0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views29 pages2 Jcomponents in Java
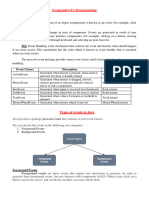
The document provides an overview of the ActionListener interface in Java AWT, which is essential for handling user interactions in GUI applications. It explains the ActionEvent class, the delegation event model, and various event classes and listener interfaces in Java. Additionally, it discusses components like JOptionPane, JScrollBar, JScrollPane, JTable, and JTree, highlighting their functionalities and uses in creating interactive Java applications.
Uploaded by
Sharda KaurCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views29 pages2 Jcomponents in Java
The document provides an overview of the ActionListener interface in Java AWT, which is essential for handling user interactions in GUI applications. It explains the ActionEvent class, the delegation event model, and various event classes and listener interfaces in Java. Additionally, it discusses components like JOptionPane, JScrollBar, JScrollPane, JTable, and JTree, highlighting their functionalities and uses in creating interactive Java applications.
Uploaded by
Sharda KaurCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 29