0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views22 pagesArray in C-1
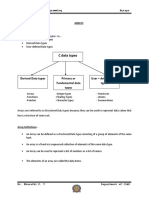
The document provides an overview of arrays, including their definition, types, and usage in programming. It covers array declaration, initialization, looping through arrays, passing arrays to functions, sorting algorithms, and searching techniques. Additionally, it discusses multiple-subscripted arrays and their initialization and referencing methods.
Uploaded by
jerry482891Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views22 pagesArray in C-1
The document provides an overview of arrays, including their definition, types, and usage in programming. It covers array declaration, initialization, looping through arrays, passing arrays to functions, sorting algorithms, and searching techniques. Additionally, it discusses multiple-subscripted arrays and their initialization and referencing methods.
Uploaded by
jerry482891Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 22