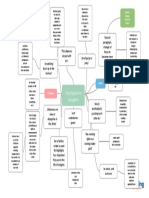
Types of Text:
By Ms. Bennett
�Text
Diction – Choice of words for a message.
Adjectives and Adverbs
Nouns
Verbs
Prepositions
Syntax – [Structure] Arrangement of words
to transmit a clear message.
Both are used to create a readable text and
sense-making communication.
�
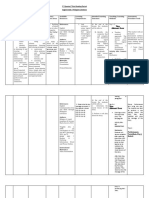
Five (5) Domains of Text:
Narrative
Autobiographical Writing
Biographical Writing
Short Story [The 5 W’s; When, Where, Who, What, Why]
Descriptive
Creative Writing
Sensory Writing [The 5 Senses; Poetry/Lyrics]
Persuasive
Editorial and Advertisement Writing
Speech Writing
Expository [Exposes the reader to new information]
Informational Writing [Encyclopedias, Dictionaries, etc.]
Research Reports
Everyday, Career, and Technical Writing
Response to Literature
Compare and Contrast Writing
Cause and Effect Writing
Writing to a Specific Task/Prompt
�We can Predict text types…
Author (Who wrote it?)
Author Background Connection
Format (How is it structured?)
Titles, Headings, Paragraphs, Stanzas, Columns
Audience (Who is it written for?)
Pictures help for this prediction
Content (What is it about?)
Pictures help for this prediction
Motive (Why is it written?)
Pleasure, Persuasion, Information, Task/Prompt
�Narrative Text =
Writing that tells a story.
Stories, novels, fables, and folk lore
are the most common narrative texts.
This text is written in the When,
Where, Who, What and Why format.
Autobiographies, biographies, and
personal stories are written narratively.
�Narrative text includes these elements:
- Exposition
setting (time/place)
character introduction
conflict (theme) introduction
-Plot [begins the Rising Action]
characters
conflicts (problems)
similes and metaphors
-Climax [begins the Falling Action]
characters meet the greatest conflict
-Resolution/Denoument
conflicts become resolved
moral and theme are realized
� Graphic Organizer for Narrative
Text: Climax
Resolution
Exposition
�Descriptive Text =
Sensory and detailed writing
Poetry and Creative text-types are the most
common descriptive texts.
This type of writing creates an experience
for the reader through the use of sensory
language.
Sight
Smell
Sound
Taste
Touch
�Persuasive Text =
Writing that tries to convince you
to think a certain way.
Speeches, advertisement writing, and
opinion letters, articles or essays are the
most common persuasive texts.
This text uses a specific format, which
includes pro and con sides of an issue.
Exclamatory and emphatic language is used
to persuade the reader to the author’s
viewpoint.
�Elements of Persuasive Text:
-Main Idea/Argument
author’s statement/side of issue
intended purpose to the reader
reveals silliness of opposing side
-Supporting Ideas [For and Against/Pro and Con]
facts vs. opinions
comparisons and contrasts
*persuasive techniques – exaggeration (over and
under statements of facts), repetition of pro or con
“catch words,” name-calling, visual examples
-Closing Argument
logic and opinion
�Expository/Informational Text =
Text that exposes new information to
the reader or explains or gives
information about a topic.
Functional Documents and Everyday
Documents are also expository text.
� Types of Expository/
Informational text:
Textbooks
Encyclopedias
Research and Data Reports
Maps, Tables, and Timelines
�Elements of Informational Text:
-A Central Purpose
What the author wants you to learn
Overview of the main points covered
- Main Idea/Point
Headings
The most important point made
- Supporting Ideas/Concepts/Details
Subheadings
Details
- Illustrations
Supporting these details
�Types of Functional Documents:
*Documents you interact with; one that requires an
action on the readers part.
Agreements/Contracts
(Rules, Policies, Loans, etc.)
Memo’s and “Fill-In” Forms
Applications (Career)
Check Lists
Rubrics and Evaluation Forms
�Types of Everyday Text:
*Documents/text you see everyday
Schedules
Directions
Instruction Manuals (Technical)
“How to Operate” Manuals (Technical)
Media-Signs and Symbols
�Elements of Functional and Everyday Text:
- Organized Information
Planned, edited, and revised
- Sequence of Data
Roman Numeral Outline Format
EX: I, A, 1, a,
- Steps to Follow
Numbered Format
EX: 1., 2., 3.
- Relevant Data – Details
Bulleted Format
EX: , ,
- Visual Schematics with Labels
�Response to Literature =
Response and Review Writing
This domain of reading and writing
includes elements of all the other domains
of text types.
The text type chosen, depends upon the
writing prompt or task assigned to the
reader.
The prompt will specify “key words” to
decode to decide which type of text to use for
your response or review.
�Elements of Literary Response -
An Example Prompt: Trace the development of
emotions through Poe’s poem “The Bells.”
- Introductory Paragraph
4 Parts to the Opening/Topic sentence:
1. Task of the prompt needed for response.
EX: A development of different emotions can be seen
in the poem, “The Bells,” by Edgar Allen Poe.
2. Type of text the response is about.
EX: …in the poem…
3. Title of text the response is about.
EX: …in the poem, “The Bells,”…
4. Author of the text the response is about.
EX: …in the poem, “The Bells,” by Edgar Allen Poe…
�Balance of the Literary Response
Body Paragraphs
Must connect to the prompt.
Separates the prompt into two or more concepts.
Must use support from the text in quotes.
Needs to include your feelings or views.
Conclusion Paragraph
Connects/restates the opening sentence.
Finalizes your feelings or views.
Leads to further connections.
�Additional Notes on Literary Response
Compare and Contrast prompts will contain 2
body paragraphs.
Cause and Effect will contain 2 body paragraphs.
Persuasive opinion prompts can contain one or
more paragraphs.
Description prompts will contain one or more
body paragraphs.
Other Task Specific prompts will contain one or
more body paragraphs.
�Comments, Questions,
Concerns?
Remember…
How we write What we write,
Makes authors of us all!