0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views7 pagesRPC Java RMI Presentation
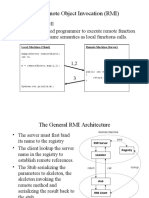
The document explains Remote Procedure Call (RPC) in Java using Remote Method Invocation (RMI), which allows remote execution of code. It outlines the steps to implement Java RMI, including defining a remote interface, creating an RMI server and client, and running the application. Example code snippets for the server and client are provided to illustrate the implementation process.
Uploaded by
ugpgcs22Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views7 pagesRPC Java RMI Presentation
The document explains Remote Procedure Call (RPC) in Java using Remote Method Invocation (RMI), which allows remote execution of code. It outlines the steps to implement Java RMI, including defining a remote interface, creating an RMI server and client, and running the application. Example code snippets for the server and client are provided to illustrate the implementation process.
Uploaded by
ugpgcs22Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 7