CONDITIONAL AND
LOOPING
STATEMENTS
�AGENDA:
Conditional Statements
IF Statement
If else Statement
Elif Statement
Nested if..else Statement
Looping Statements
For Loop
While Loop
�CONDITIONAL STATEMENTS
Conditional statements in Python are used to execute certain blocks of code
based on specific conditions.
These statements help control the flow of a program, making it behave differently
in different situations.
TYPES OF CONDITIONAL STATEMENTS:
IF Statement
If else Statement
Elif Statement
Nested if..else Statement
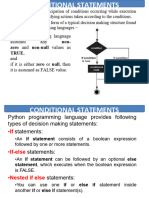
�IF STATEMENT
If statement is the simplest form of a conditional statement.
It executes a block of code if the given condition is true.
Syntax of If Statement:
if condition:
# Statements to execute if
# condition is true
Example:
age = 20
if age >= 18:
print("Eligible to vote.")
�IF ELSE STATEMENT
It allows us to specify a block of code that will execute if the condition(s) associated with an if
or elif statement evaluates to False.
Else block provides a way to handle all other cases that don't meet the specified conditions.
Syntax of If Else Statement:
if condition:
# code to execute if condition is true
else:
# code to execute if condition is false
Example:
age = 10
if age <= 12:
print("Travel for free.")
else:
print("Pay for ticket.")
�ELIF STATEMENT
Elif statement in Python stands for "else if."
It allows us to check multiple conditions , providing a way to execute different blocks
of code based on which condition is true.
Using Elif statements makes our code more readable and efficient by eliminating the
need for multiple nested if statements.
Syntax of Elif Statement:
if condition1:
# code to execute if condition1 is true
elif condition2:
# code to execute if condition2 is true
else:
# code to execute if none of the above
conditions are true
�EXAMPLE:
age = 25
if age <= 12:
print("Child.")
elif age <= 19:
print("Teenager.")
elif age <= 35:
print("Young adult.")
else:
print("Adult.")
�NESTED IF..ELSE STATEMENT
Nested if..else means an if-else statement inside another if statement.
We can use nested if statements to check conditions within conditions.
Example:
age = 70
is_member = True
if age >= 60:
if is_member:
print("30% senior discount!")
else:
print("20% senior discount.")
else:
print("Not eligible for a senior discount.")
�LOOPING STATEMENT
In programming, the loops are the constructs that repeatedly execute a piece of
code based on the conditions.
These are useful in many situations like going through every element of a list,
doing an operation on a range of values, etc.
Loops in Python provides two ways for executing the loops.
They are:
For Loop y
While Loop
�FOR LOOP
For loops are used for sequential traversal.
For example: traversing a list or string or array etc.
In Python, there is “for in” loop which is similar to foreach loop in other
languages.
It can be used to iterate over a range and iterators.
For Loop Syntax:
for iterator_var in sequence:
statements(s)
Example:
n=5
for i in range(0, n):
print(i)
�WHILE LOOP
In Python, a while loop is used to execute a block of statements repeatedly until a given
condition is satisfied.
When the condition becomes false, the line immediately after the loop in the program is
executed.
All the statements indented by the same number of character spaces after a programming
construct are considered to be part of a single block of code.
Python uses indentation as its method of grouping statements.
While Loop Syntax:
while expression:
statement(s)
Example:
count = 0
while (count <= 3):
count = count + 1
print("Hiii Everyone")
�THANK YOU