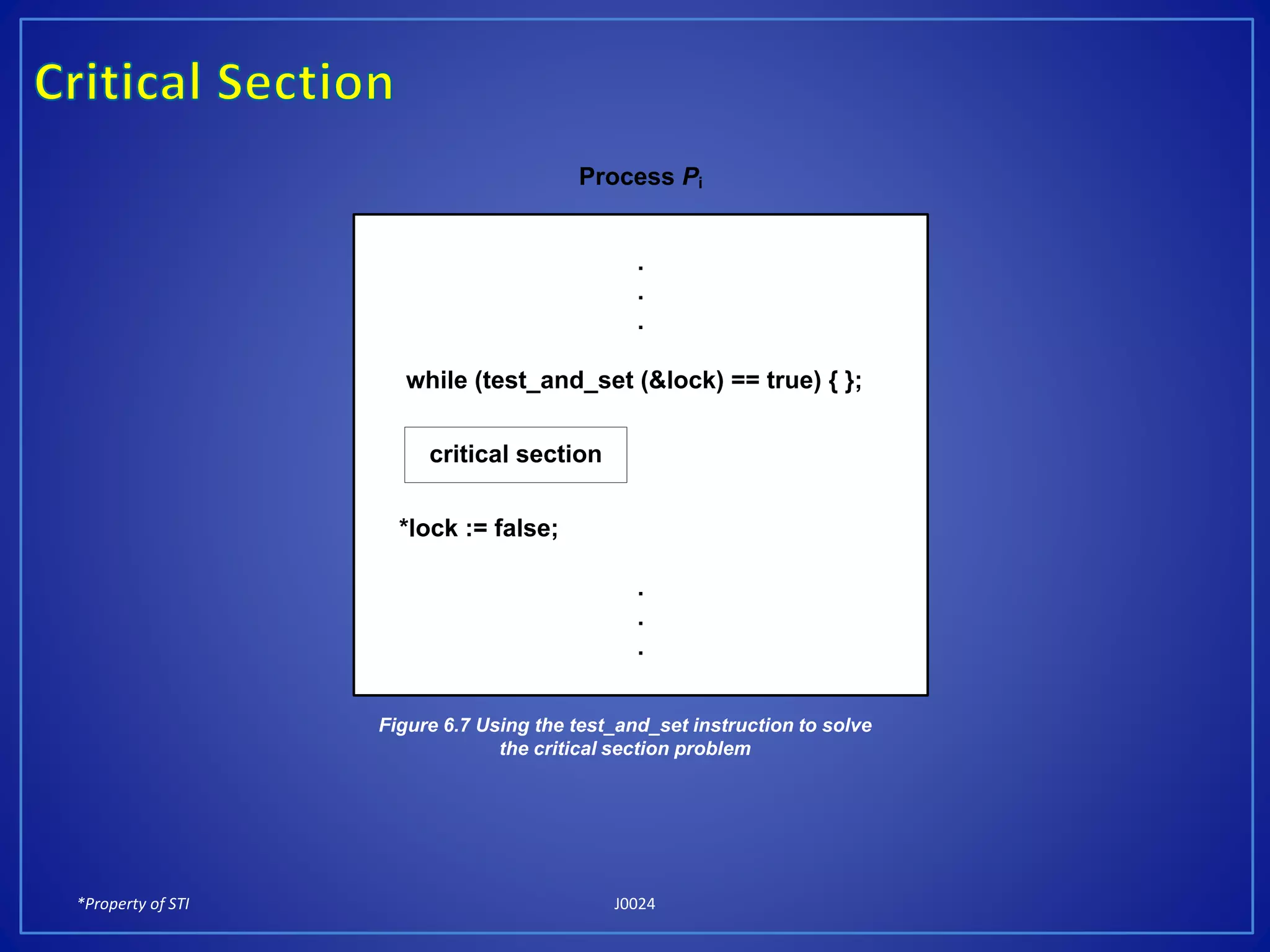
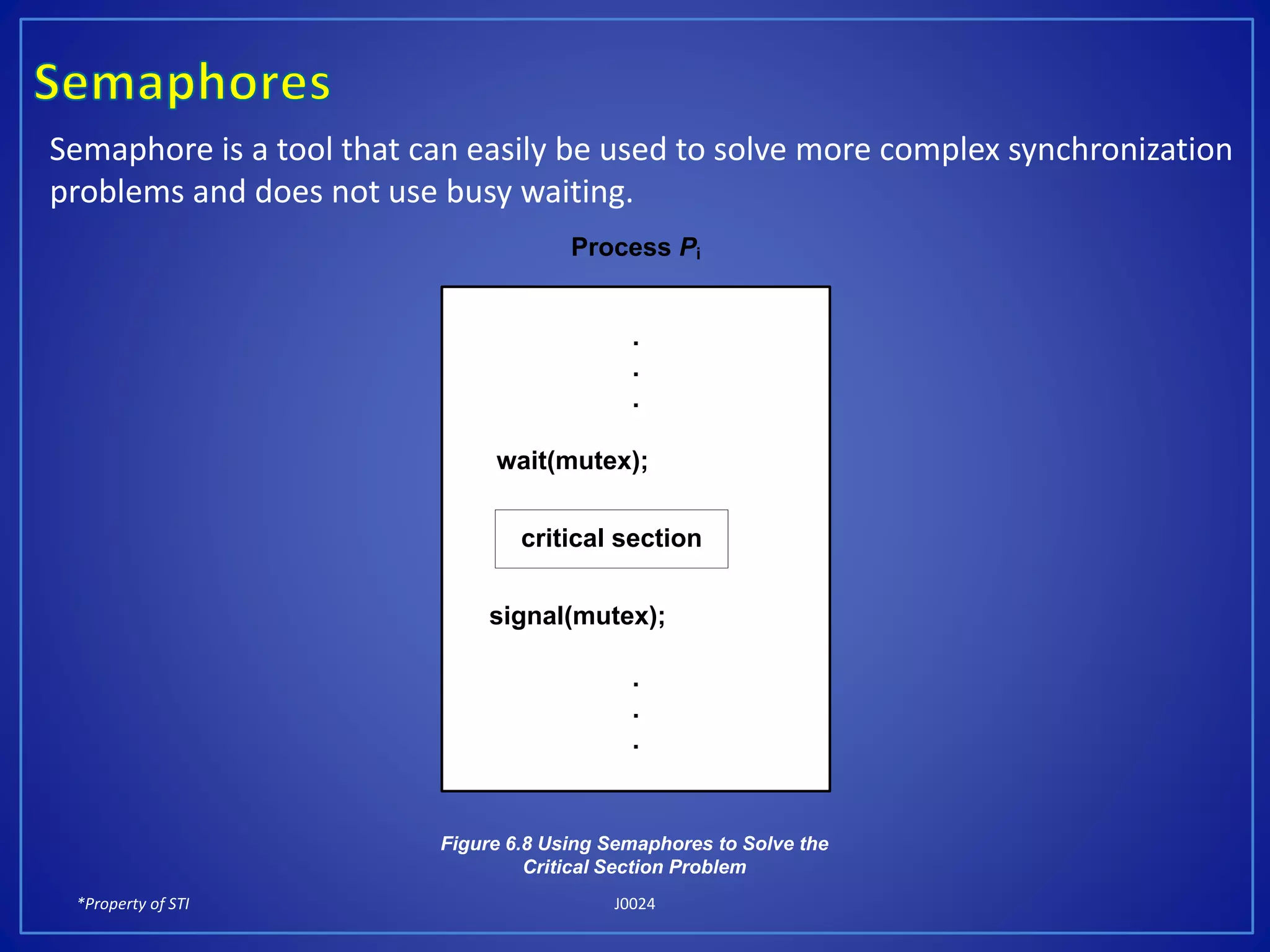
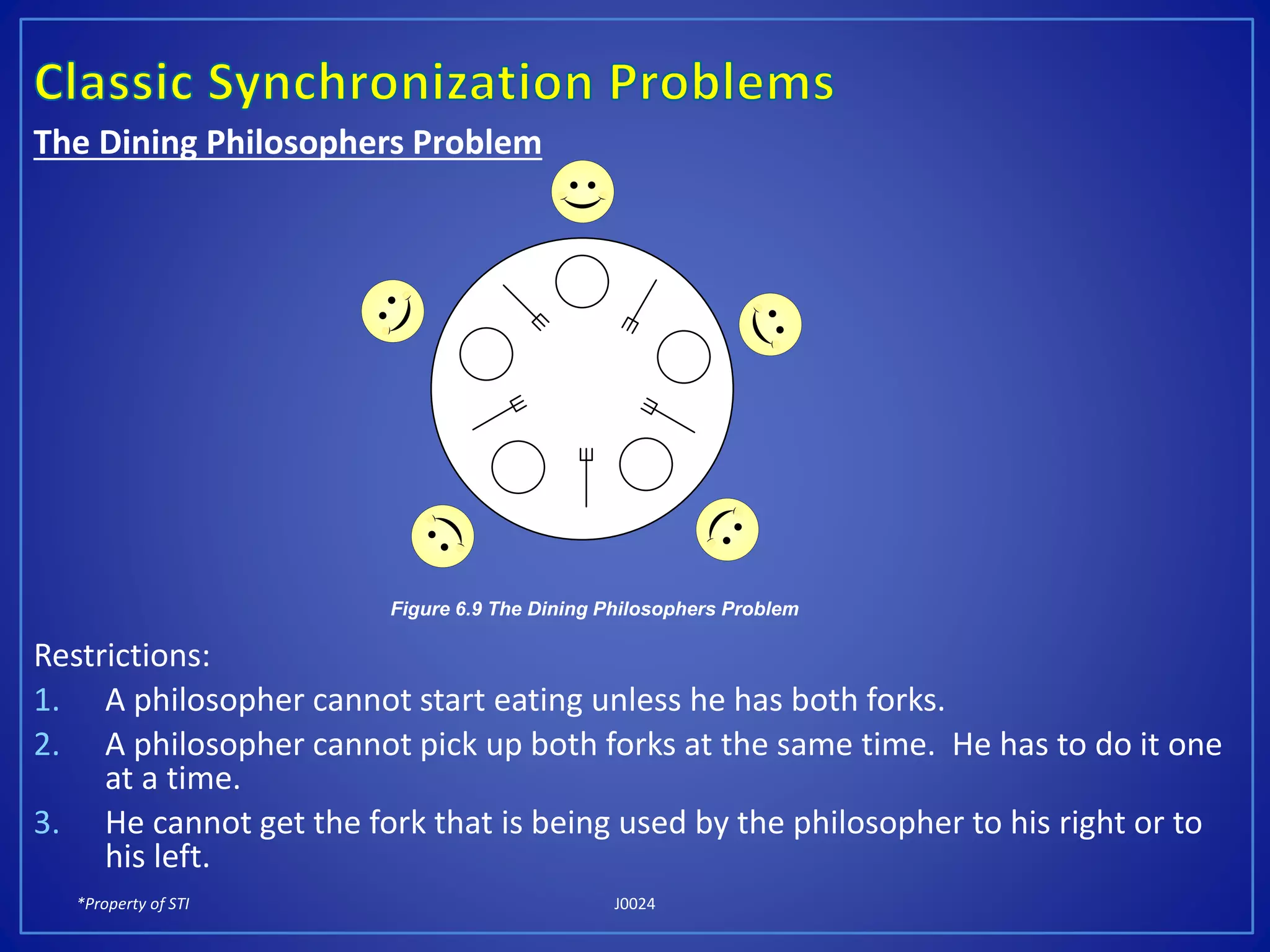
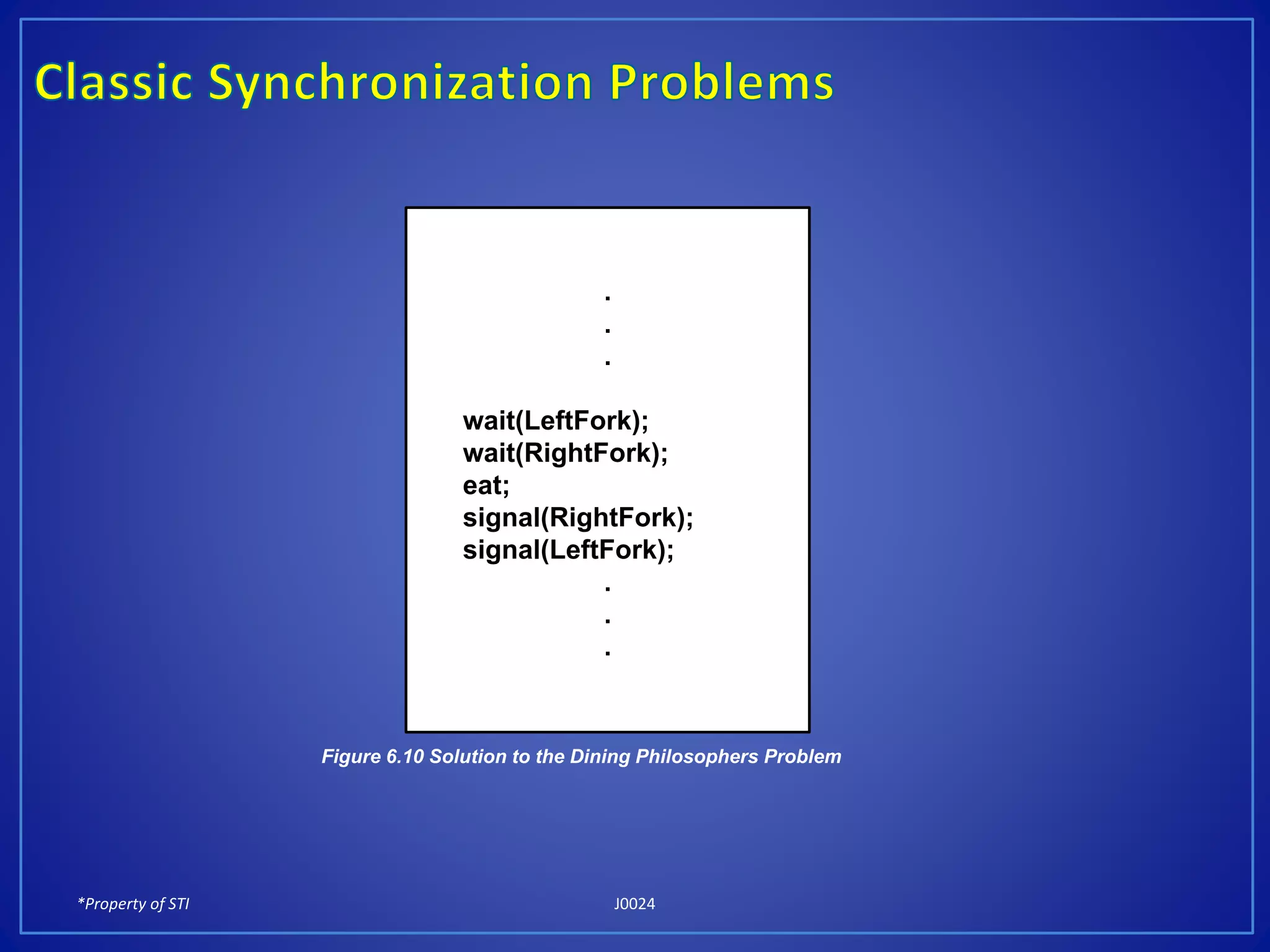
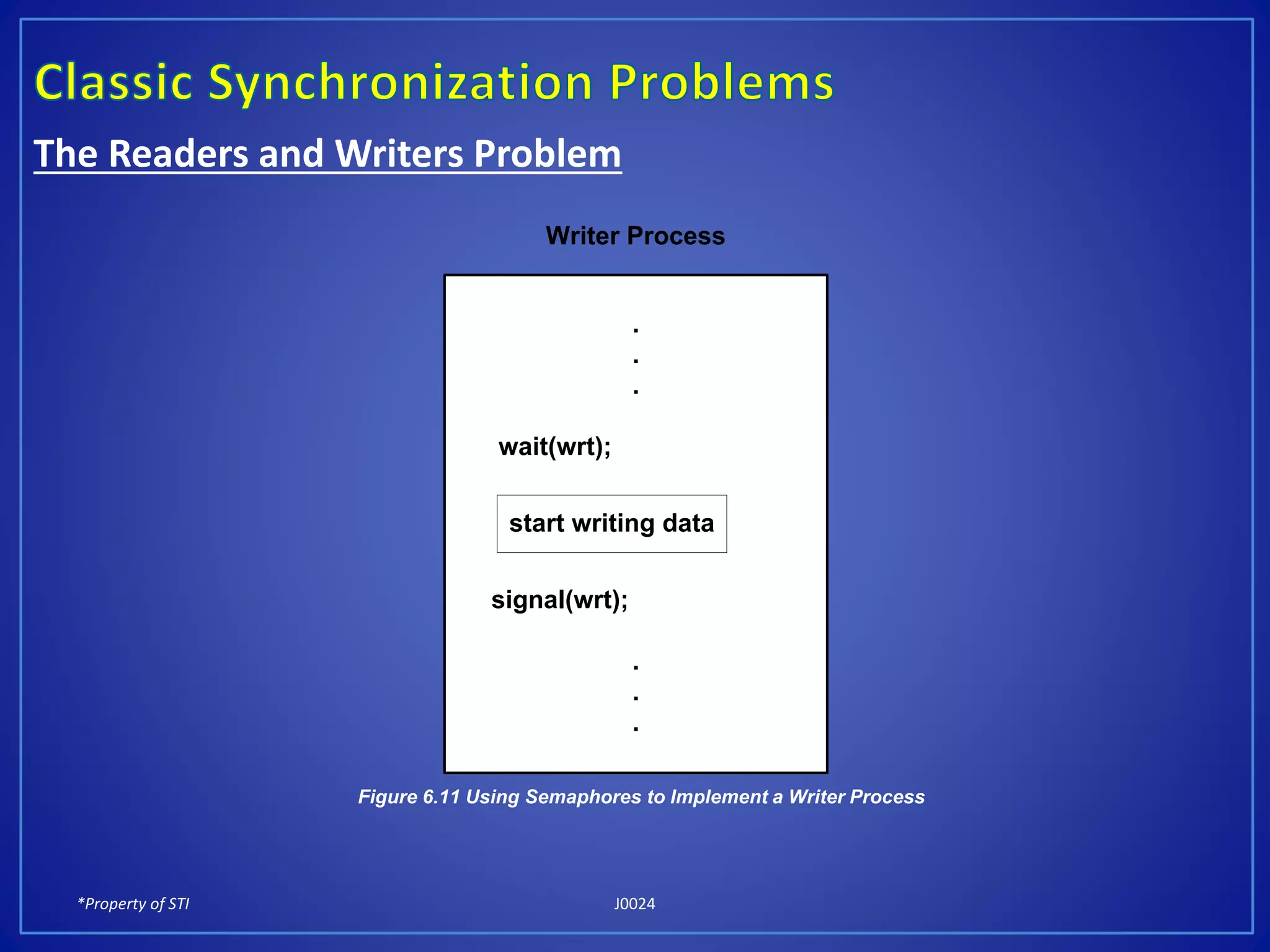
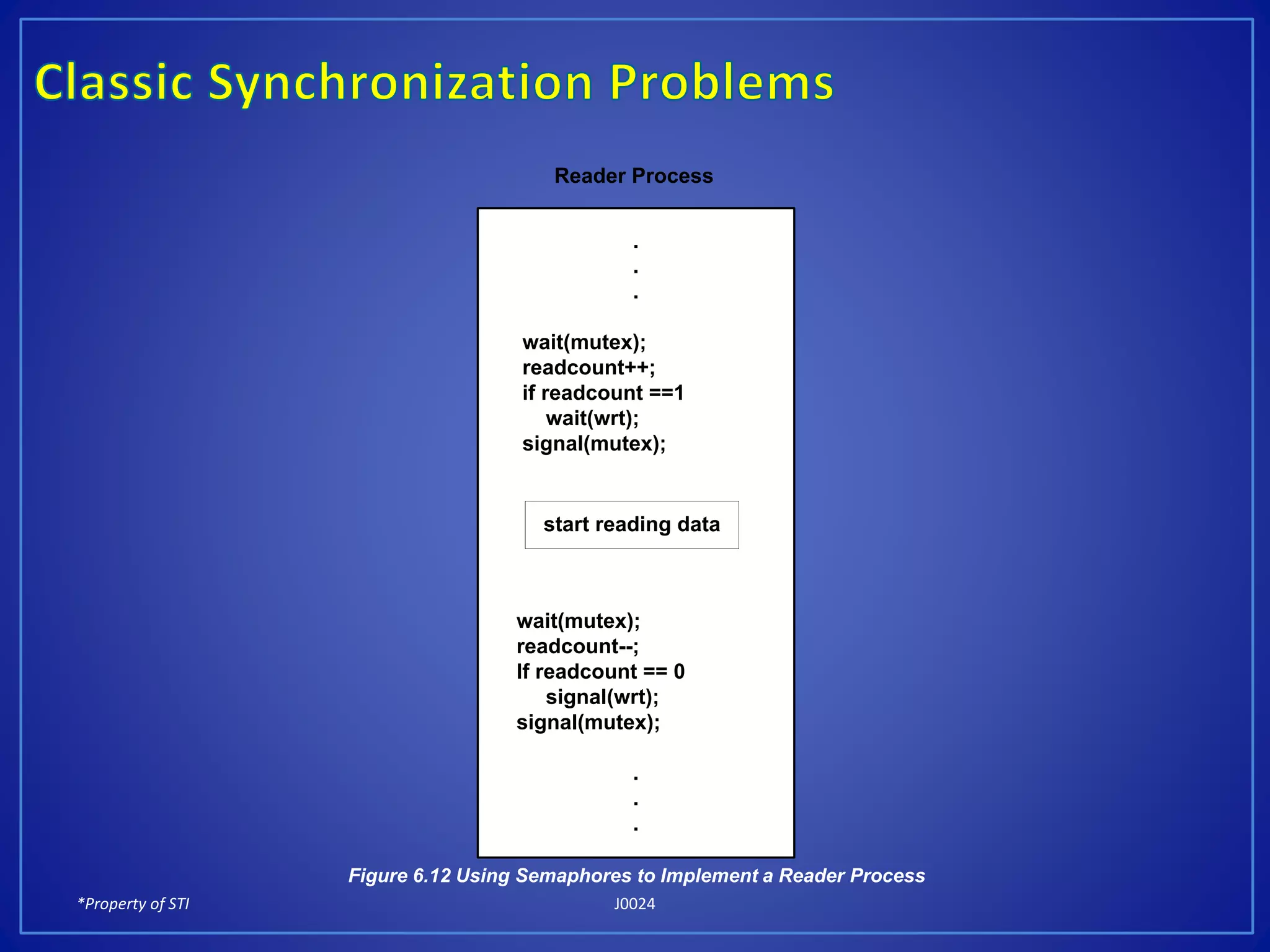
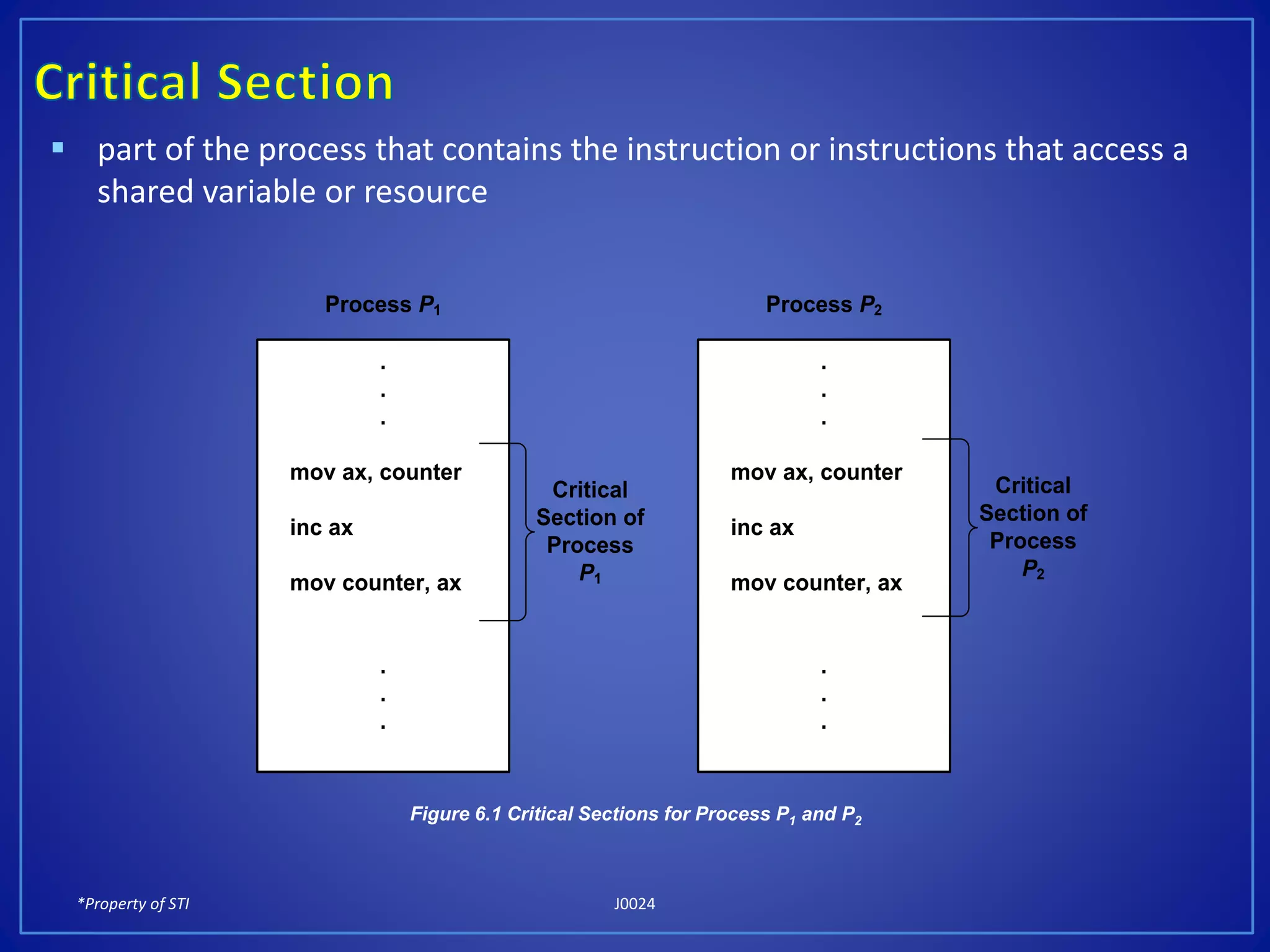
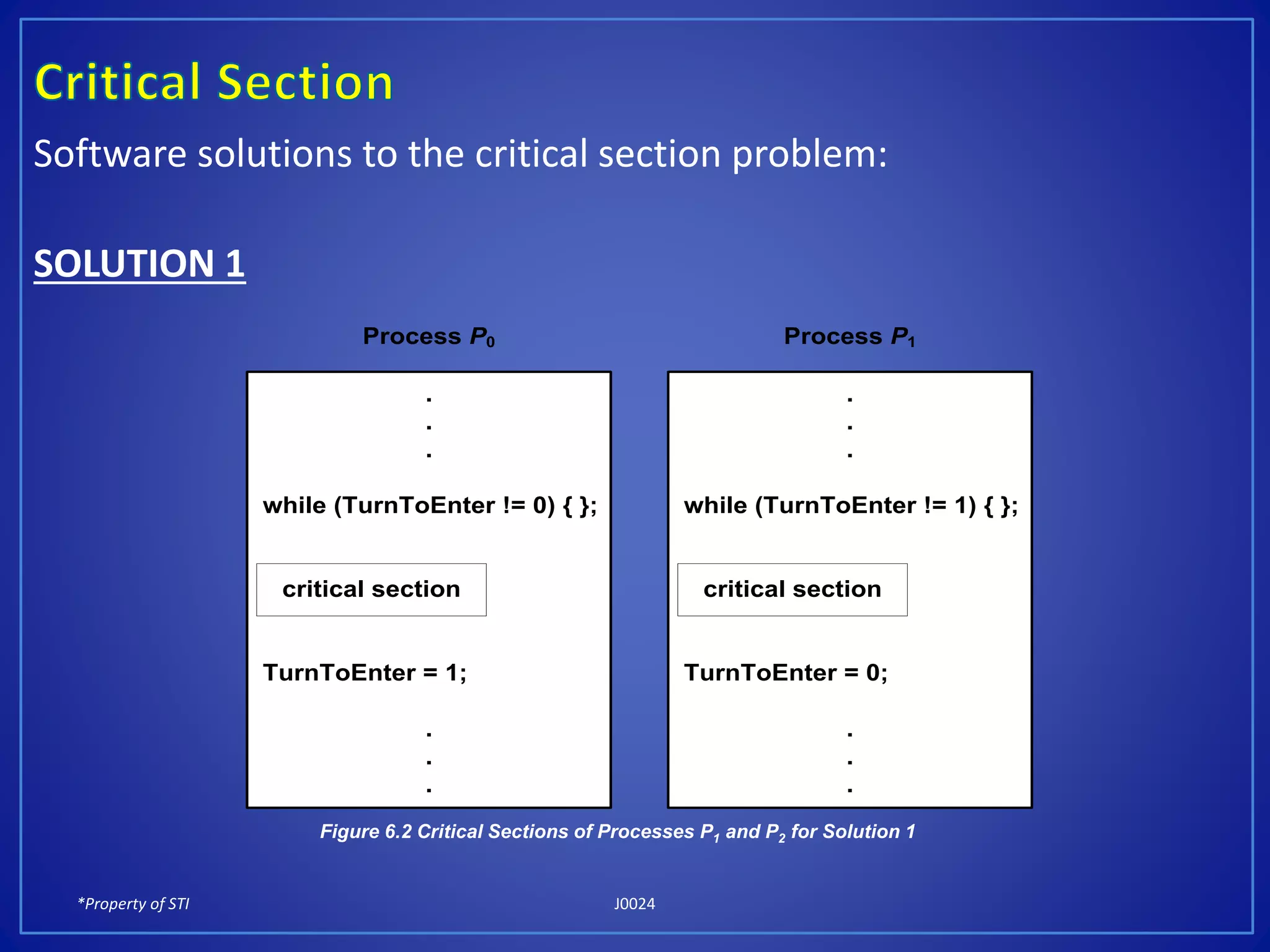
The document discusses process synchronization and solutions to classic synchronization problems. It describes race conditions that can occur when processes modify shared variables simultaneously. To prevent race conditions, only one process is allowed to access shared resources at a time through the use of critical sections. The document outlines software and hardware solutions for processes to enter critical sections, including semaphores, and discusses solutions to synchronization problems like the dining philosophers problem and readers-writers problem using semaphores.

![*Property of STI J0024
SOLUTION 2
Process P0
.
.
.
WantToEnter[0] = true;
while (WantToEnter[1] == true) { };
WantToEnter[0] = false;
.
.
.
critical section
Process P1
.
.
.
WantToEnter[1] = true;
while (WantToEnter[0] == true) { };
WantToEnter[1] = false;
.
.
.
critical section
Figure 6.3 Critical Section P1 and P2 for Solution 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/06lcdslides1-150820121547-lva1-app6892/75/06-lcd-slides-1-PROCESS-SYNCHRONIZATION-POWERPOINT-5-2048.jpg)
![*Property of STI J0024
SOLUTION 3 (Peterson’s Algorithm)
Process P0
.
.
.
WantToEnter[0] = true;
TurnToEnter = 1;
while (WantToEnter[1] == true && TurnToEnter == 1) { };
WantToEnter[0] = false;
.
.
.
critical section
Process P1
.
.
.
WantToEnter[1] = true;
TurnToEnter = 0;
while (WantToEnter[0] == true && TurnToEnter == 0) { };
WantToEnter[1] = false;
.
.
.
critical section
Figure 6.4 Critical Sections of Processes P1 and P2 for Solution 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/06lcdslides1-150820121547-lva1-app6892/75/06-lcd-slides-1-PROCESS-SYNCHRONIZATION-POWERPOINT-6-2048.jpg)
![*Property of STI J0024
SOLUTION TO THE CRITICAL SECTION PROBLEM INVOLVING SEVERAL
PROCESS ( Bakery Algorithm)
Process Pi
.
.
.
choosing[i] = true;
number[i] = max(number[0], ... , number[n – 1]) + 1;
choosing[i] = false;
for (j = 1; j < n; j++) {
while (choosing[j] == true) { }
while ((number[j] != 0) &&
((number[j] < number[i]) || (number[j] == number[i]) && (j < i))) { };
}
number[i] = 0;
.
.
.
critical section
Figure 6.5 Critical Section of Process P1 for the Bakery Algorithm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/06lcdslides1-150820121547-lva1-app6892/75/06-lcd-slides-1-PROCESS-SYNCHRONIZATION-POWERPOINT-7-2048.jpg)