0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views51 pagesIntroduction
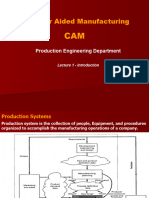
The document provides an overview of Computer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM), detailing the components of production systems, including facilities and manufacturing support systems. It discusses various plant layouts, types of automation, and the relationship between production quantity and product variety. Additionally, it outlines the roles of computerized systems in enhancing manufacturing processes and the integration of design, planning, and control functions within a manufacturing firm.
Uploaded by
arodionphotographyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views51 pagesIntroduction
The document provides an overview of Computer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM), detailing the components of production systems, including facilities and manufacturing support systems. It discusses various plant layouts, types of automation, and the relationship between production quantity and product variety. Additionally, it outlines the roles of computerized systems in enhancing manufacturing processes and the integration of design, planning, and control functions within a manufacturing firm.
Uploaded by
arodionphotographyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 51