0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views16 pagesModule 2 Data Structures Expanded
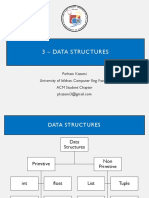
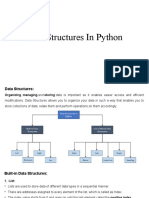
This document provides an overview of intermediate Python data structures including lists, tuples, dictionaries, and sets. It covers their characteristics, common methods, use cases, and best practices for selecting the appropriate structure for specific tasks. Additionally, it includes practice exercises to reinforce the concepts learned.
Uploaded by
Erdey SyoumCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views16 pagesModule 2 Data Structures Expanded
This document provides an overview of intermediate Python data structures including lists, tuples, dictionaries, and sets. It covers their characteristics, common methods, use cases, and best practices for selecting the appropriate structure for specific tasks. Additionally, it includes practice exercises to reinforce the concepts learned.
Uploaded by
Erdey SyoumCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 16