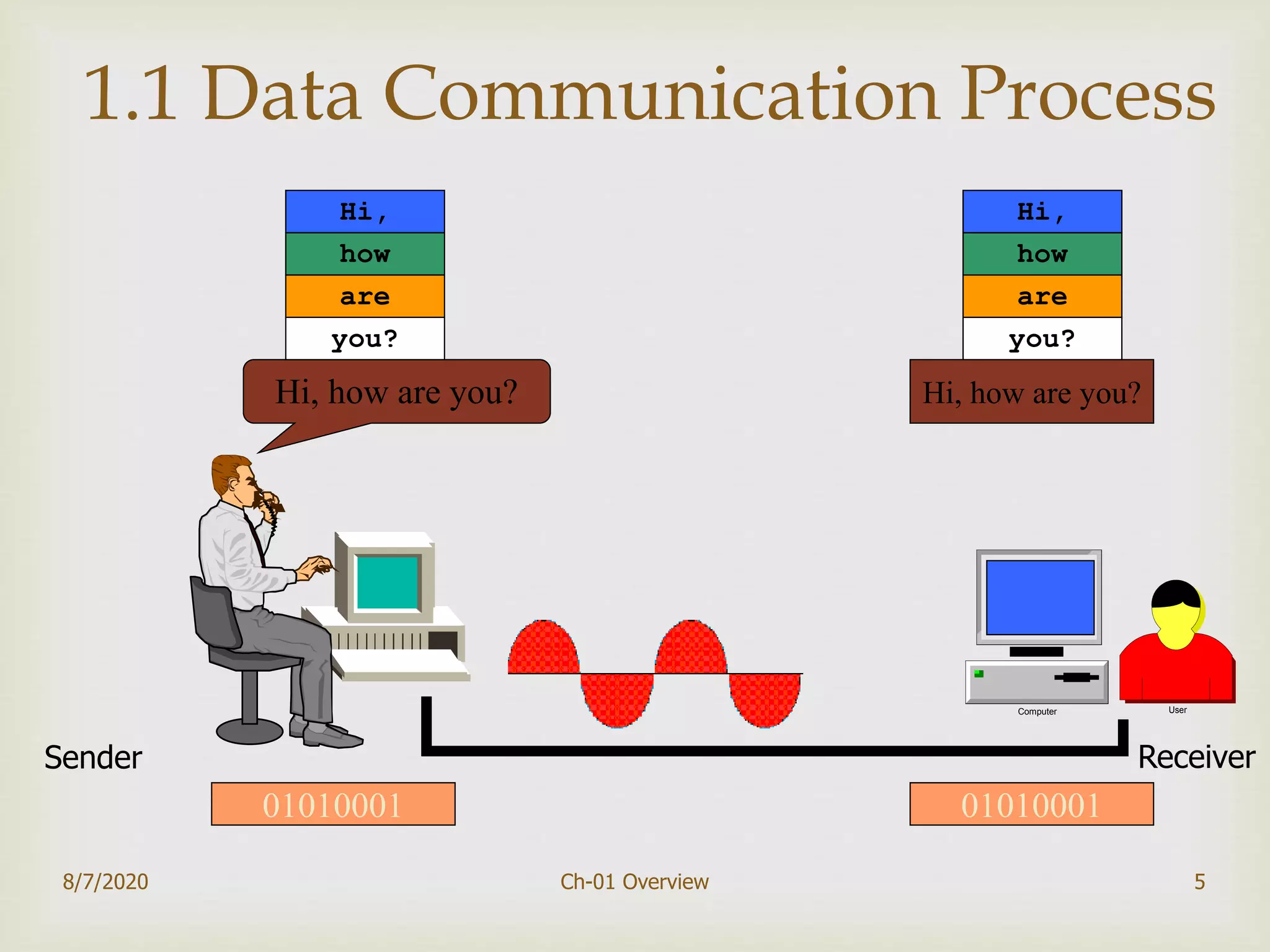
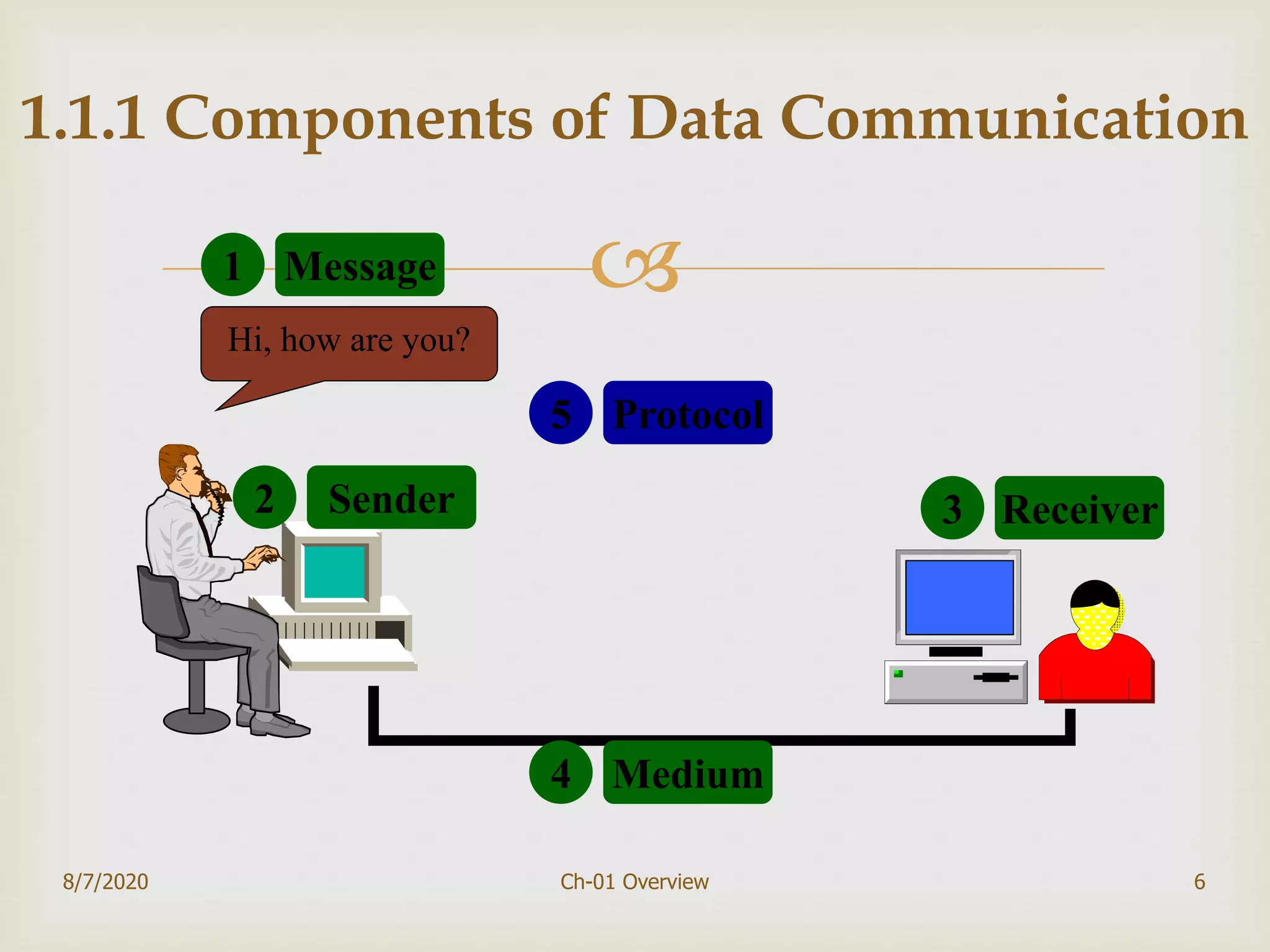
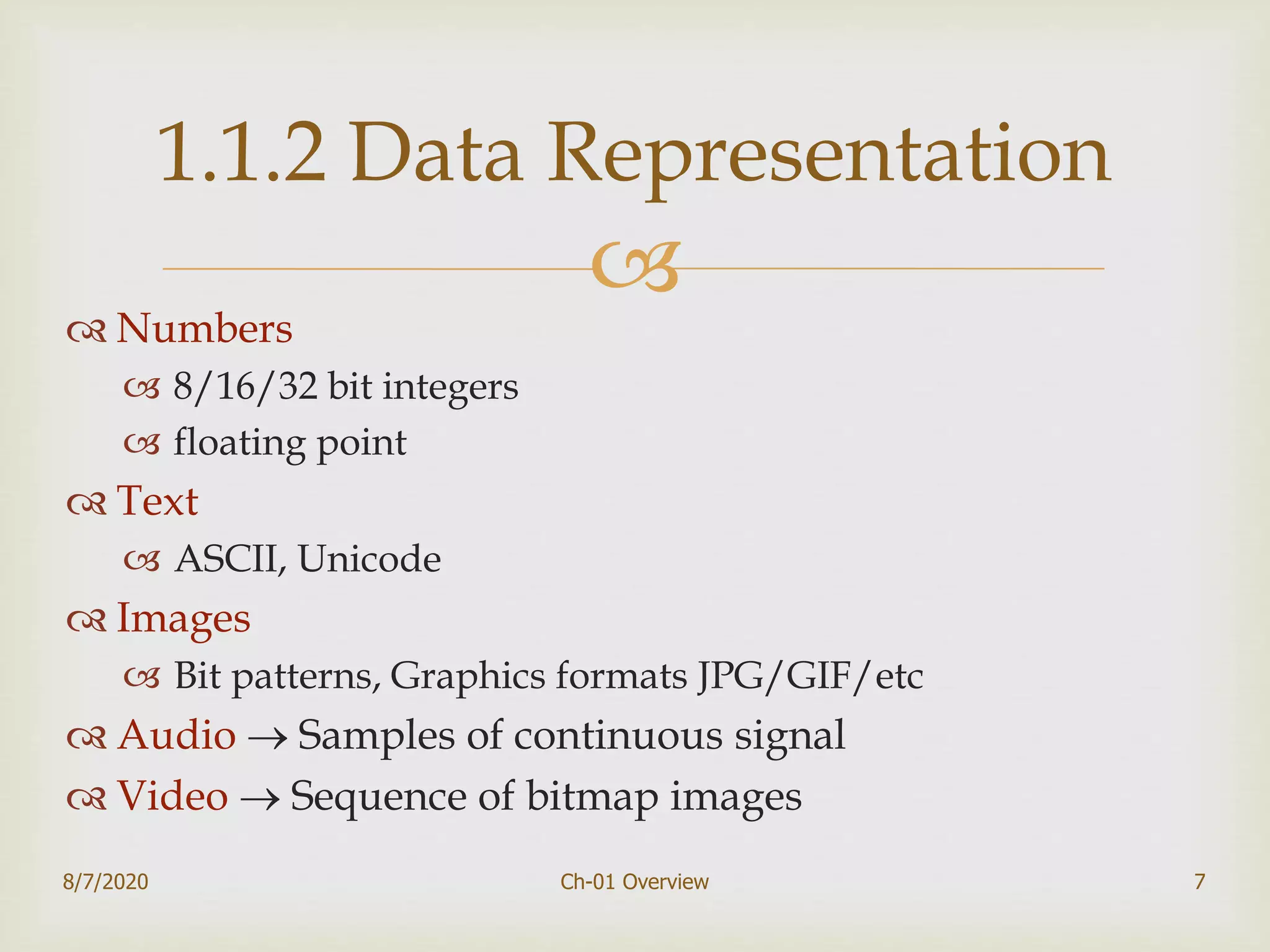
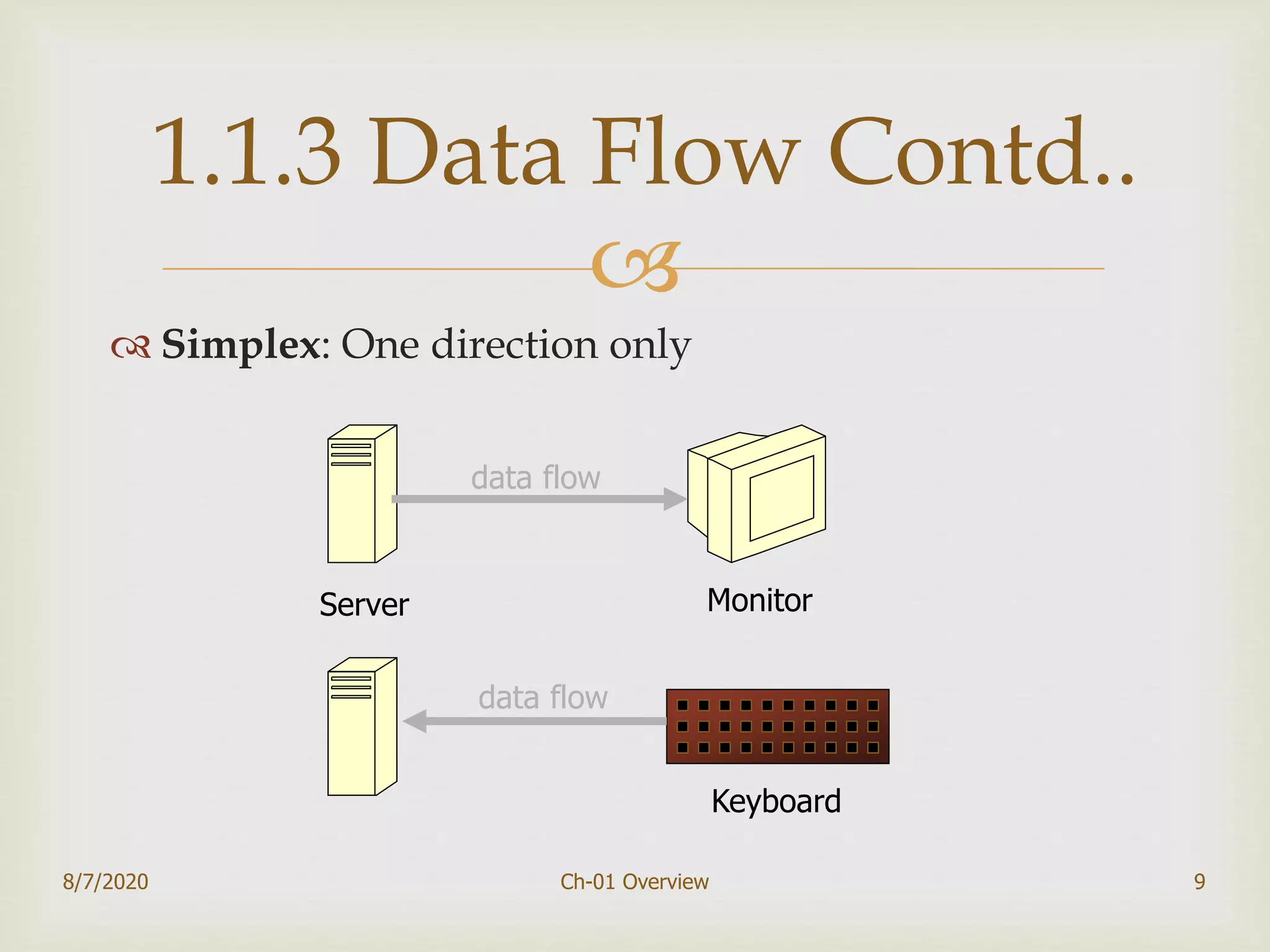
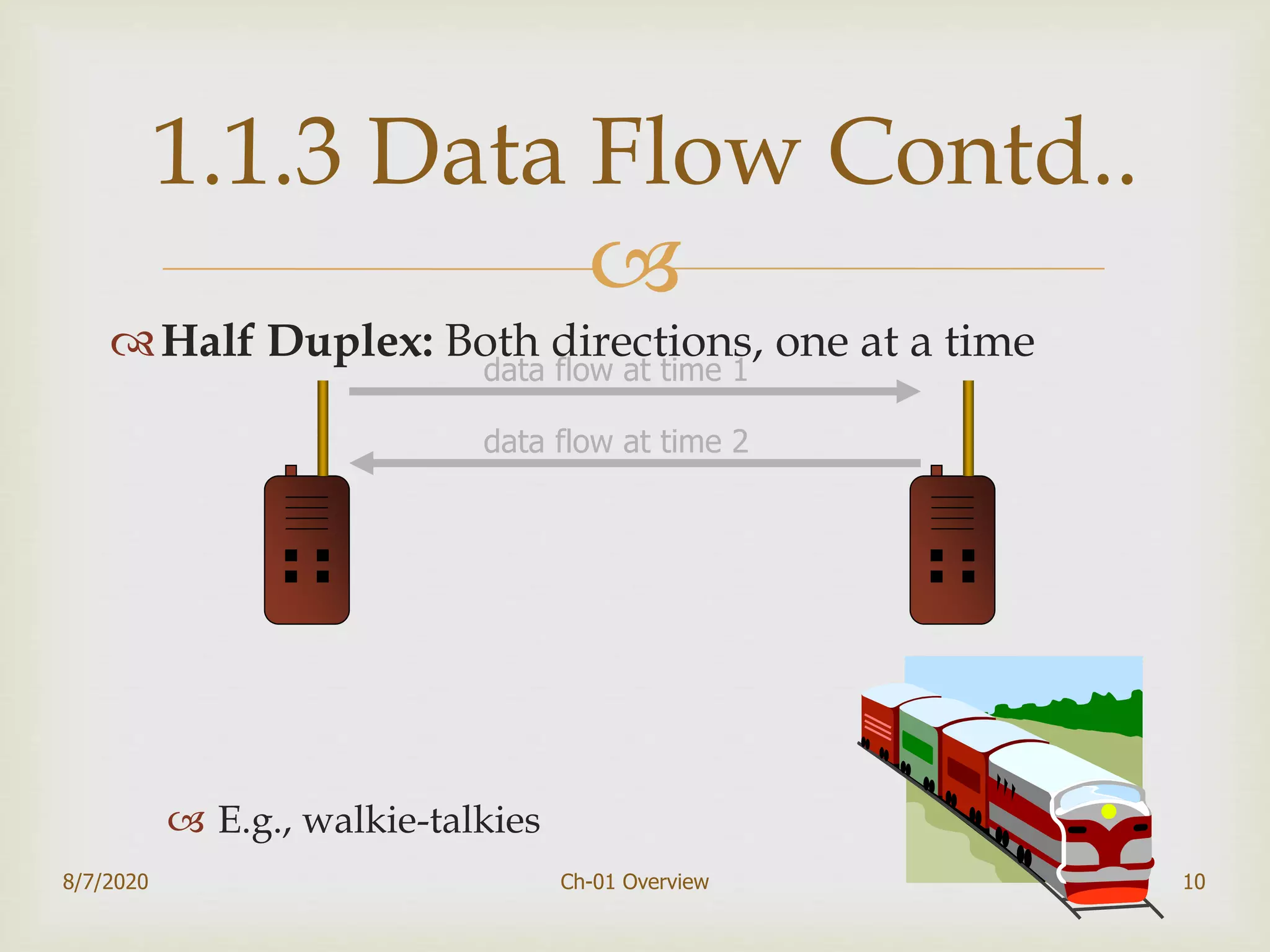
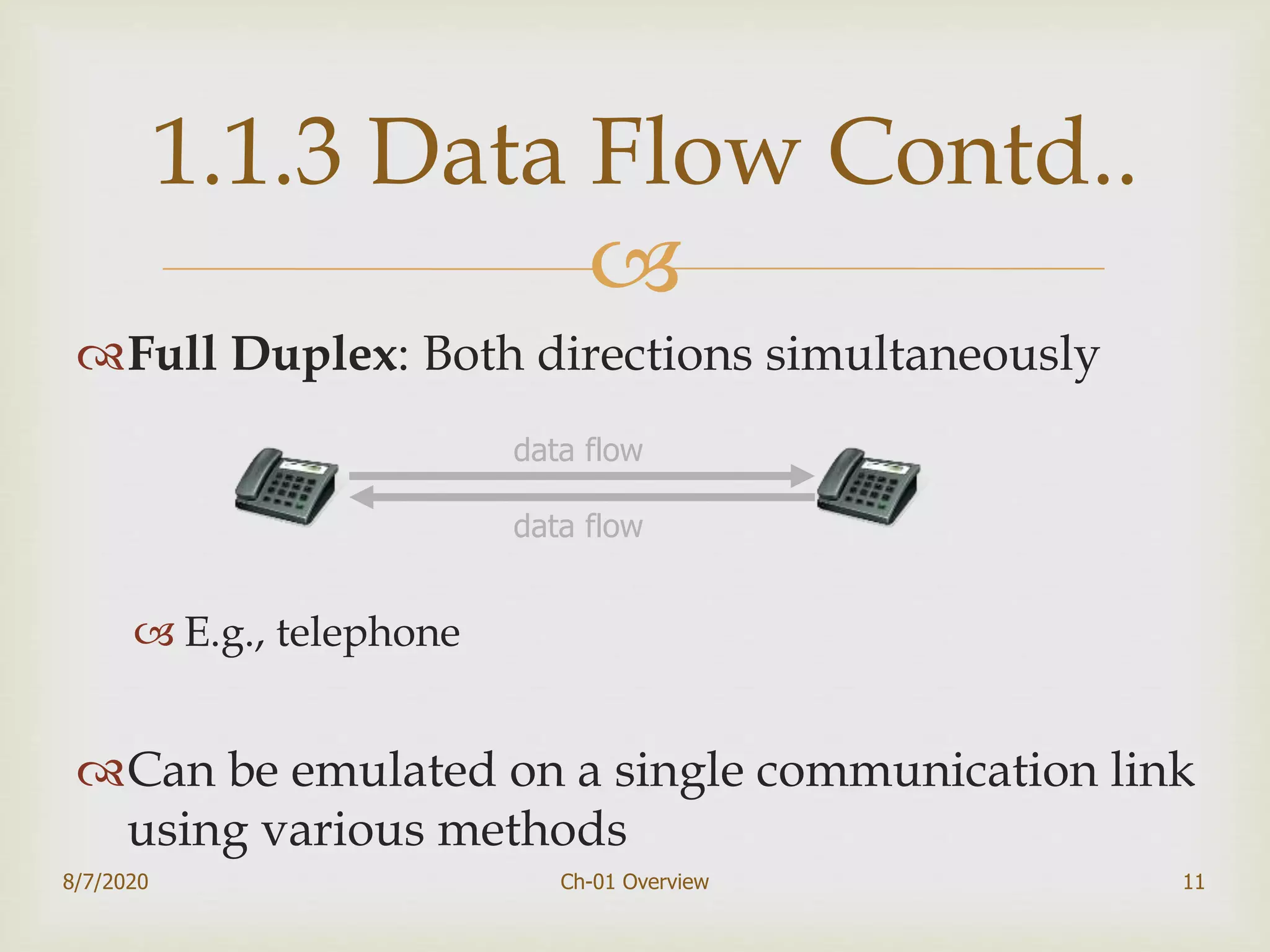
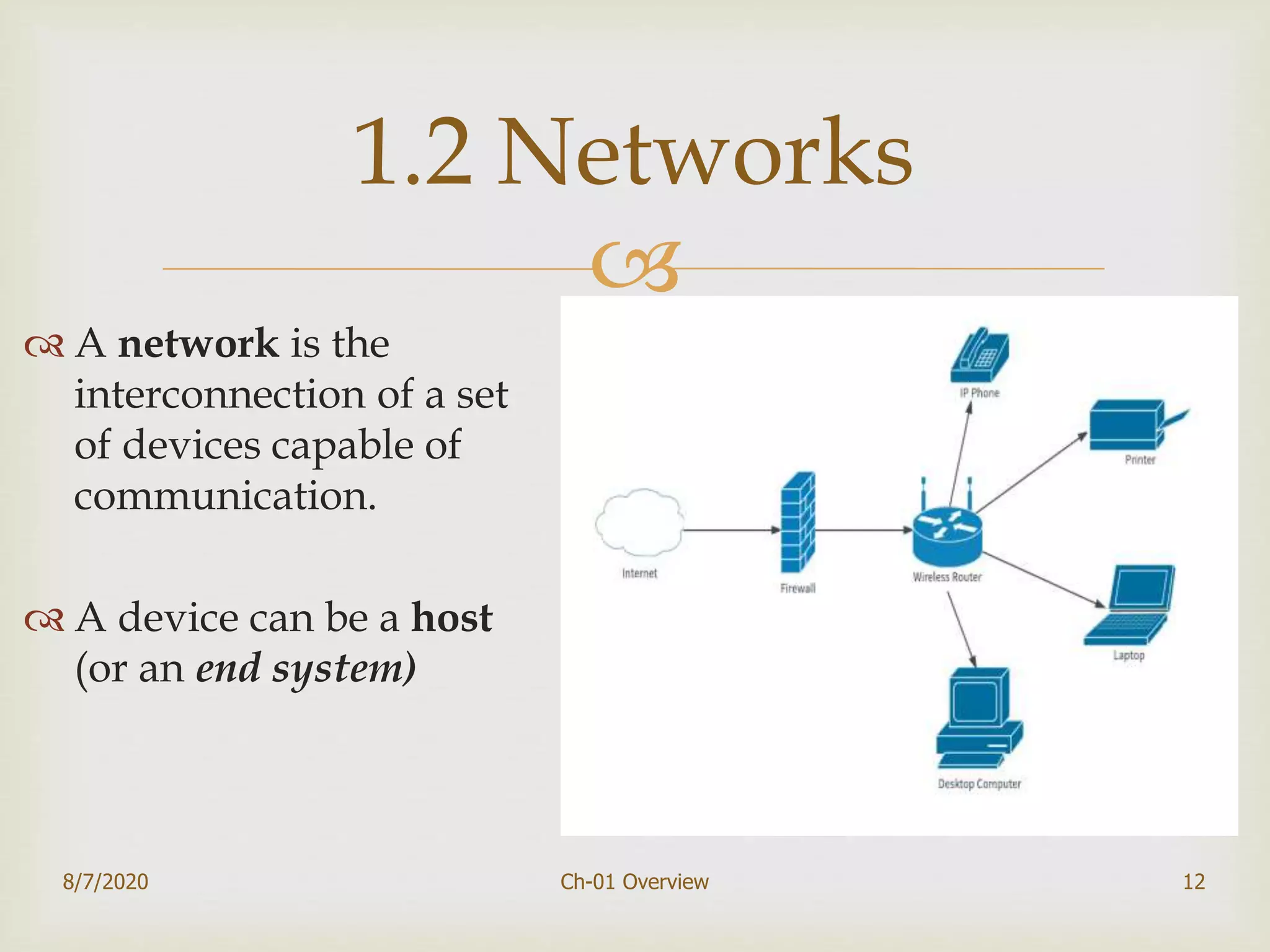
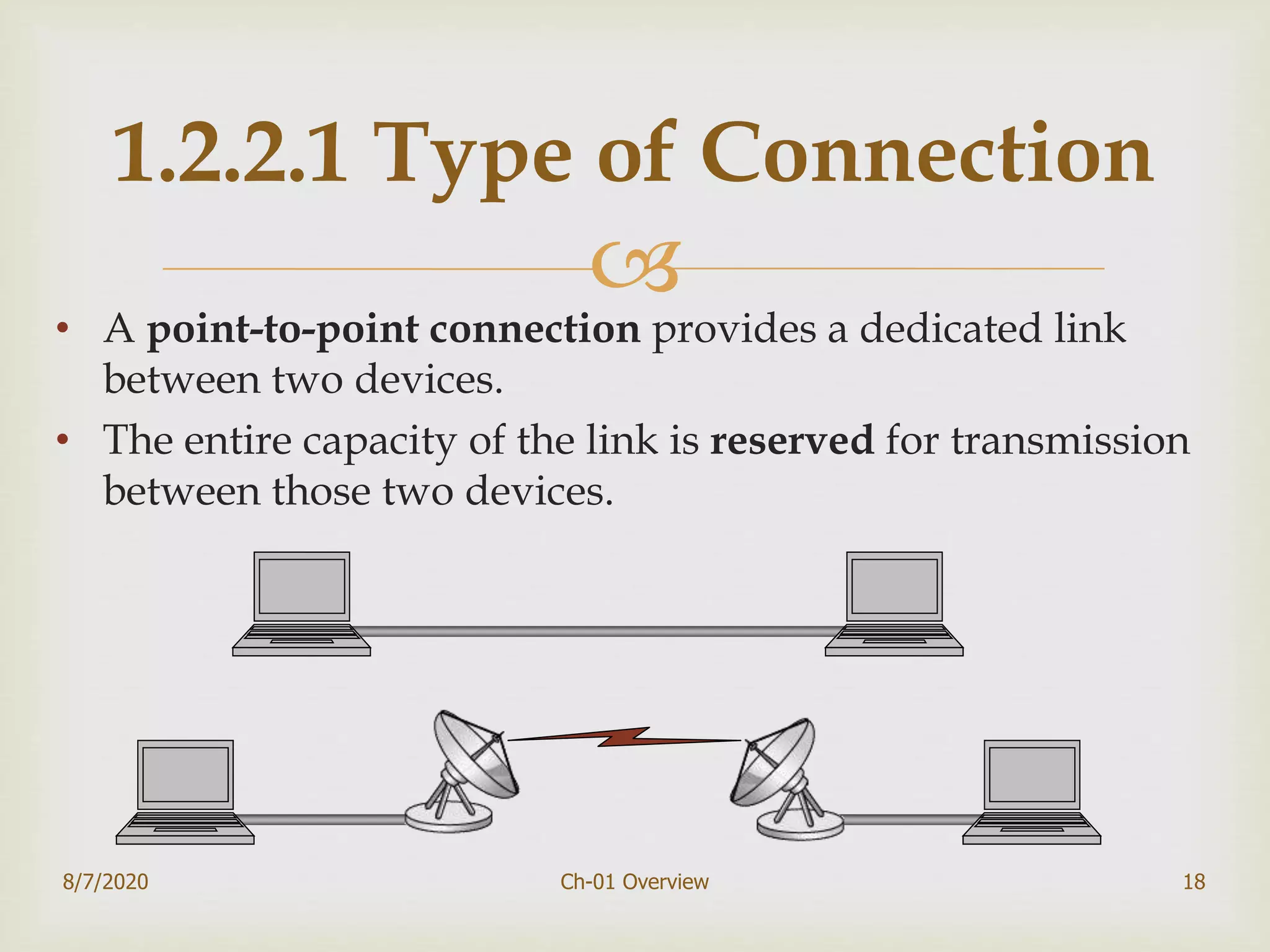
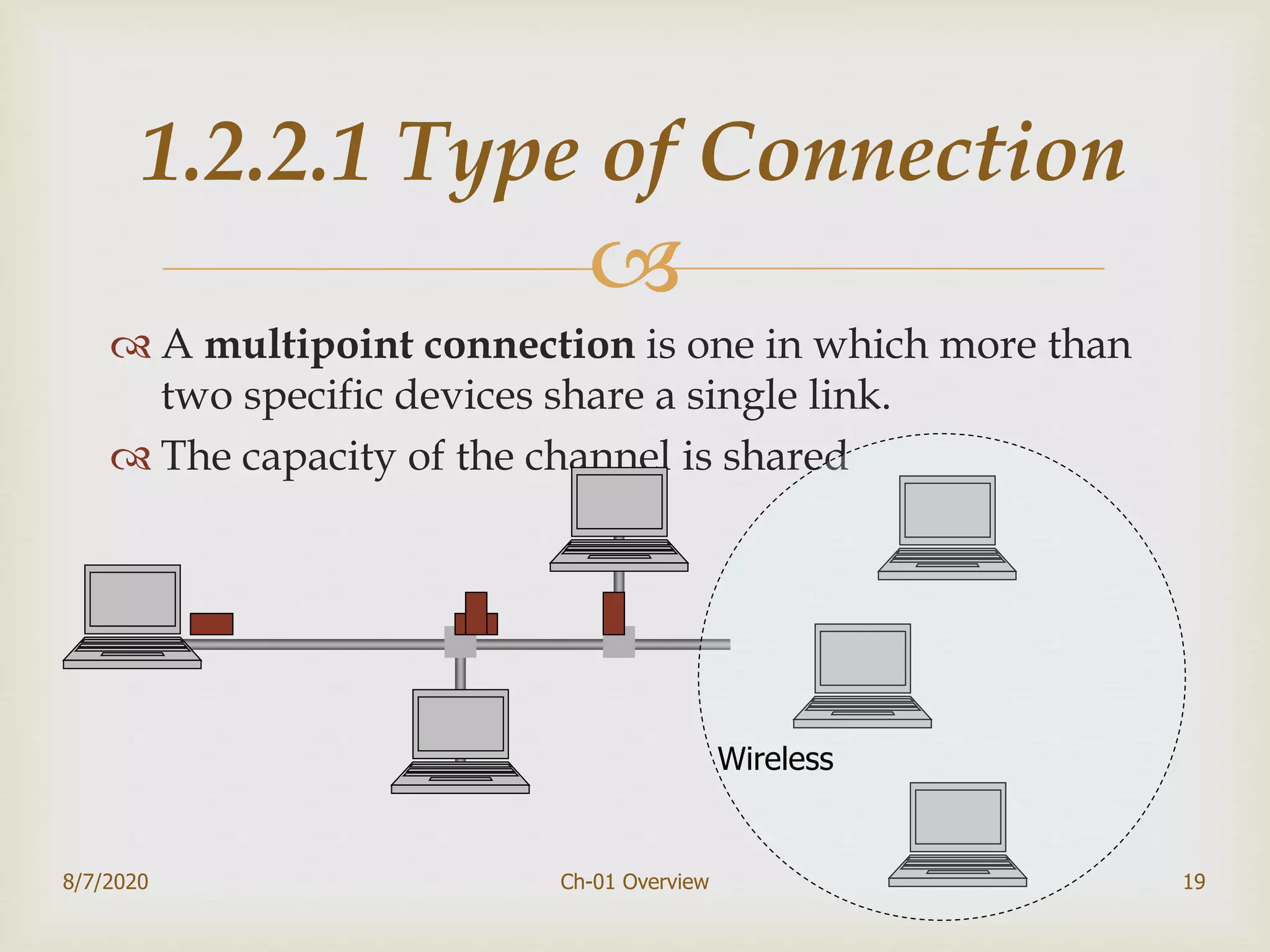
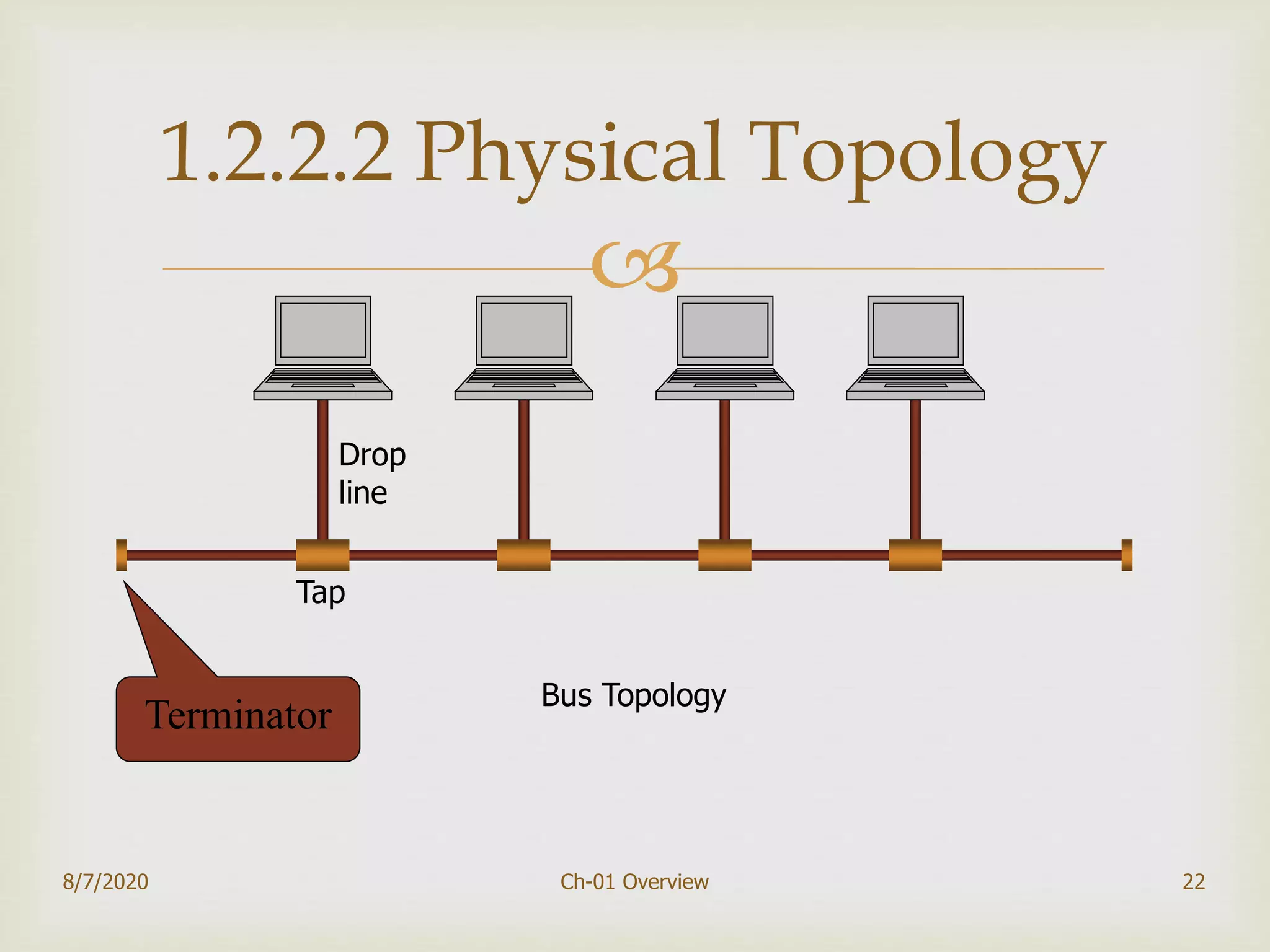
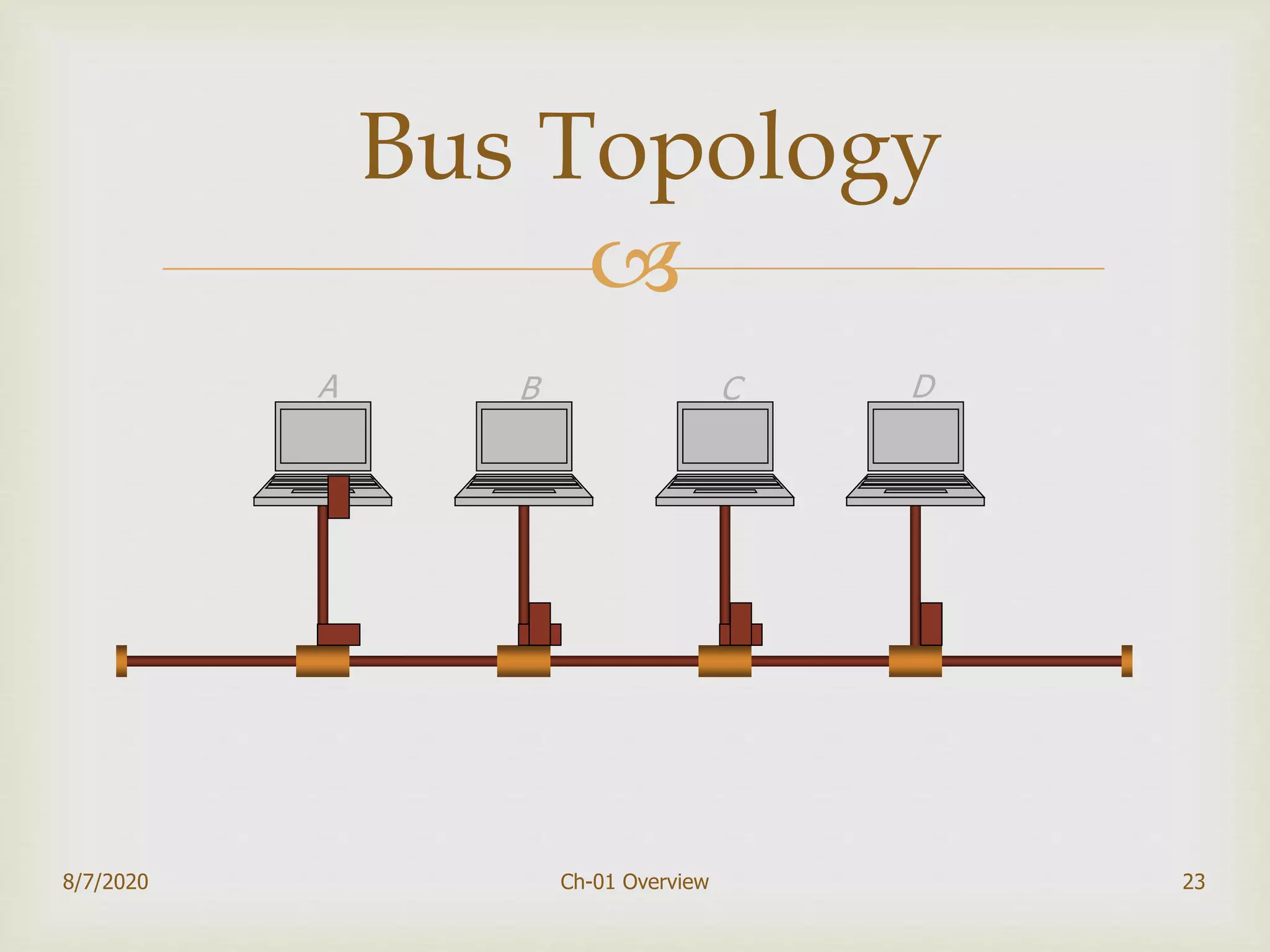
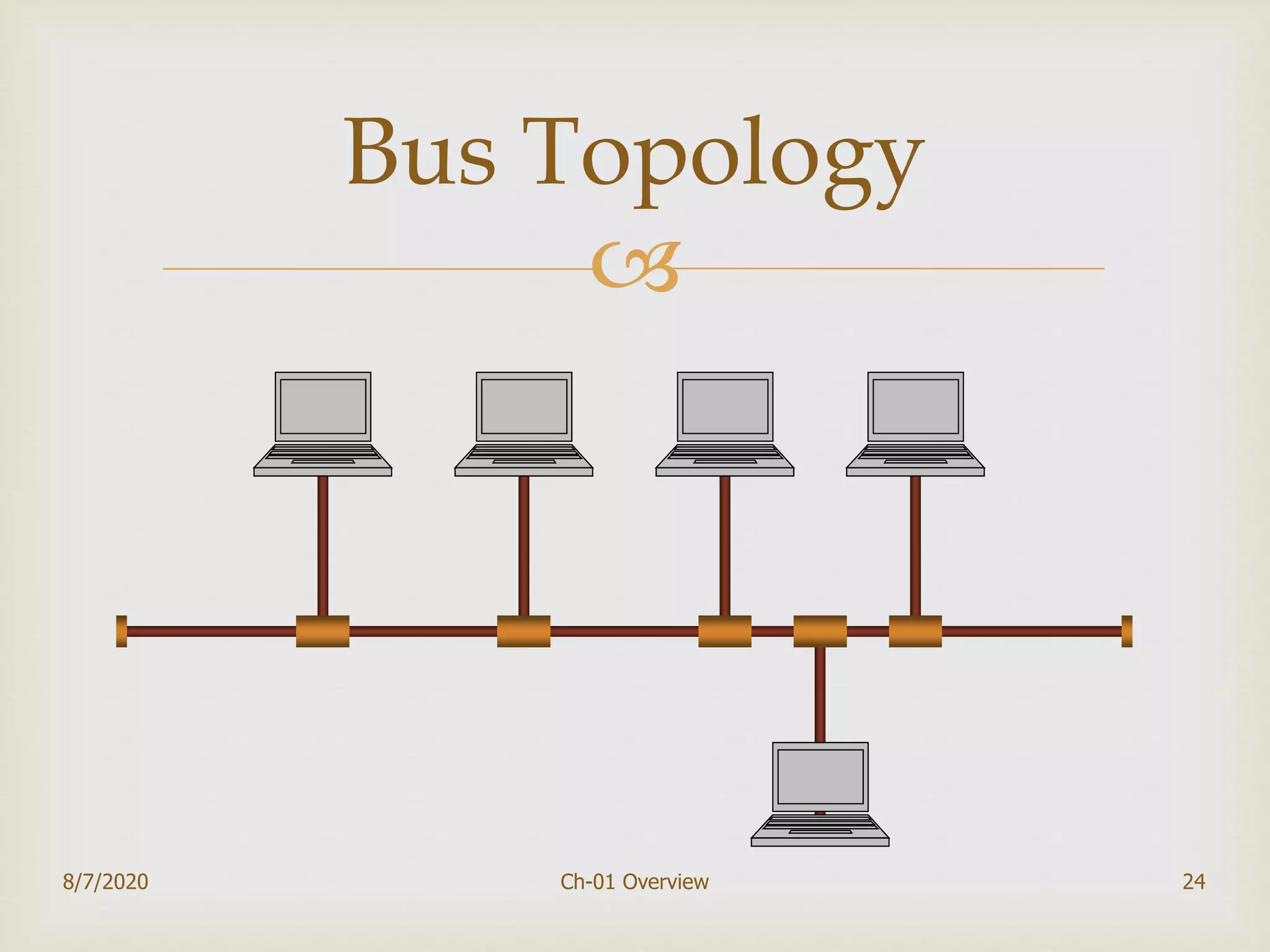
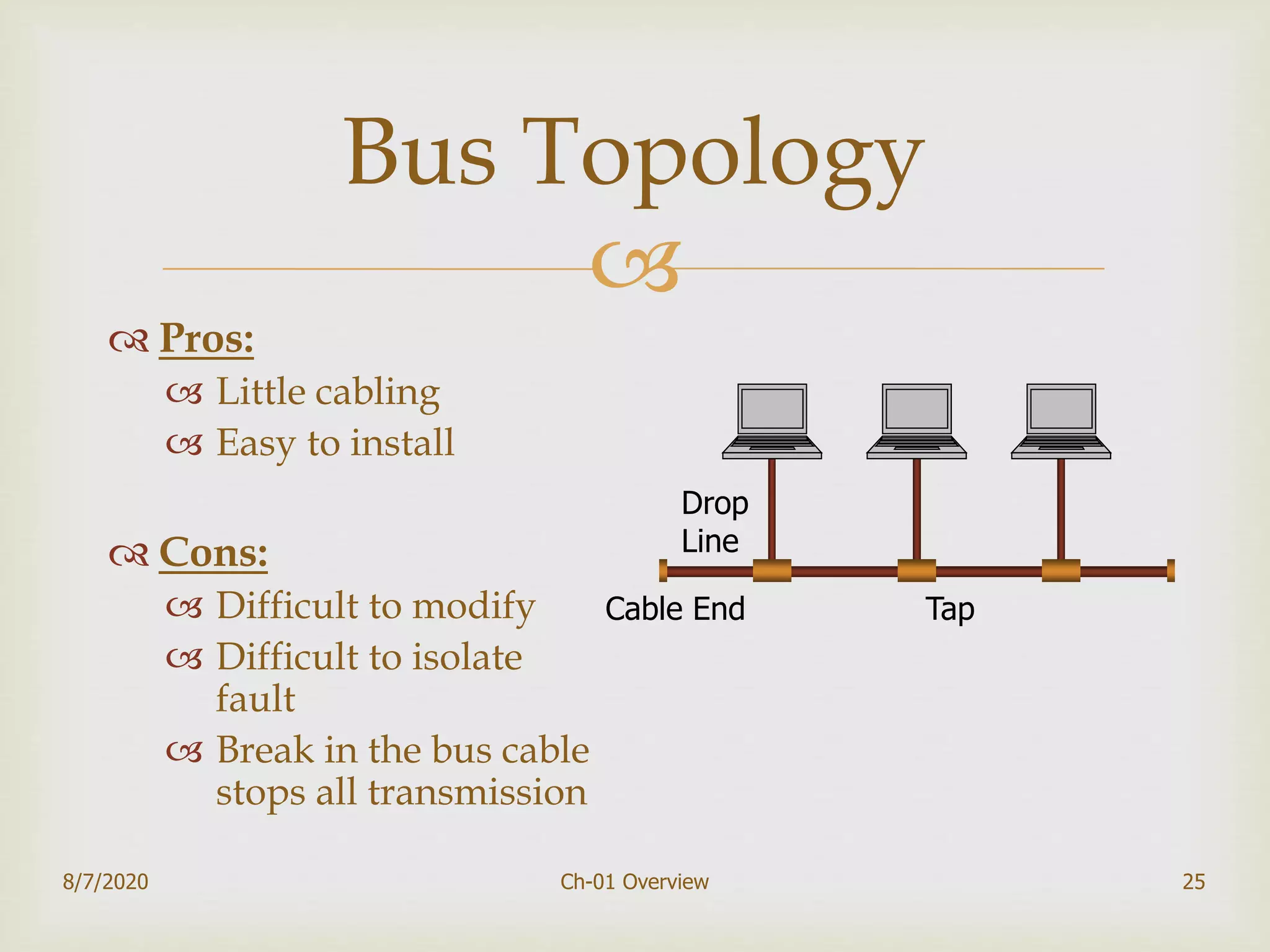
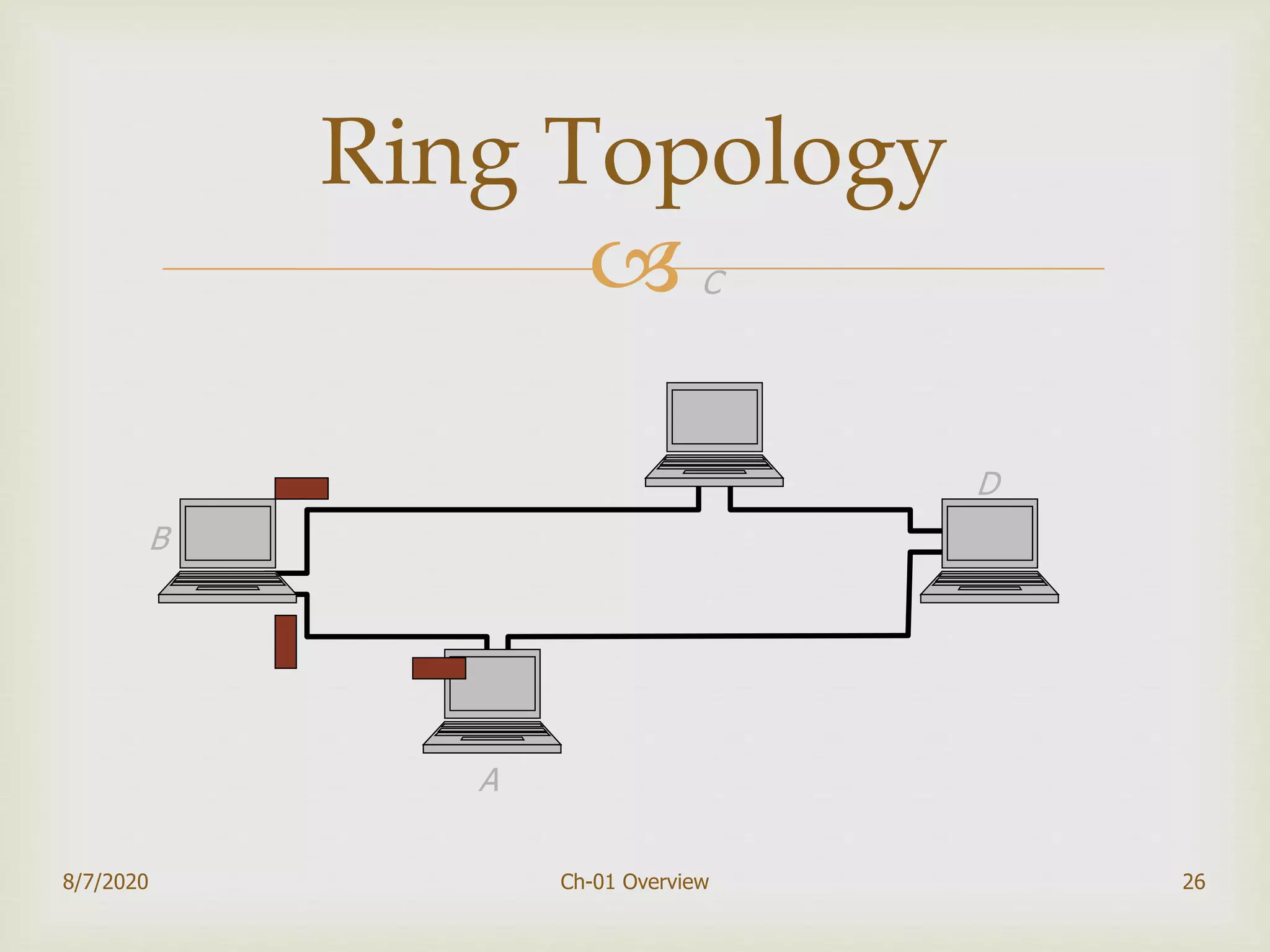
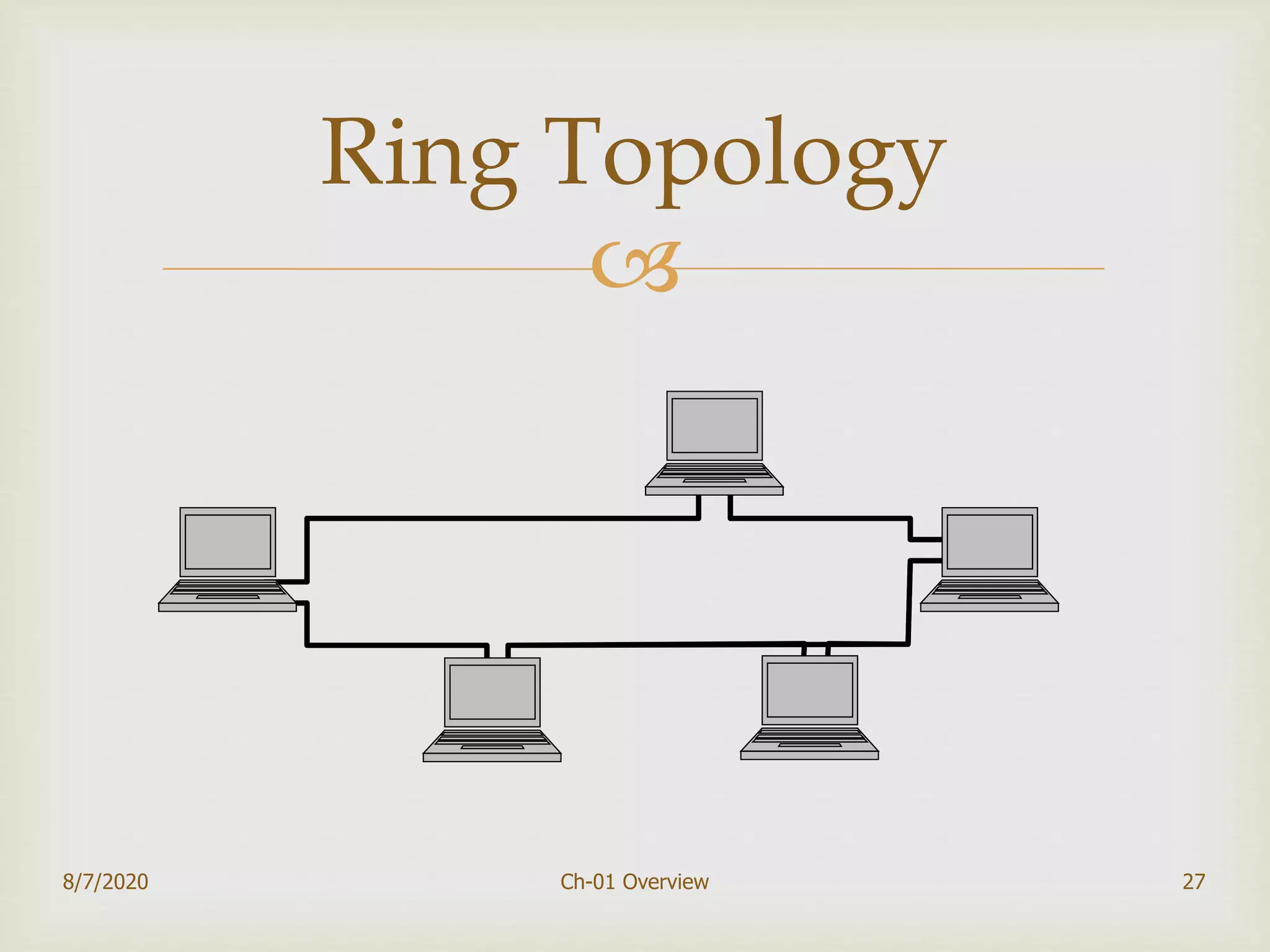
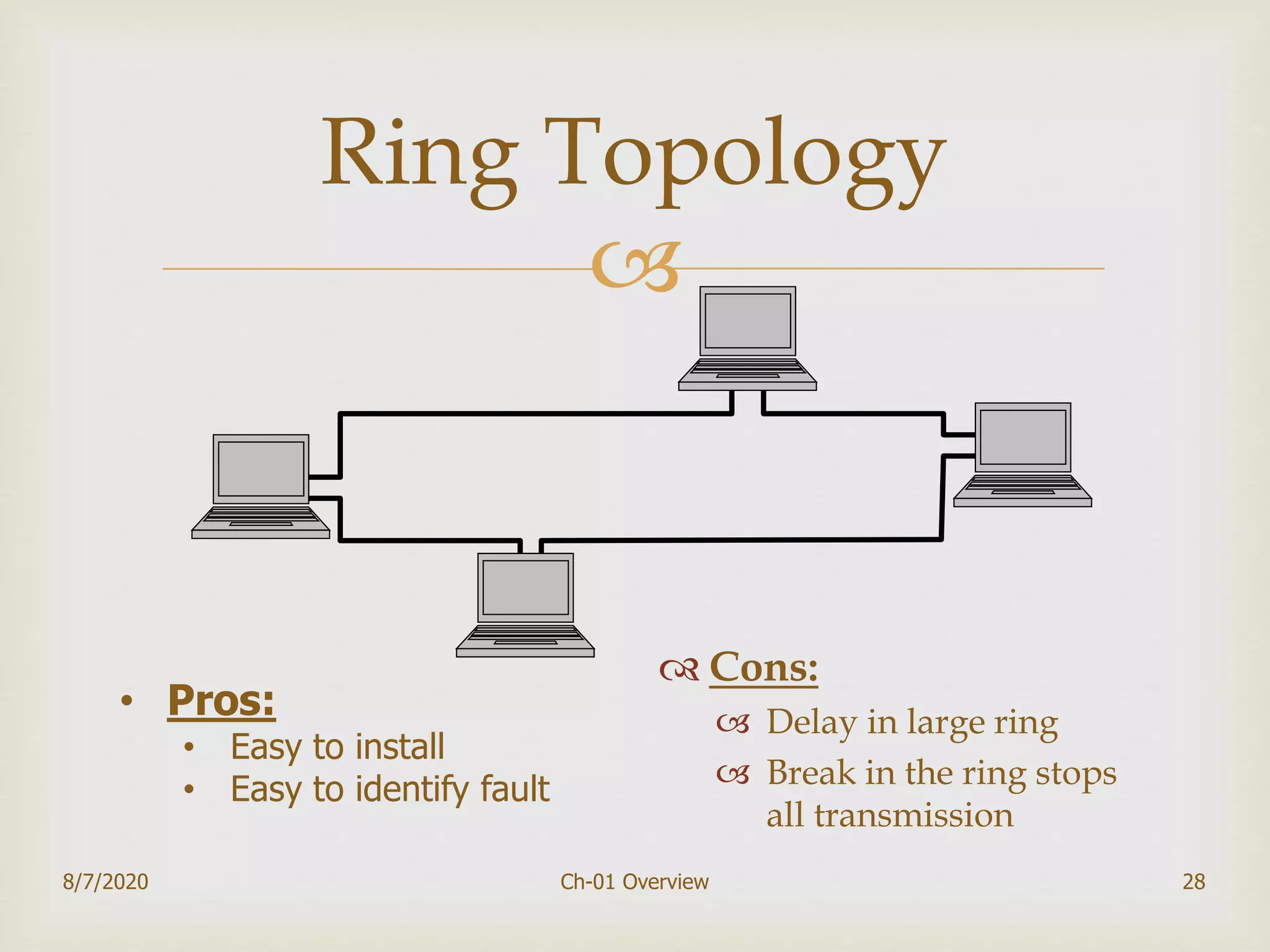
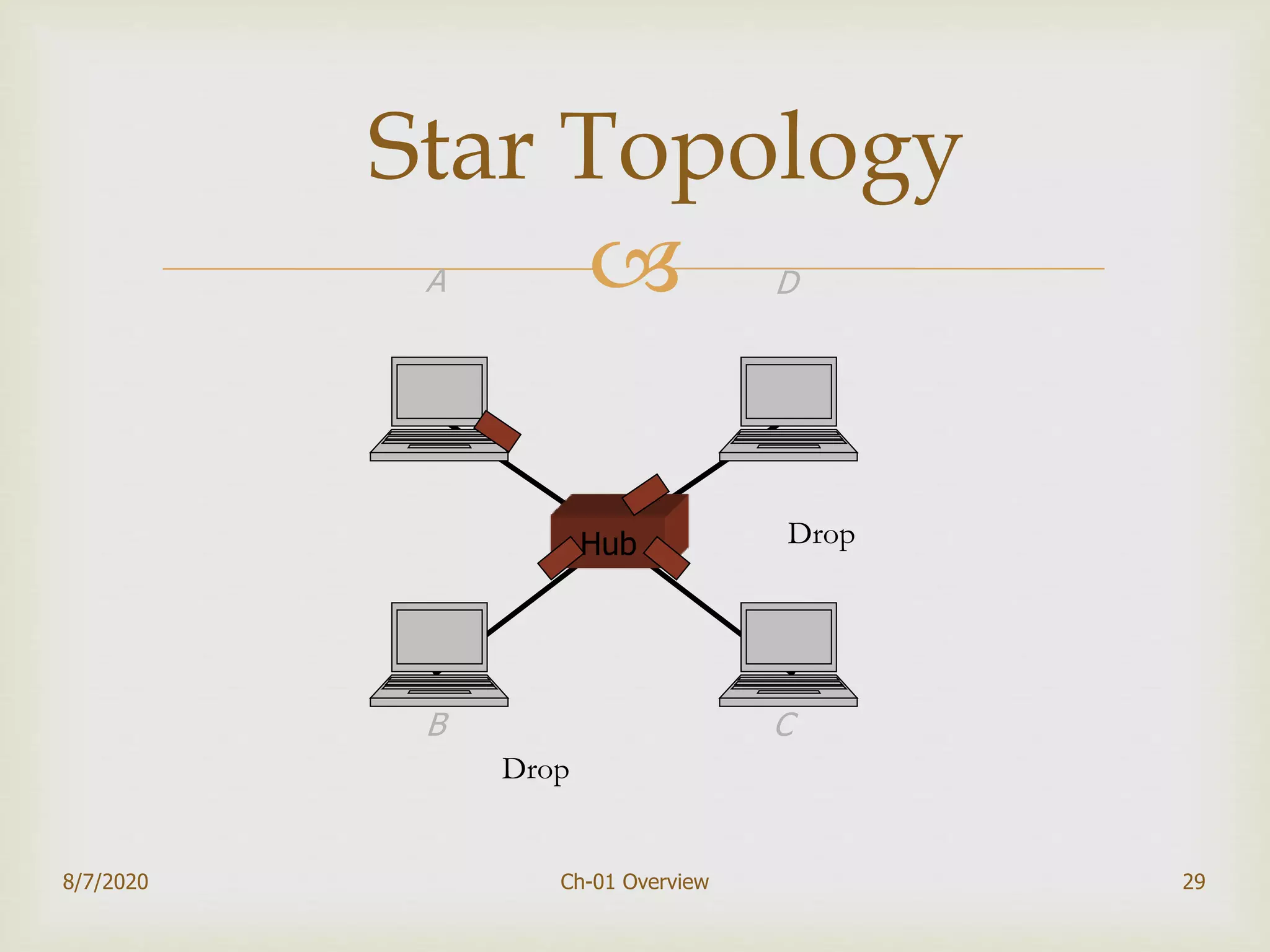
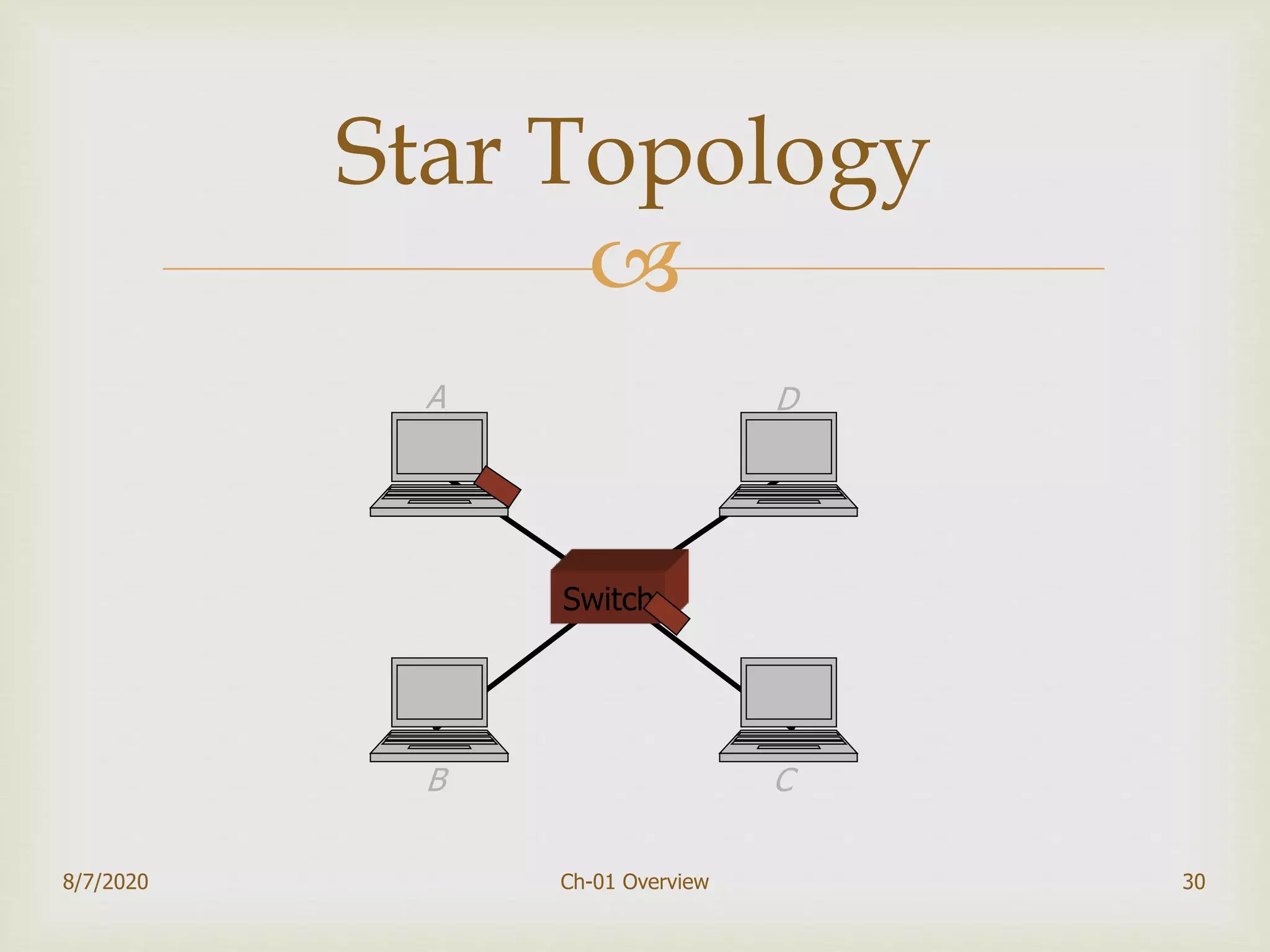
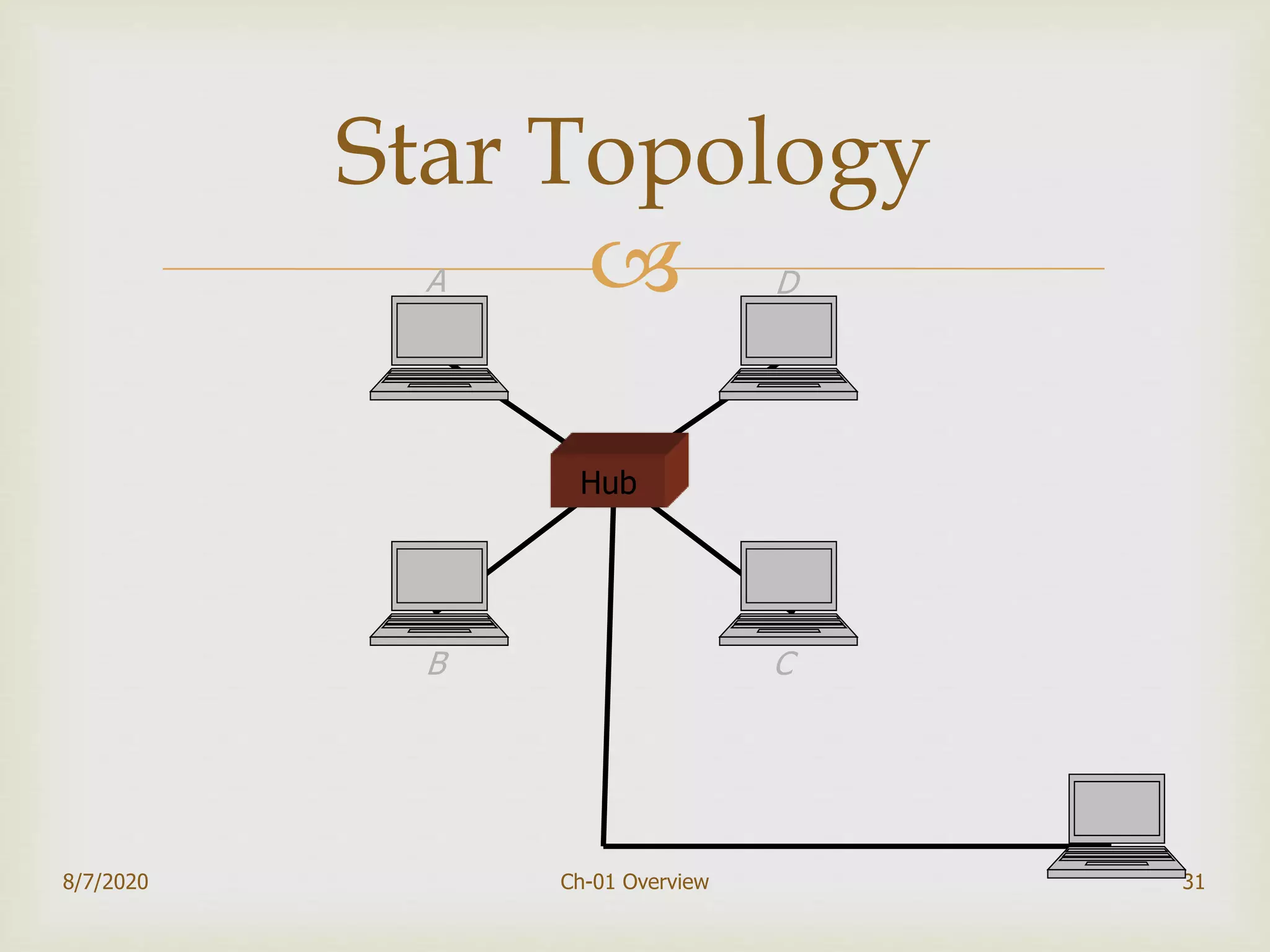
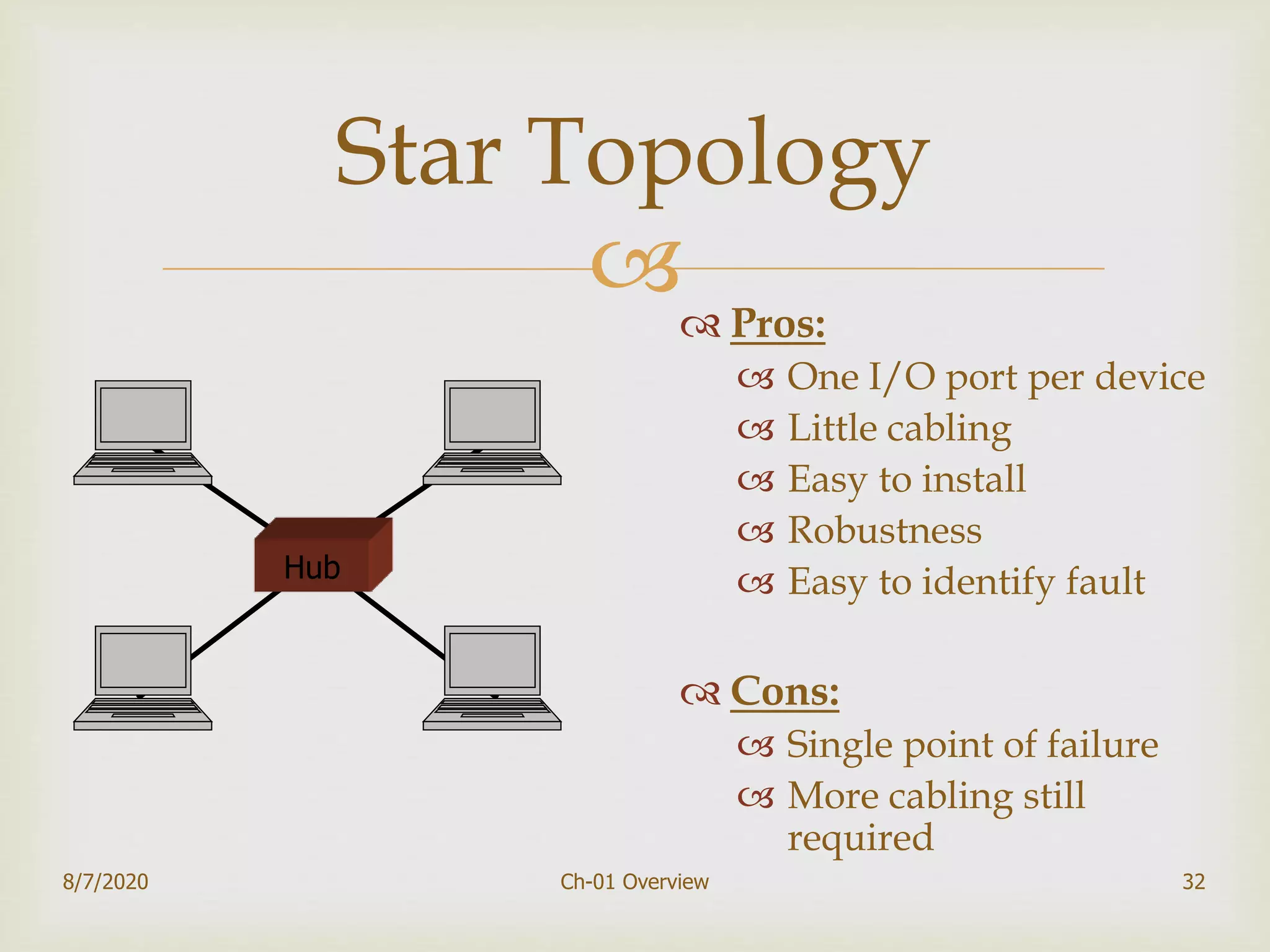
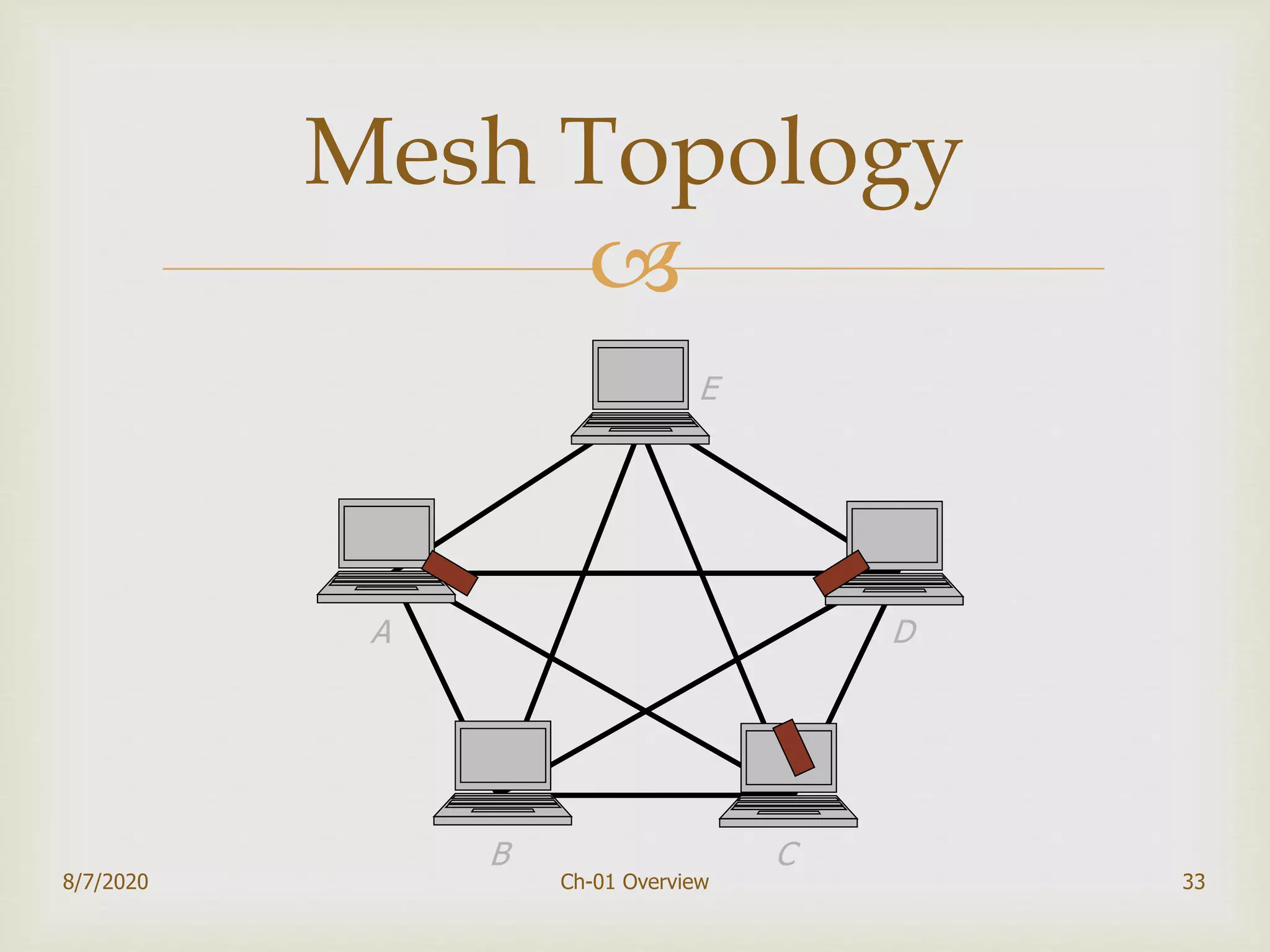
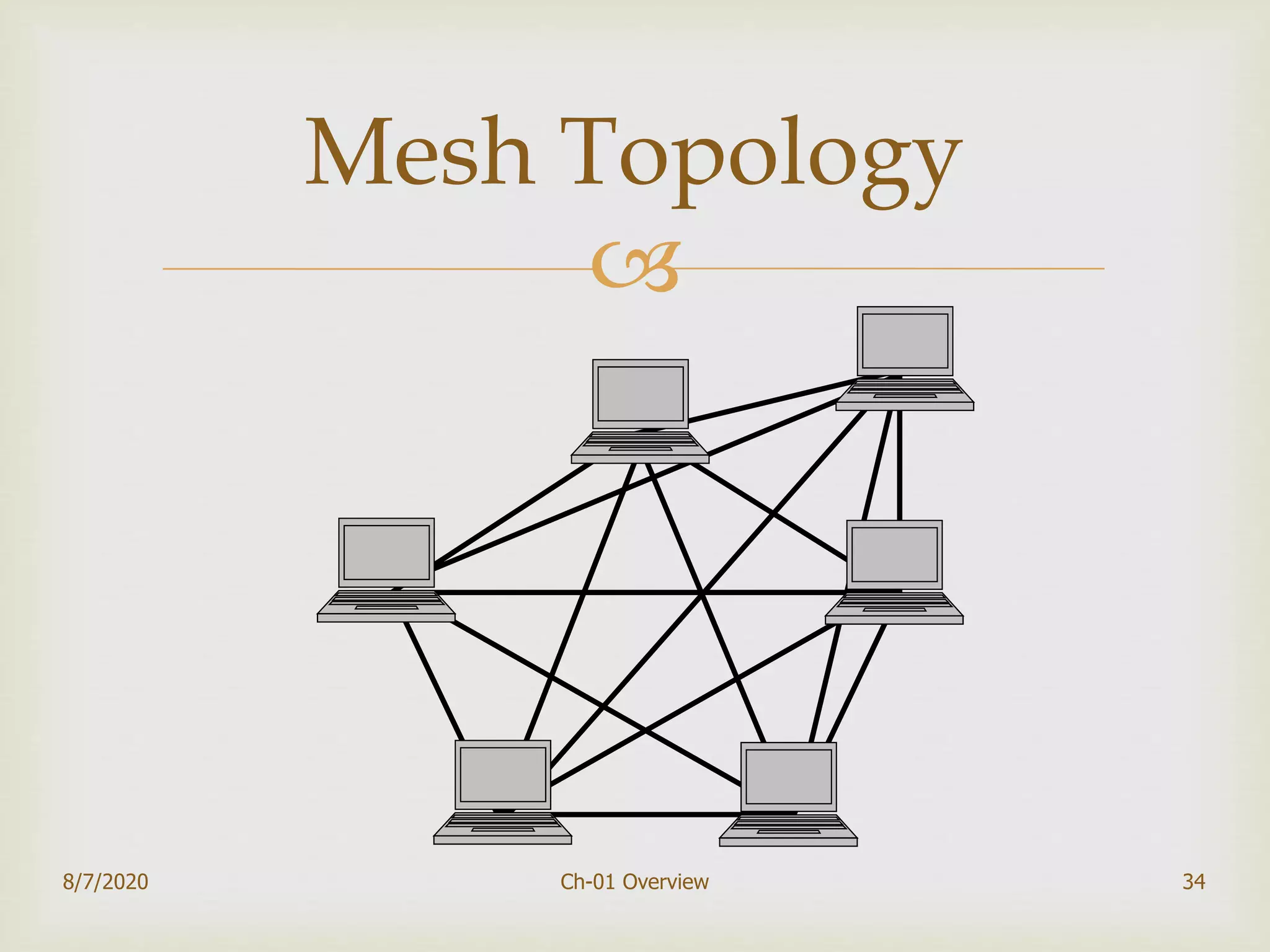
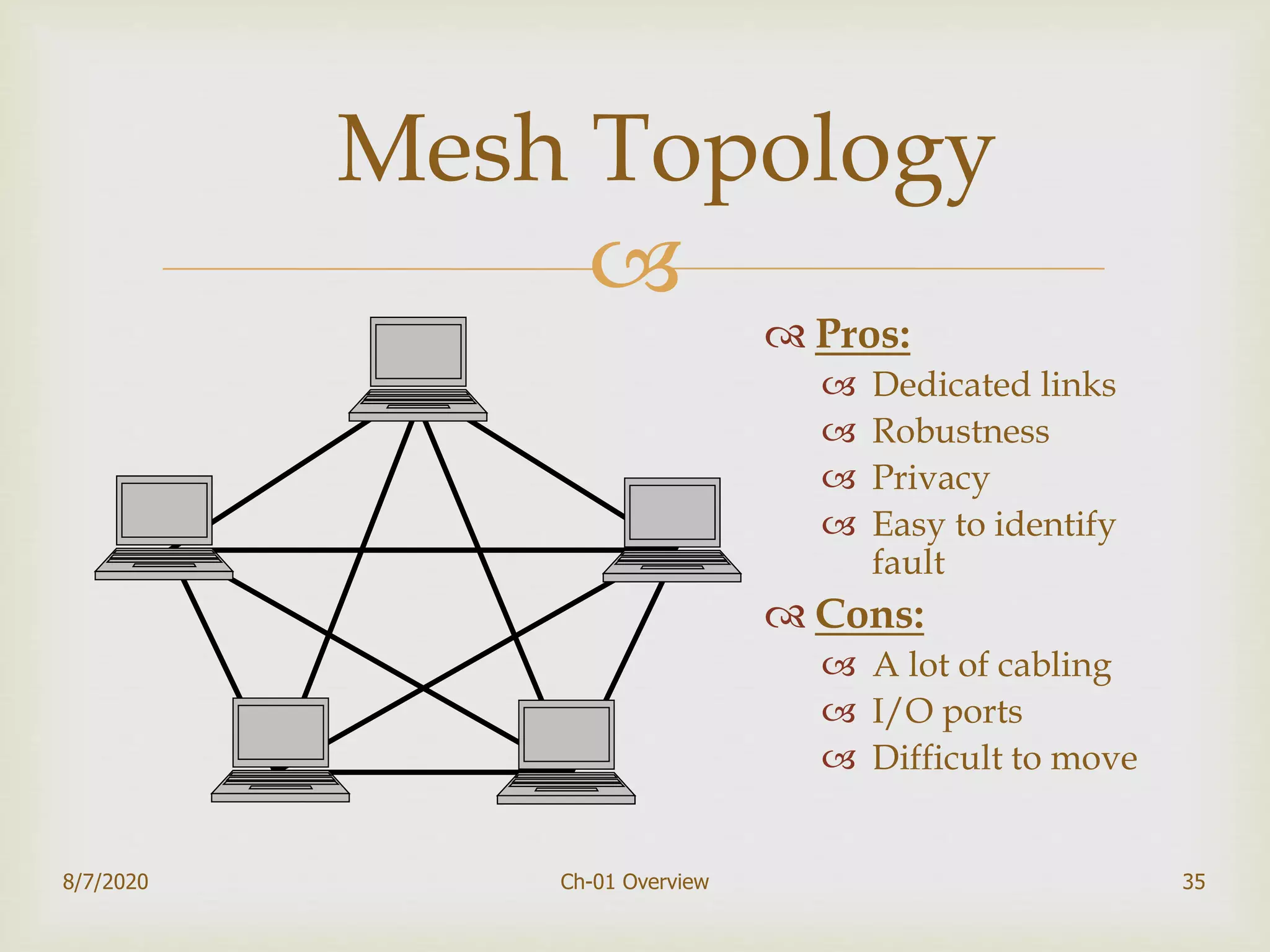
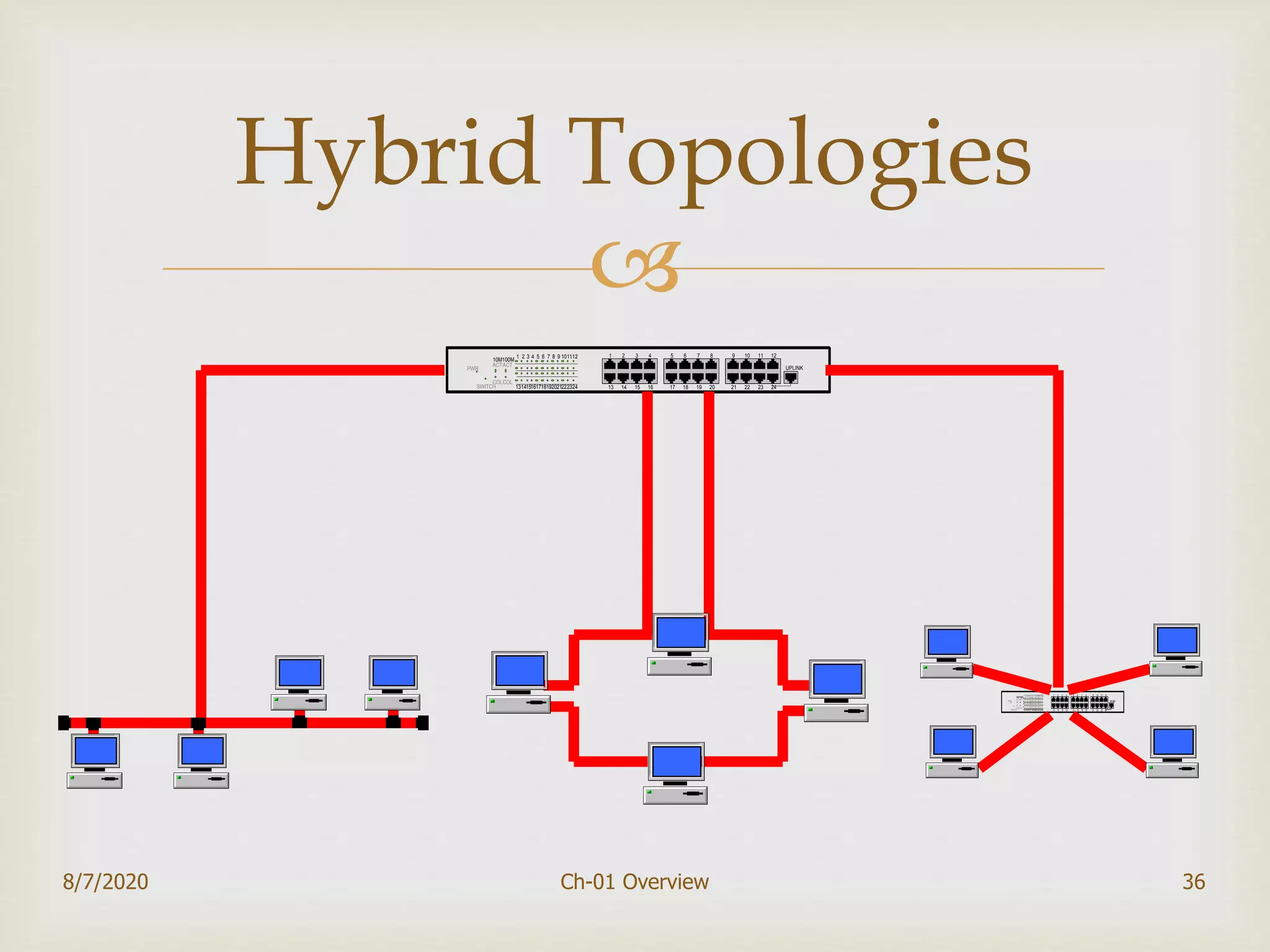
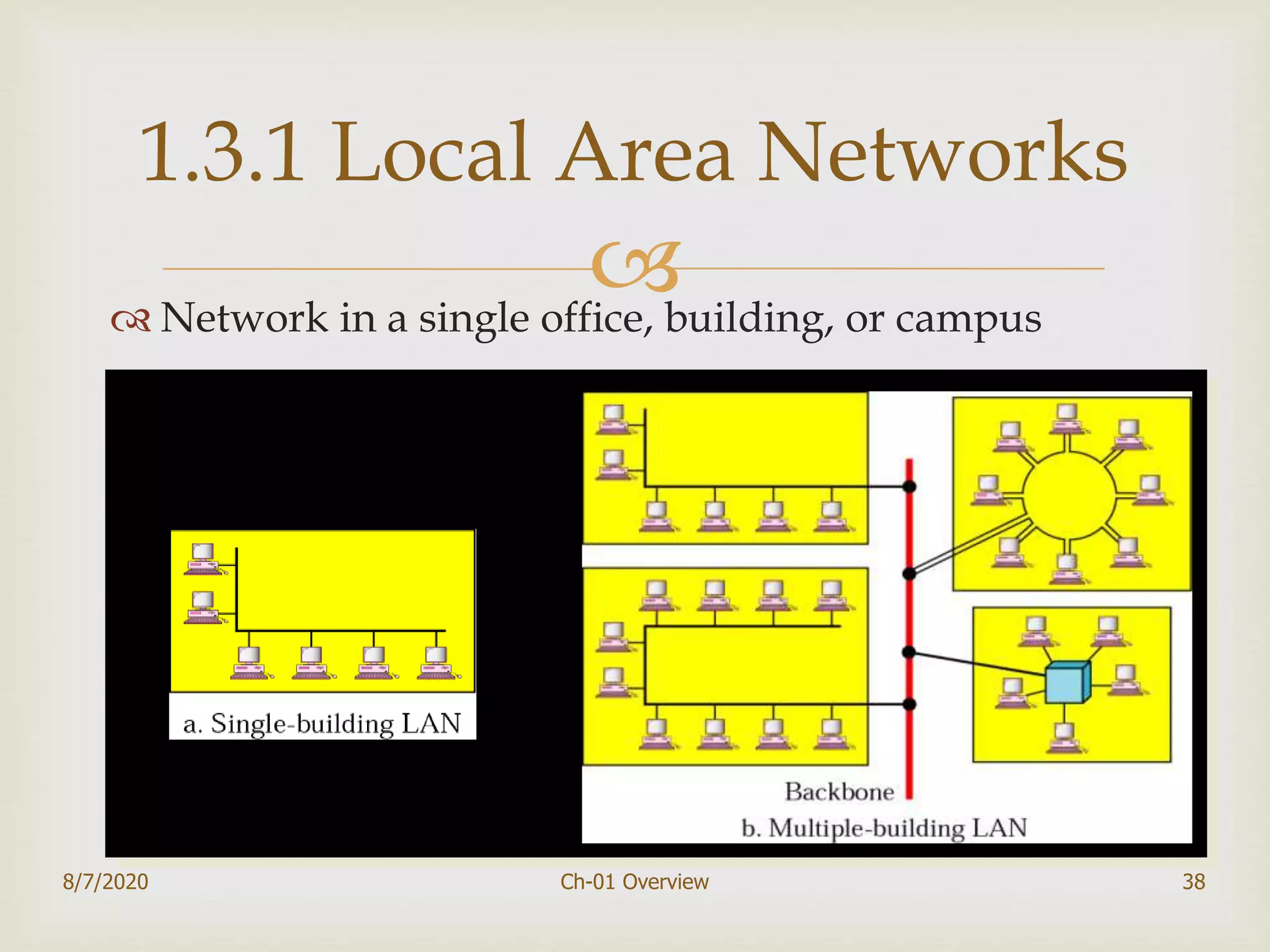
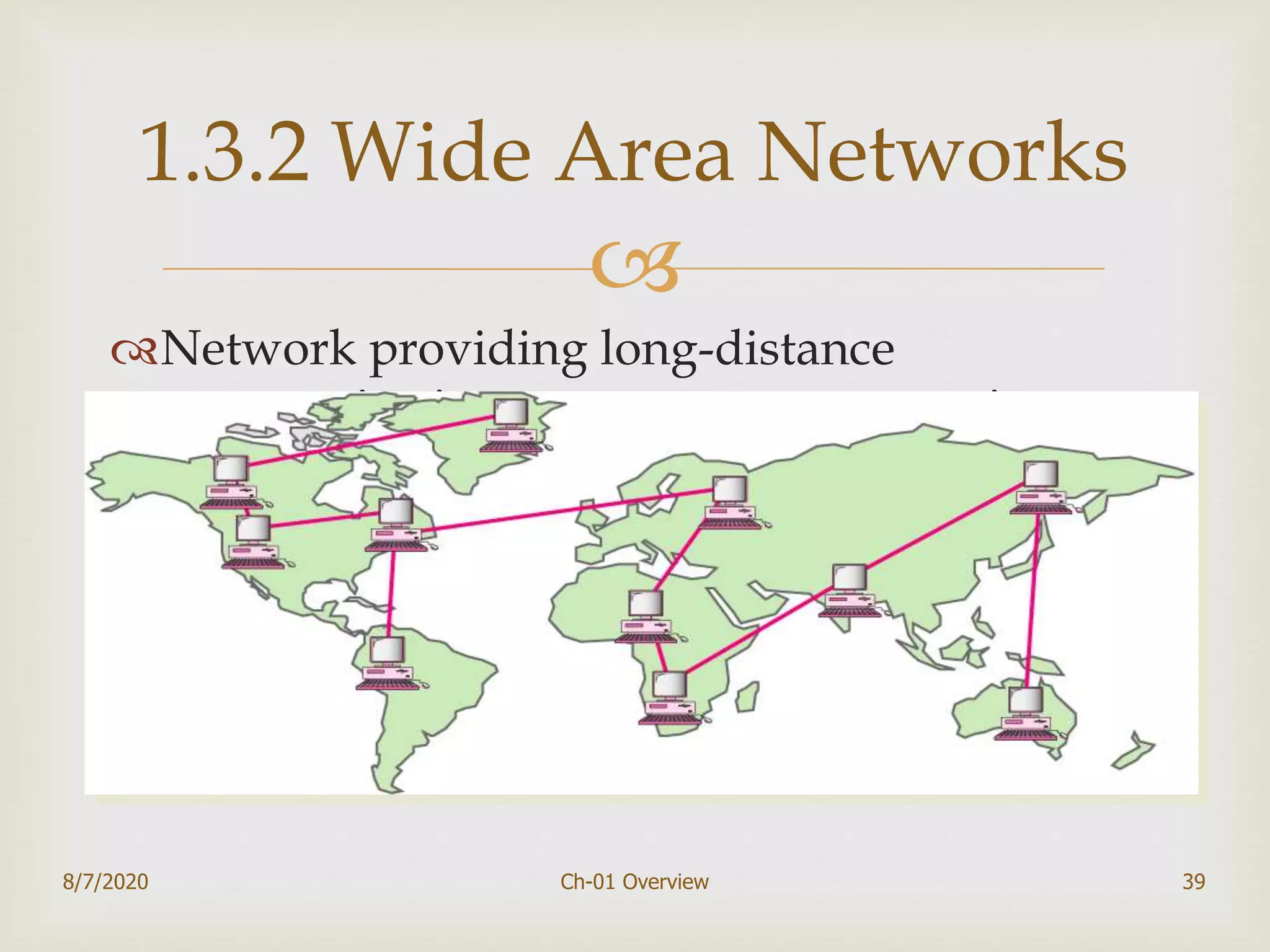
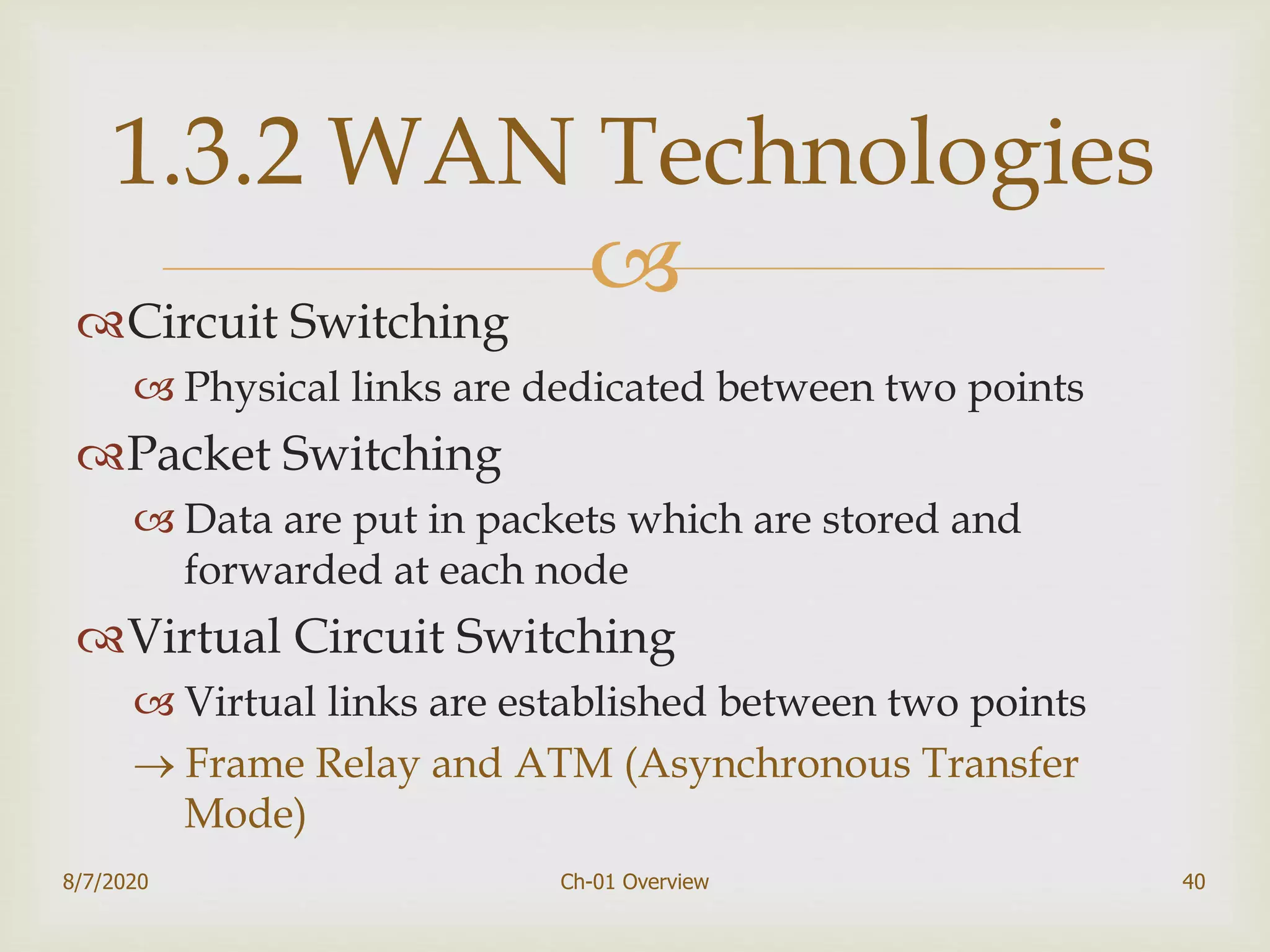
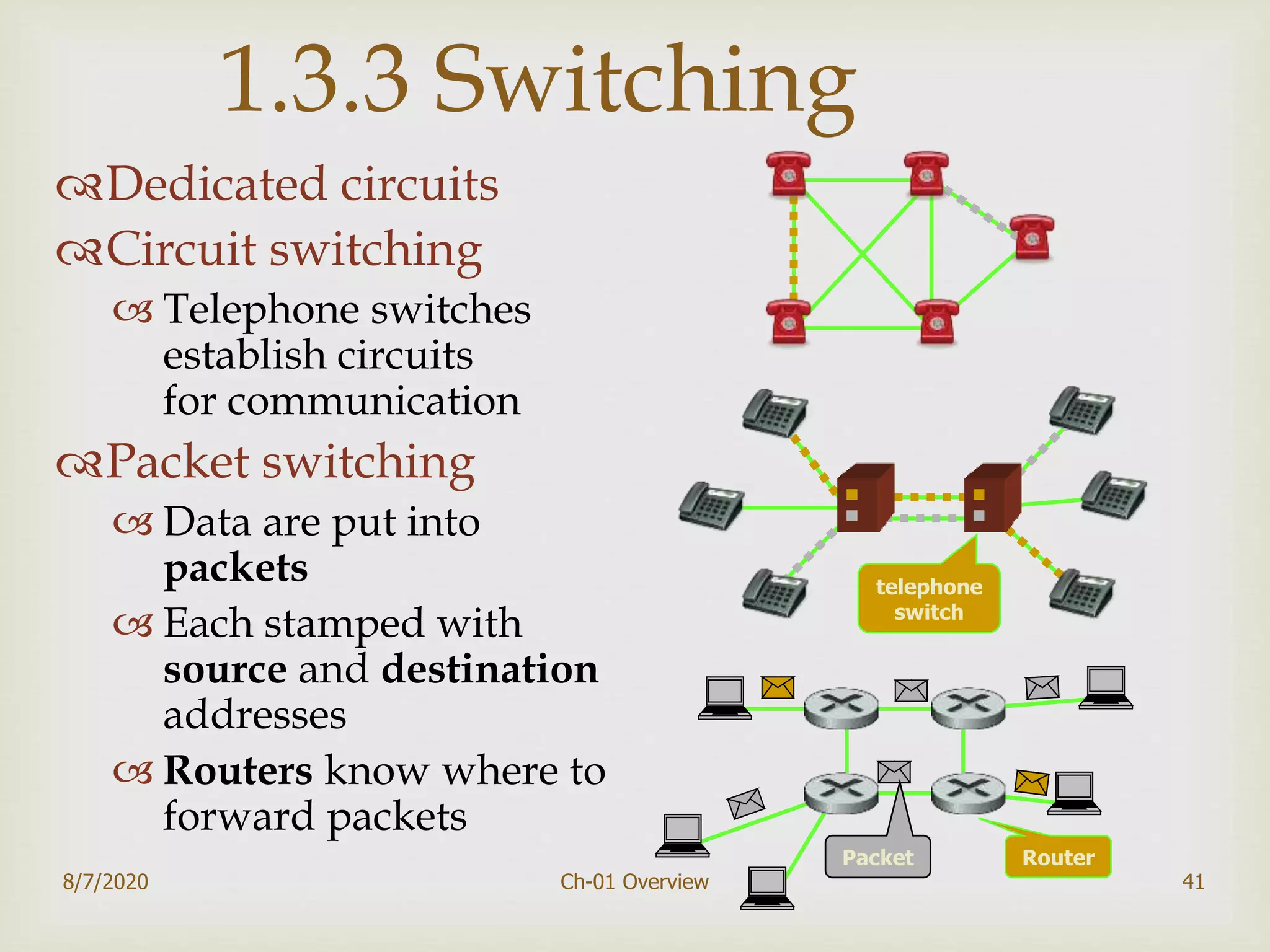
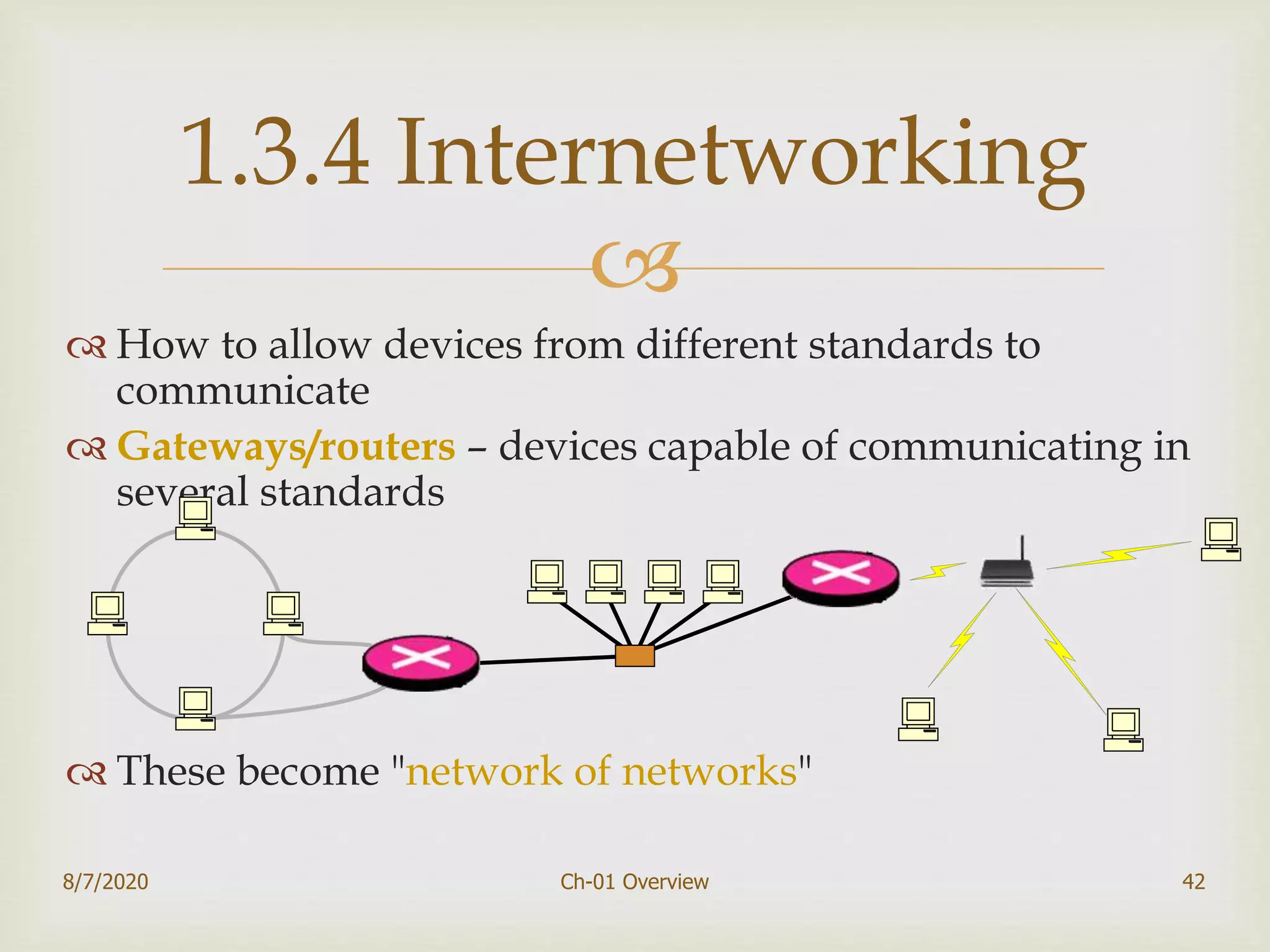
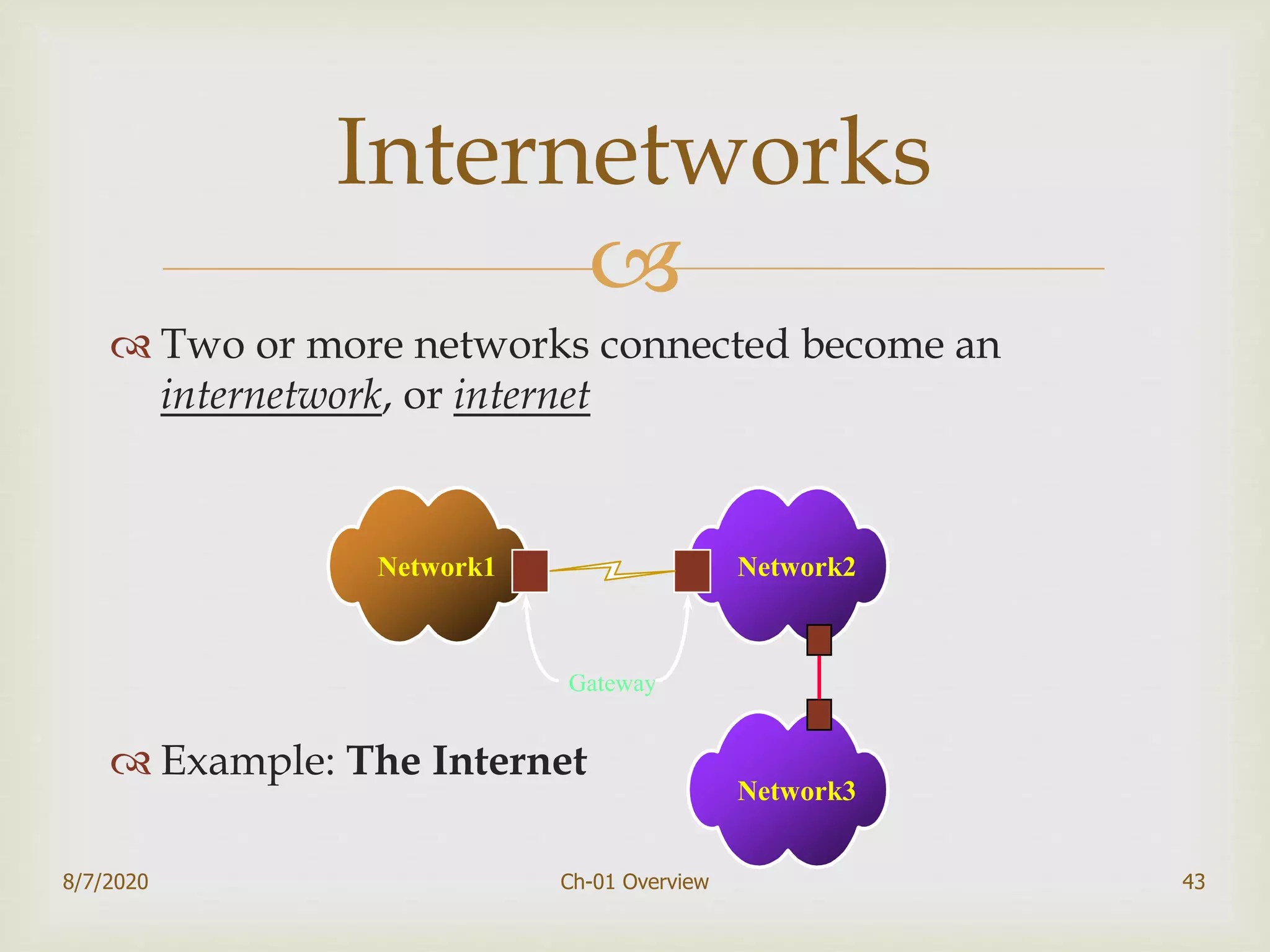
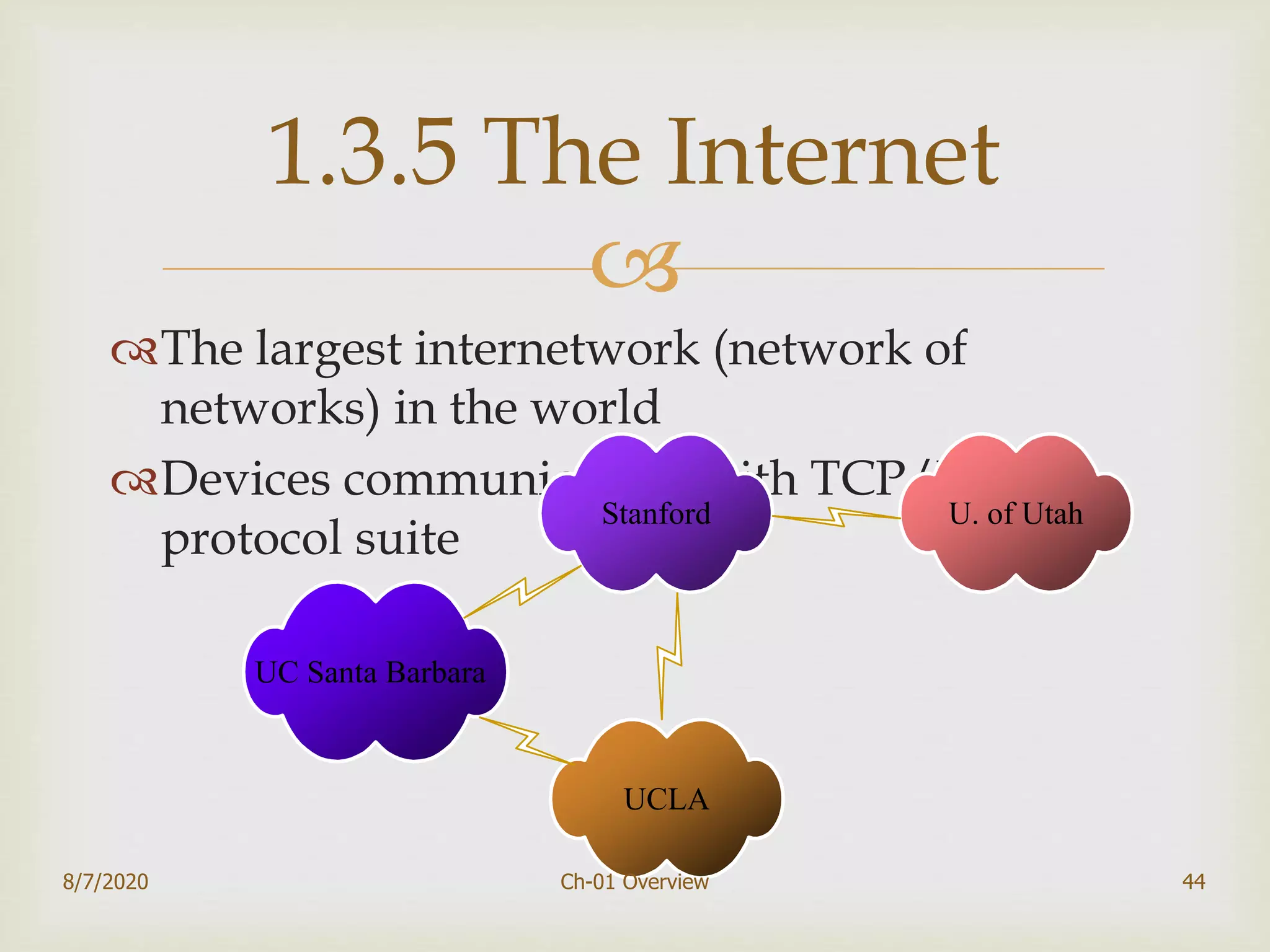
The document provides an overview of data communication and networking, covering components, data representation, data flow types, and network criteria such as performance, reliability, and security. It discusses various network types including local area networks and wide area networks, along with the characteristics of different topologies like bus, ring, star, and mesh. Additionally, it touches on internetworking, the role of switches and routers, and the history and standards of the internet.