0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views19 pagesK-Map Example
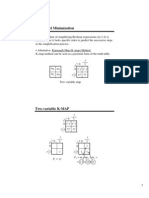
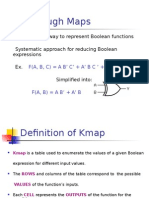
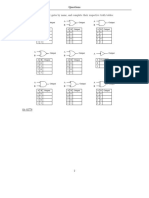
The document provides a detailed explanation of simplification techniques using Karnaugh Maps (K-maps) for Boolean functions. It includes examples for 2-variable, 3-variable, and 4-variable K-maps, illustrating how to group minterms and derive simplified functions. Key rules for variable selection and grouping strategies are also discussed to aid in the minimization process.
Uploaded by
juliedickson575Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views19 pagesK-Map Example
The document provides a detailed explanation of simplification techniques using Karnaugh Maps (K-maps) for Boolean functions. It includes examples for 2-variable, 3-variable, and 4-variable K-maps, illustrating how to group minterms and derive simplified functions. Key rules for variable selection and grouping strategies are also discussed to aid in the minimization process.
Uploaded by
juliedickson575Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 19