0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views37 pagesFSD - Unit 1 Part 2
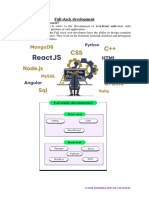
Unit 1 covers the fundamentals of JavaScript and the MERN stack, which includes MongoDB, Express.js, React, and Node.js, essential for full-stack web development. It details front-end and back-end development, the roles of each MERN component, and the need for this stack in creating interactive web applications. The document also provides insights into setting up a JavaScript environment, using npm, and managing project dependencies.
Uploaded by
venkat MohanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views37 pagesFSD - Unit 1 Part 2
Unit 1 covers the fundamentals of JavaScript and the MERN stack, which includes MongoDB, Express.js, React, and Node.js, essential for full-stack web development. It details front-end and back-end development, the roles of each MERN component, and the need for this stack in creating interactive web applications. The document also provides insights into setting up a JavaScript environment, using npm, and managing project dependencies.
Uploaded by
venkat MohanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 37