100% found this document useful (1 vote)
25 views20 pagesInput Protection Using Discrete Components
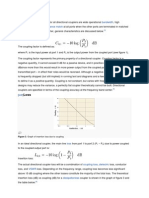
The document outlines various types of input protection including over-voltage, under-voltage, over-current, and reverse polarity protection. It details the principles and components used for each protection type, such as Zener diodes, TVS diodes, and fuses, along with selection parameters for effective implementation. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of these protections in preventing damage to electronic circuits from voltage fluctuations and incorrect connections.
Uploaded by
chirag.thakarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
25 views20 pagesInput Protection Using Discrete Components
The document outlines various types of input protection including over-voltage, under-voltage, over-current, and reverse polarity protection. It details the principles and components used for each protection type, such as Zener diodes, TVS diodes, and fuses, along with selection parameters for effective implementation. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of these protections in preventing damage to electronic circuits from voltage fluctuations and incorrect connections.
Uploaded by
chirag.thakarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 20