0% found this document useful (0 votes)
185 views24 pagesPrimitive and Non-Primitive Data Structures
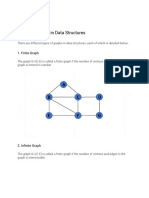
The document outlines the course AI203 on Data Structures and Algorithms, focusing on the classification of data structures into primitive and non-primitive types. It details various data structures such as arrays, stacks, queues, linked lists, trees, and graphs, explaining their properties and operations. Additionally, it covers concepts like complexity analysis and abstract data types.
Uploaded by
AthuCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
185 views24 pagesPrimitive and Non-Primitive Data Structures
The document outlines the course AI203 on Data Structures and Algorithms, focusing on the classification of data structures into primitive and non-primitive types. It details various data structures such as arrays, stacks, queues, linked lists, trees, and graphs, explaining their properties and operations. Additionally, it covers concepts like complexity analysis and abstract data types.
Uploaded by
AthuCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 24