent.
– It cannot analyze a problem and come up with a
solution.
– Instead, a human (the programmer) must analyze
the problem, develop a sequence of instructions
for solving the problem, and then communicate it
to the computer.
�Programming Process
� Programming Language
• A set of rules, symbols, and special words
used to construct a computer program
� Program Working
• Translating an algorithm into a programming
language is called coding the algorithm.
• The product of that translation—the program
—is tested by running (executing) it on the
computer.
� Program Working
• If the program fails to produce the desired
results, the programmer must debug it—that
is, determine what is wrong and then modify
the program, or even the algorithm, to fix it.
• The combination of coding and testing an
algorithm is called implementation.
�Program Working
� Program Working
• Documentation
– The written text and comments that make a
program easier for others to understand, use,and
modify.
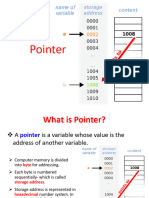
� Information vs. Data
• Data: raw, unprocessed
– Data of temperature of Islamabad
• Information: process, organized, meaning full
– Table representing temperature of Islamabad in
February
� Data Representation
• Binary
• Octal
• Decimal
• Hex decimal
�Data Representation
� Computer runs a Program
• Machine language: The language understands
1s and 0s. Communicate directly with the HW.
• Assembly language: A low-level programming
language in which a mnemonic (instructions in
AL) is used to represent each of the machine
language instructions for a particular
computer.
� Computer runs a Program
• Assembler: A program to translate the
assembly language instructions into machine
code.
• Compiler: A program translates programs
written in certain highlevel languages (C++,
Java, Visual Basic, and Ada, for example) into
machine language.
���� Computer Programming
• Compiler vs. Interpreter
• High level language vs. Low level Languages