0% found this document useful (0 votes)
111 views23 pagesBasic Paco Call Flow and Interfaces
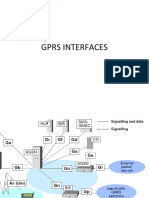
The document outlines the architecture and interfaces of 2G, 3G, and 4G networks, detailing various interfaces such as Gb, Gn, Gp, Gi, Gr, Gy, Gx, S1, S3, S4, S10, S11, S6a, S13, X2, and S5/S8. Each interface serves specific functions for signaling, data transfer, and user authentication within mobile networks. Additionally, it highlights the evolution of network components and protocols to support seamless mobility and efficient data management.
Uploaded by
Vijendra SahuCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
111 views23 pagesBasic Paco Call Flow and Interfaces
The document outlines the architecture and interfaces of 2G, 3G, and 4G networks, detailing various interfaces such as Gb, Gn, Gp, Gi, Gr, Gy, Gx, S1, S3, S4, S10, S11, S6a, S13, X2, and S5/S8. Each interface serves specific functions for signaling, data transfer, and user authentication within mobile networks. Additionally, it highlights the evolution of network components and protocols to support seamless mobility and efficient data management.
Uploaded by
Vijendra SahuCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 23