0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views13 pagesVol 2 - Section 2 - Chapter 4 - HAP
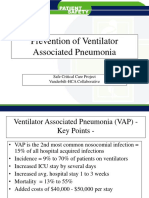
This chapter from the Federal Ministry of Health focuses on health care associated pneumonia (HCAP), including ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP), outlining its epidemiology, risk factors, and prevention strategies. It emphasizes the importance of infection prevention and control (IPC) practices to reduce the incidence of HCAP and VAP, which are significant contributors to healthcare-associated infections. The chapter also highlights the necessity of monitoring and surveillance to improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs.
Uploaded by
gmel80629Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views13 pagesVol 2 - Section 2 - Chapter 4 - HAP
This chapter from the Federal Ministry of Health focuses on health care associated pneumonia (HCAP), including ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP), outlining its epidemiology, risk factors, and prevention strategies. It emphasizes the importance of infection prevention and control (IPC) practices to reduce the incidence of HCAP and VAP, which are significant contributors to healthcare-associated infections. The chapter also highlights the necessity of monitoring and surveillance to improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs.
Uploaded by
gmel80629Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 13