0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views10 pagesMidpoint Circle Drawing Algorithm
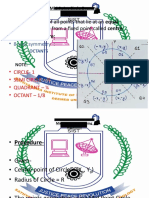
The Mid-point Circle Drawing Algorithm efficiently draws circles on raster displays using integer arithmetic and symmetry across octants. It has applications in computer graphics, digital art, medical imaging, robotics, and CAD, offering advantages like efficiency and simplicity, but is limited to raster graphics and lacks anti-aliasing. Despite its drawbacks, it remains widely utilized in various fields due to its effectiveness in producing smooth circular shapes.
Uploaded by
kamunguwilliamCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views10 pagesMidpoint Circle Drawing Algorithm
The Mid-point Circle Drawing Algorithm efficiently draws circles on raster displays using integer arithmetic and symmetry across octants. It has applications in computer graphics, digital art, medical imaging, robotics, and CAD, offering advantages like efficiency and simplicity, but is limited to raster graphics and lacks anti-aliasing. Despite its drawbacks, it remains widely utilized in various fields due to its effectiveness in producing smooth circular shapes.
Uploaded by
kamunguwilliamCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 10