Download to read offline

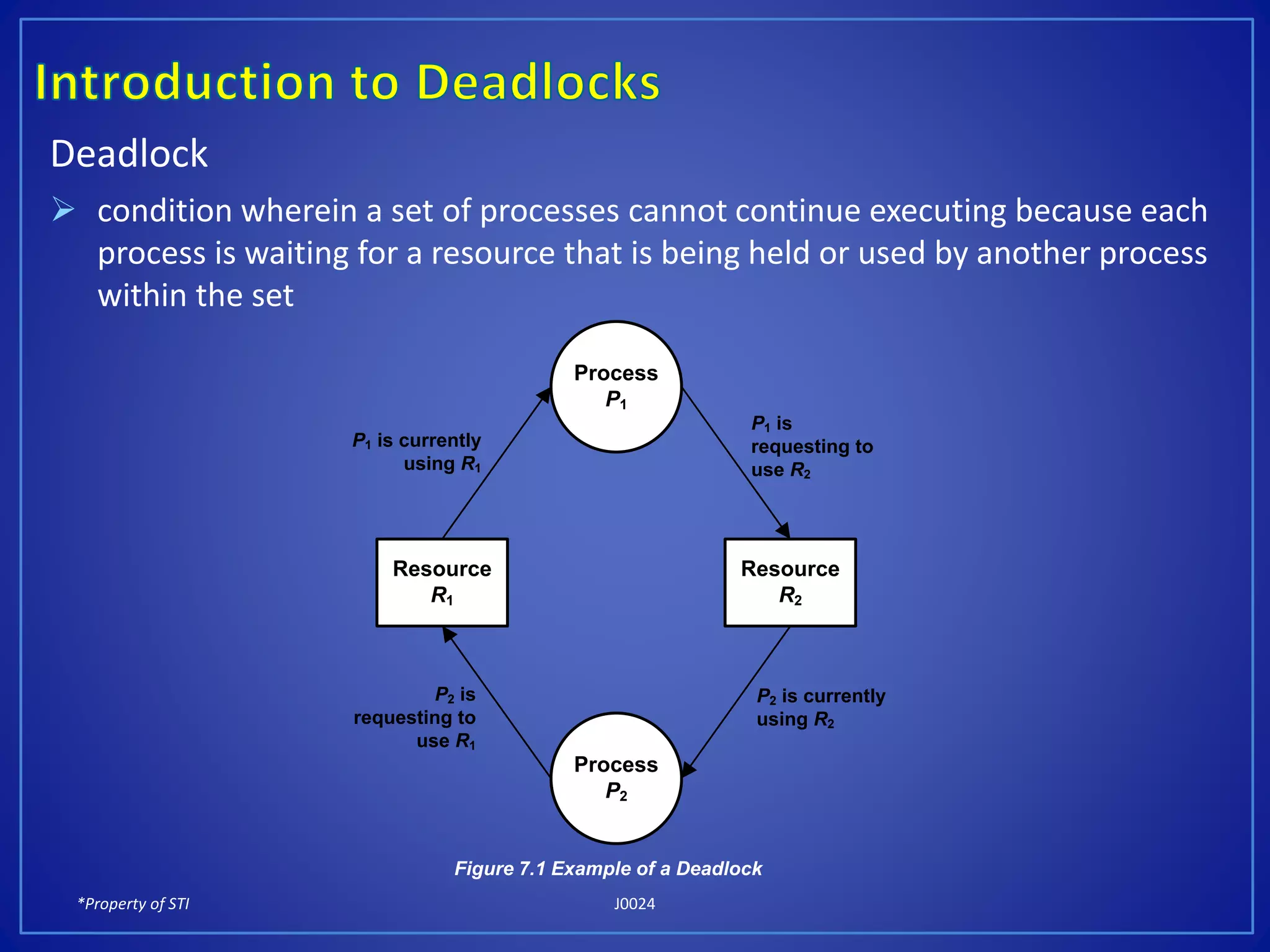
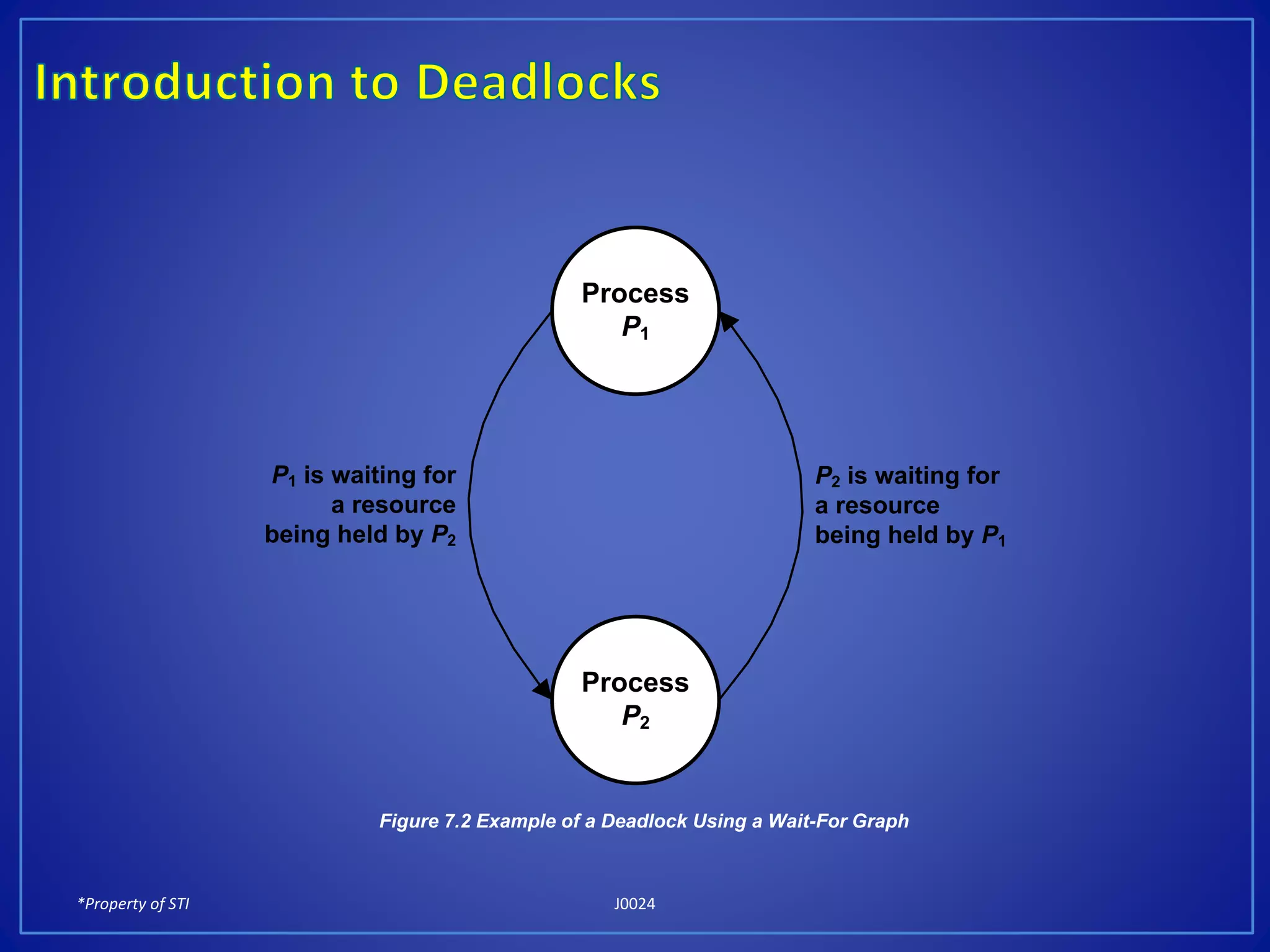
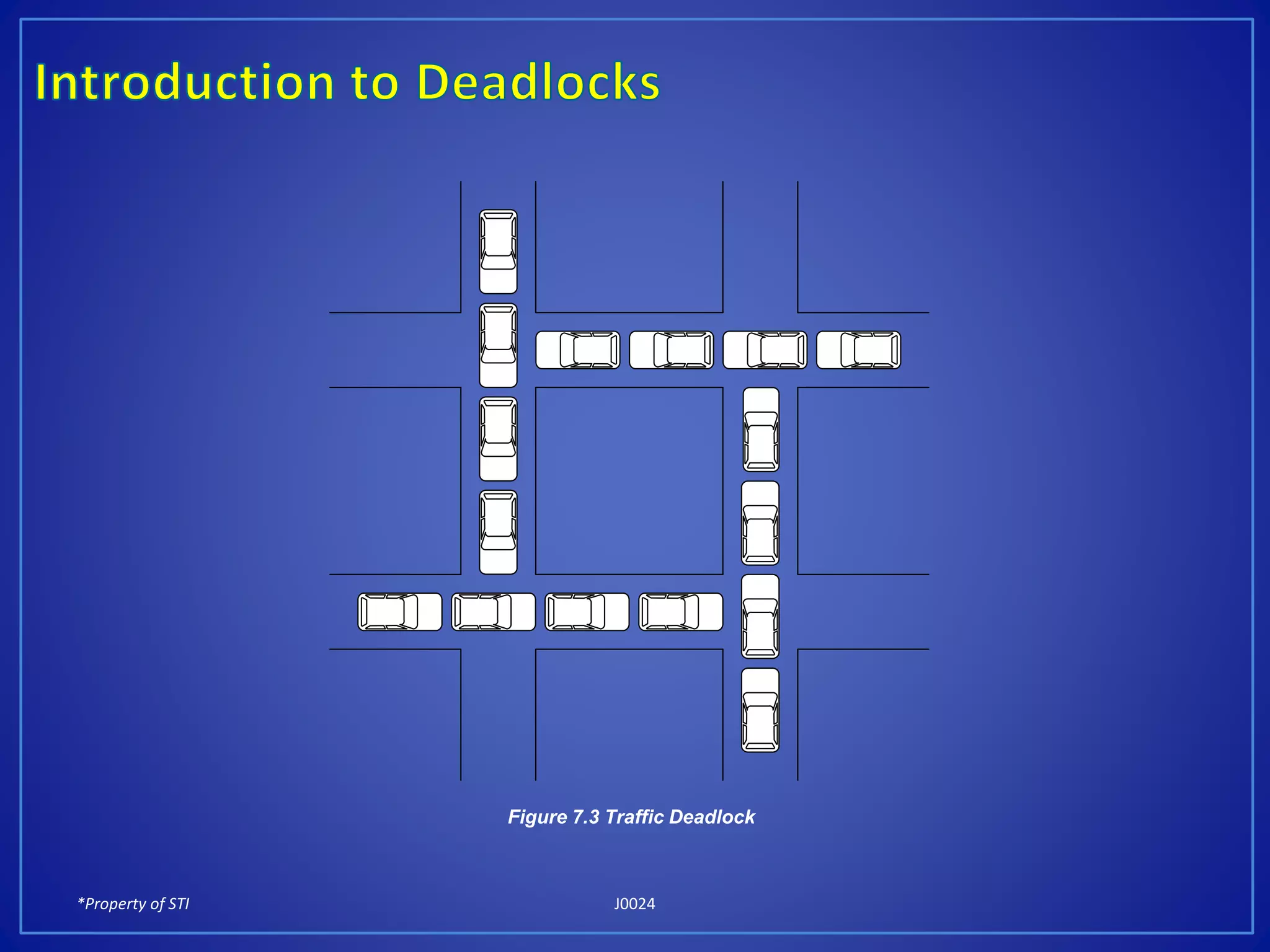



Deadlocks occur when a set of processes cannot continue execution because each process is waiting for a resource held by another process in the set, creating a circular wait. There are four necessary conditions for a deadlock: mutual exclusion, hold and wait, no preemption, and circular wait. Deadlocks can be prevented by removing at least one of these four conditions, such as removing the mutual exclusion of resources or removing the ability of processes to wait for resources.





