Chapter 15: File System
Internals
Operating System Concepts – 10th Edition Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2018
� Chapter 15: File System Internals
File Systems
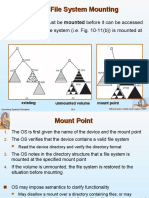
File-System Mounting
Partitions and Mounting
File Sharing
Virtual File Systems
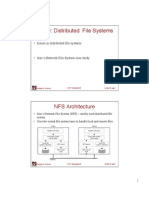
Remote File Systems
Consistency Semantics
NFS
Operating System Concepts – 10th Edition 15.2 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2018
� Objectives
Delve into the details of file systems and their
implementation
Explore booting and file sharing
Describe remote file systems, using NFS as an example
Operating System Concepts – 10th Edition 15.3 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2018
� File System
General-purpose computers can have multiple storage devices
Devices can be sliced into partitions, which hold volumes
Volumes can span multiple partitions
Each volume usually formatted into a file system
# of file systems varies, typically dozens available to choose from
Typical storage device organization:
Operating System Concepts – 10th Edition 15.4 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2018
� Example Mount Points and File Systems - Solaris
Operating System Concepts – 10th Edition 15.5 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2018
� Partitions and Mounting
Partition can be a volume containing a file system (“cooked”) or raw –
just a sequence of blocks with no file system
Boot block can point to boot volume or boot loader set of blocks that
contain enough code to know how to load the kernel from the file
system
Or a boot management program for multi-os booting
Root partition contains the OS, other partitions can hold other Oses,
other file systems, or be raw
Mounted at boot time
Other partitions can mount automatically or manually on mount
points – location at which they can be accessed
At mount time, file system consistency checked
Is all metadata correct?
If not, fix it, try again
If yes, add to mount table, allow access
Operating System Concepts – 10th Edition 15.6 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2018
� File Systems and Mounting
(a) Unix-like file
system directory
tree
(b)Unmounted file
system
After mounting (b)
into the existing
directory tree
Operating System Concepts – 10th Edition 15.7 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2018
� File Sharing
Allows multiple users / systems access to the same files
Permissions / protection must be implement and accurate
Most systems provide concepts of owner, group member
Must have a way to apply these between systems
Operating System Concepts – 10th Edition 15.8 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2018
� Virtual File Systems
Virtual File Systems (VFS) on Unix provide an object-oriented
way of implementing file systems
VFS allows the same system call interface (the API) to be used
for different types of file systems
Separates file-system generic operations from
implementation details
Implementation can be one of many file systems types, or
network file system
Implements vnodes which hold inodes or network file
details
Then dispatches operation to appropriate file system
implementation routines
Operating System Concepts – 10th Edition 15.9 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2018
� Virtual File Systems (Cont.)
The API is to the VFS interface, rather than any specific type of
file system
Operating System Concepts – 10th Edition 15.10 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2018
� Virtual File System Implementation
For example, Linux has four object types:
inode, file, superblock, dentry
VFS defines set of operations on the objects that must be
implemented
Every object has a pointer to a function table
Function table has addresses of routines to implement that
function on that object
For example:
• int open(. . .)—Open a file
• int close(. . .)—Close an already-open file
• ssize t read(. . .)—Read from a file
• ssize t write(. . .)—Write to a file
• int mmap(. . .)—Memory-map a file
Operating System Concepts – 10th Edition 15.11 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2018
� Remote File Systems
Sharing of files across a network
First method involved manually sharing each file – programs
like ftp
Second method uses a distributed file system (DFS)
Remote directories visible from local machine
Third method – World Wide Web
A bit of a revision to first method
Use browser to locate file/files and download /upload
Anonymous access doesn’t require authentication
Operating System Concepts – 10th Edition 15.12 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2018
� Client-Server Model
Sharing between a server (providing access to a file system
via a network protocol) and a client (using the protocol to
access the remote file system)
Identifying each other via network ID can be spoofed,
encryption can be performance expensive
NFS an example
User auth info on clients and servers must match
(UserIDs for example)
Remote file system mounted, file operations sent on
behalf of user across network to server
Server checks permissions, file handle returned
Handle used for reads and writes until file closed
Operating System Concepts – 10th Edition 15.13 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2018
� Distributed Information Systems
Aka distributed naming services, provide unified access to
info needed for remote computing
Domain name system (DNS) provides host-name-to-
network-address translations for the Internet
Others like network information service (NIS) provide user-
name, password, userID, group information
Microsoft’s common Internet file system (CIFS) network
info used with user auth to create network logins that server
uses to allow to deny access
Active directory distributed naming service
Kerberos-derived network authentication protocol
Industry moving toward lightweight directory-access
protocol (LDAP) as secure distributed naming mechanism
Operating System Concepts – 10th Edition 15.14 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2018
� Consistency Semantics
Important criteria for evaluating file sharing-file systems
Specify how multiple users are to access shared file simultaneously
When modifications of data will be observed by other users
Directly related to process synchronization algorithms, but atomicity across a
network has high overhead (see Andrew File System)
The series of accesses between file open and closed called file session
UNIX semantics
Writes to open file immediately visible to others with file open
One mode of sharing allows users to share pointer to current I/O location in
file
Single physical image, accessed exclusively, contention causes process
delays
Session semantics (Andrew file system (OpenAFS))
Writes to open file not visible during session, only at close
Can be several copies, each changed independently
Operating System Concepts – 10th Edition 15.15 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2018
� The Sun Network File System (NFS)
An implementation and a specification of a software system
for accessing remote files across LANs (or WANs)
The implementation originally part of SunOS operating
system, now industry standard / very common
Can use unreliable datagram protocol (UDP/IP) or TCP/IP,
over Ethernet or other network
Operating System Concepts – 10th Edition 15.16 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2018
� NFS (Cont.)
Interconnected workstations viewed as a set of independent machines
with independent file systems, which allows sharing among these file
systems in a transparent manner
A remote directory is mounted over a local file system directory
The mounted directory looks like an integral subtree of the local
file system, replacing the subtree descending from the local
directory
Specification of the remote directory for the mount operation is
nontransparent; the host name of the remote directory has to be
provided
Files in the remote directory can then be accessed in a
transparent manner
Subject to access-rights accreditation, potentially any file system
(or directory within a file system), can be mounted remotely on top
of any local directory
Operating System Concepts – 10th Edition 15.17 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2018
� NFS (Cont.)
NFS is designed to operate in a heterogeneous environment of
different machines, operating systems, and network architectures;
the NFS specifications independent of these media
This independence is achieved through the use of RPC primitives
built on top of an External Data Representation (XDR) protocol used
between two implementation-independent interfaces
The NFS specification distinguishes between the services provided
by a mount mechanism and the actual remote-file-access services
Operating System Concepts – 10th Edition 15.18 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2018
� Three Independent File Systems
Operating System Concepts – 10th Edition 15.19 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2018
� Mounting in NFS
Mounts Cascading mounts
Operating System Concepts – 10th Edition 15.20 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2018
� NFS Mount Protocol
Establishes initial logical connection between server and client
Mount operation includes name of remote directory to be mounted
and name of server machine storing it
Mount request is mapped to corresponding RPC and forwarded
to mount server running on server machine
Export list – specifies local file systems that server exports for
mounting, along with names of machines that are permitted to
mount them
Following a mount request that conforms to its export list, the
server returns a file handle—a key for further accesses
File handle – a file-system identifier, and an inode number to
identify the mounted directory within the exported file system
The mount operation changes only the user’s view and does not
affect the server side
Operating System Concepts – 10th Edition 15.21 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2018
� NFS Protocol
Provides a set of remote procedure calls for remote file operations.
The procedures support the following operations:
searching for a file within a directory
reading a set of directory entries
manipulating links and directories
accessing file attributes
reading and writing files
NFS servers are stateless; each request has to provide a full set
of arguments (NFS V4 is newer, less used – very different,
stateful)
Modified data must be committed to the server’s disk before
results are returned to the client (lose advantages of caching)
The NFS protocol does not provide concurrency-control
mechanisms
Operating System Concepts – 10th Edition 15.22 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2018
� Three Major Layers of NFS Architecture
UNIX file-system interface (based on the open, read, write, and
close calls, and file descriptors)
Virtual File System (VFS) layer – distinguishes local files from
remote ones, and local files are further distinguished according to
their file-system types
The VFS activates file-system-specific operations to handle
local requests according to their file-system types
Calls the NFS protocol procedures for remote requests
NFS service layer – bottom layer of the architecture
Implements the NFS protocol
Operating System Concepts – 10th Edition 15.23 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2018
� Schematic View of NFS Architecture
Operating System Concepts – 10th Edition 15.24 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2018
� NFS Path-Name Translation
Performed by breaking the path into component names and
performing a separate NFS lookup call for every pair of
component name and directory vnode
To make lookup faster, a directory name lookup cache on the
client’s side holds the vnodes for remote directory names
Operating System Concepts – 10th Edition 15.25 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2018
� NFS Remote Operations
Nearly one-to-one correspondence between regular UNIX system
calls and the NFS protocol RPCs (except opening and closing
files)
NFS adheres to the remote-service paradigm, but employs
buffering and caching techniques for the sake of performance
File-blocks cache – when a file is opened, the kernel checks with
the remote server whether to fetch or revalidate the cached
attributes
Cached file blocks are used only if the corresponding cached
attributes are up to date
File-attribute cache – the attribute cache is updated whenever new
attributes arrive from the server
Clients do not free delayed-write blocks until the server confirms
that the data have been written to disk
Operating System Concepts – 10th Edition 15.26 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2018
� End of Chapter 15
Operating System Concepts – 10th Edition Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2018