0% found this document useful (0 votes)
96 views18 pagesSetting and Characterization
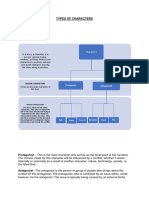
The document provides an overview of characters in storytelling, defining major characters such as protagonists and antagonists, as well as various types of minor characters like foils, static, dynamic, flat, round, and stock characters. It also explains the concept of setting as the time and place of a story, typically introduced during the exposition. Overall, it serves as a guide for understanding plot, setting, and characterization in literature.
Uploaded by
Avianna CruzCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
96 views18 pagesSetting and Characterization
The document provides an overview of characters in storytelling, defining major characters such as protagonists and antagonists, as well as various types of minor characters like foils, static, dynamic, flat, round, and stock characters. It also explains the concept of setting as the time and place of a story, typically introduced during the exposition. Overall, it serves as a guide for understanding plot, setting, and characterization in literature.
Uploaded by
Avianna CruzCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 18