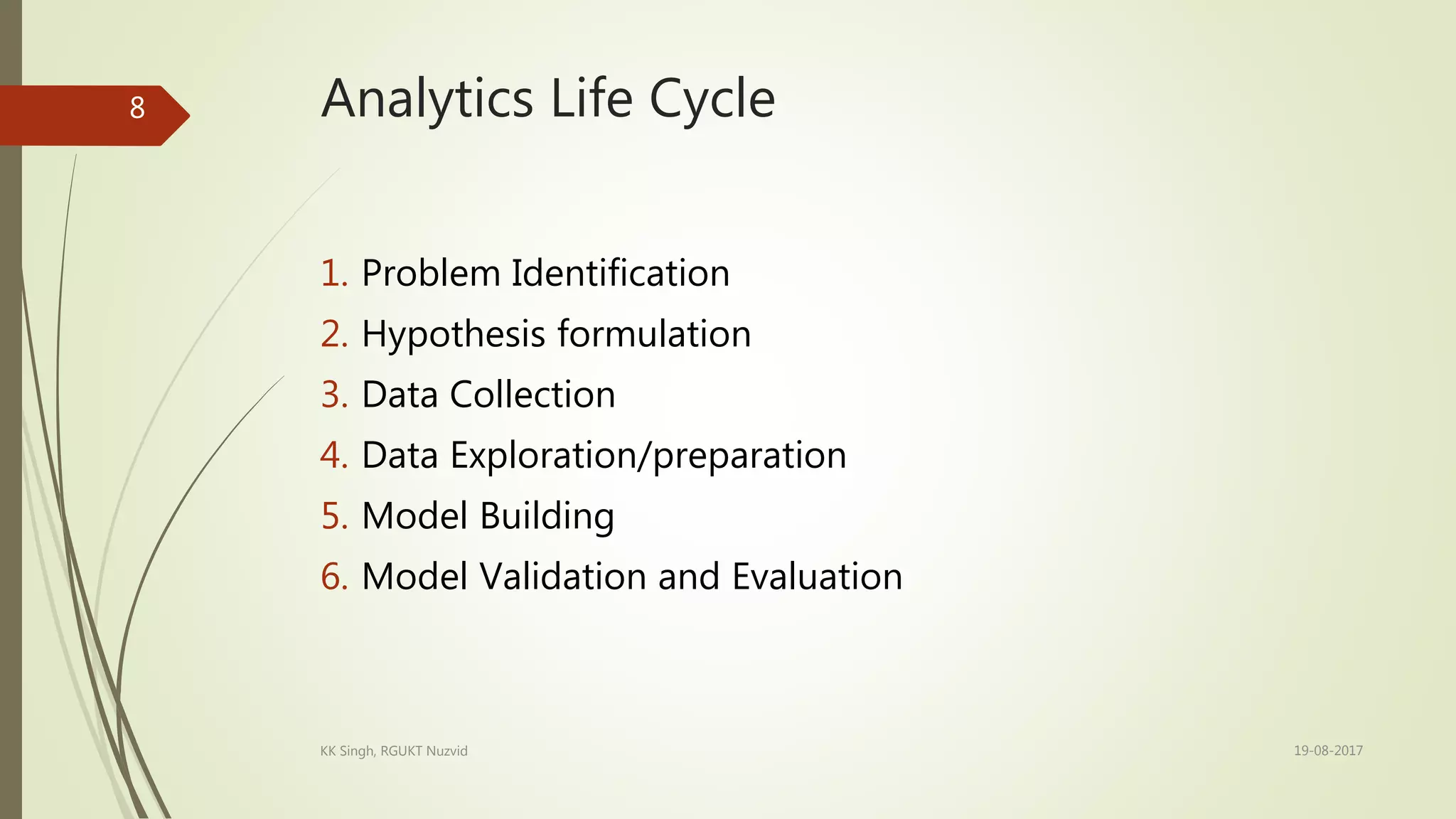
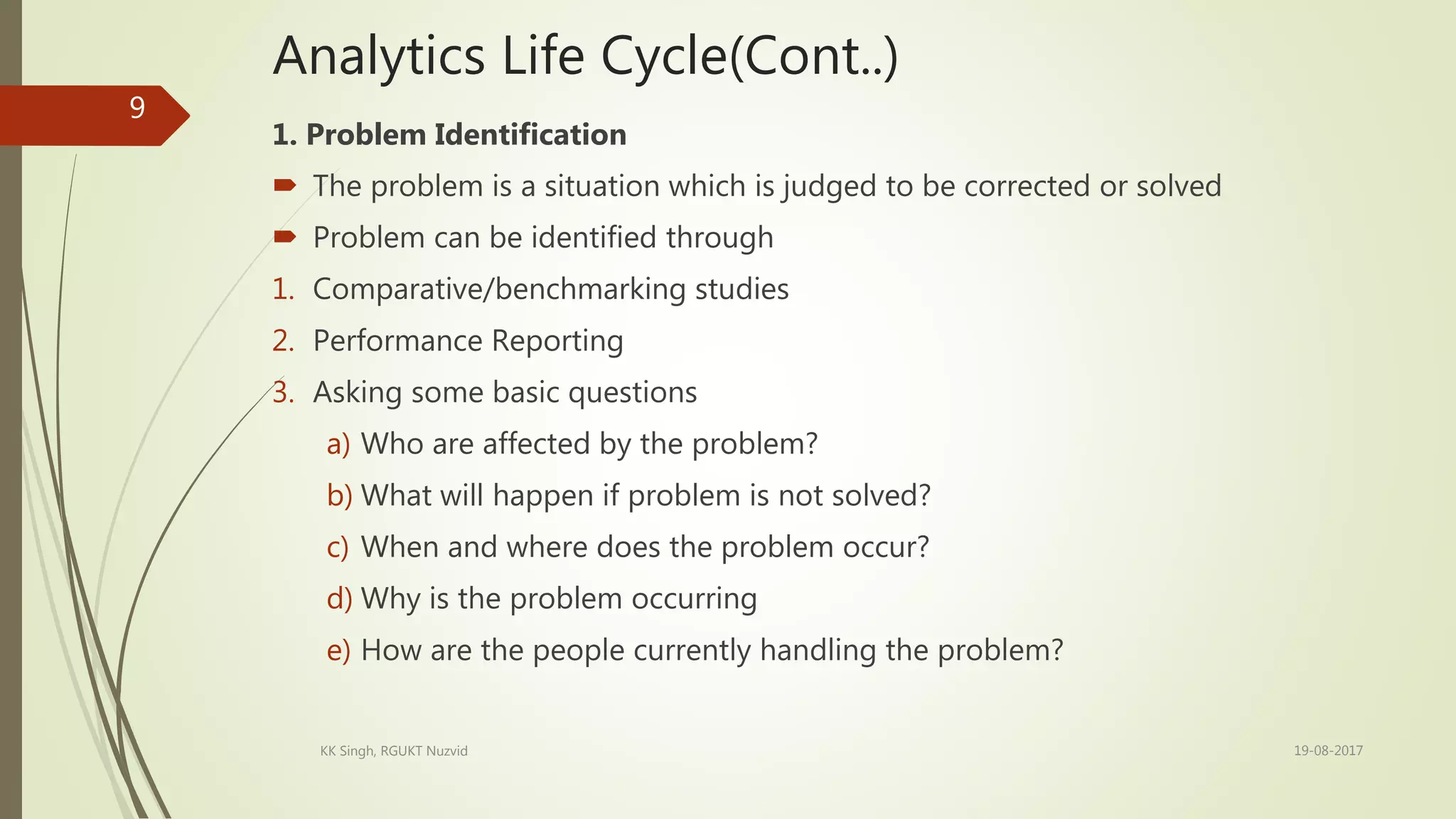
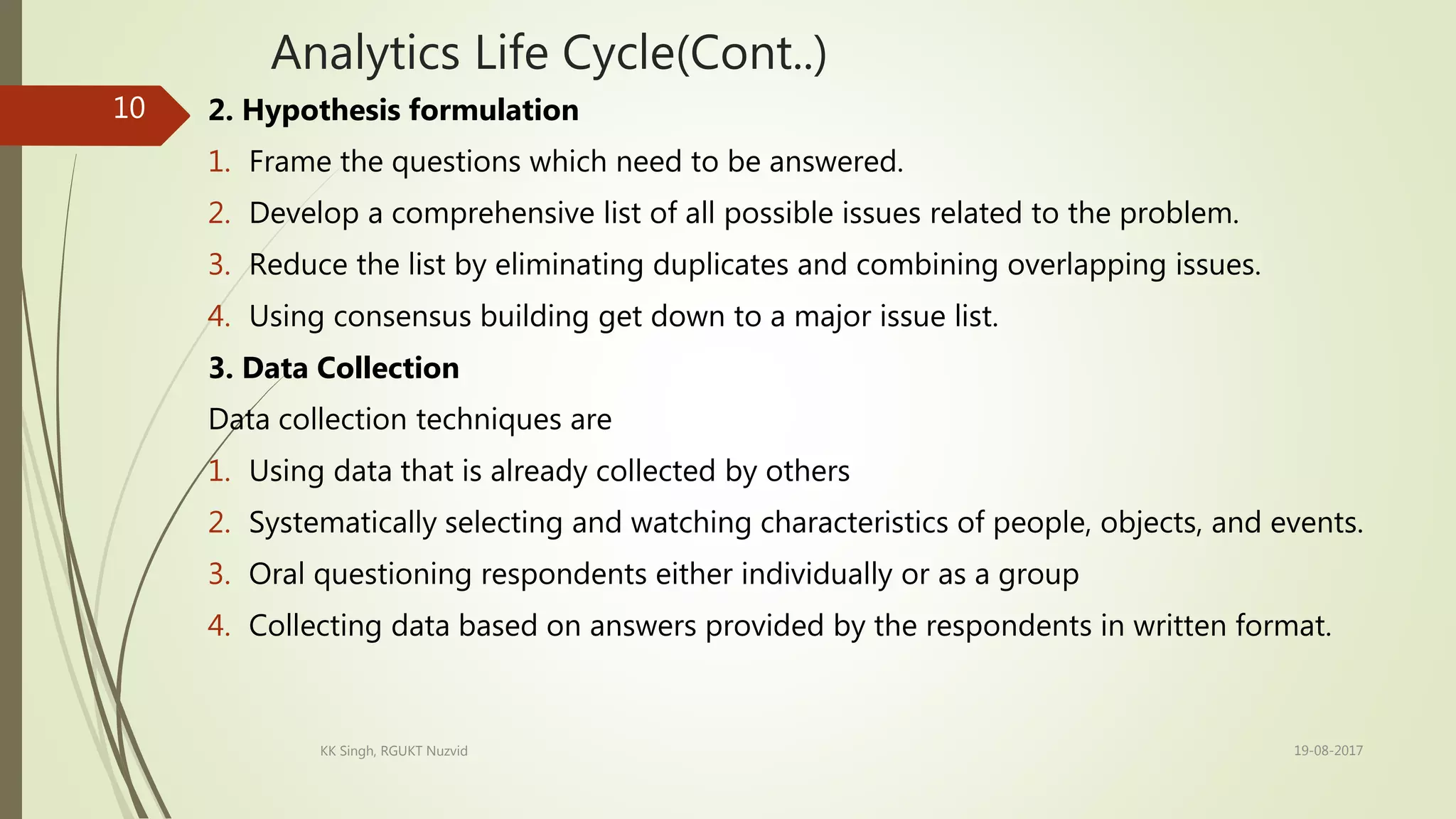
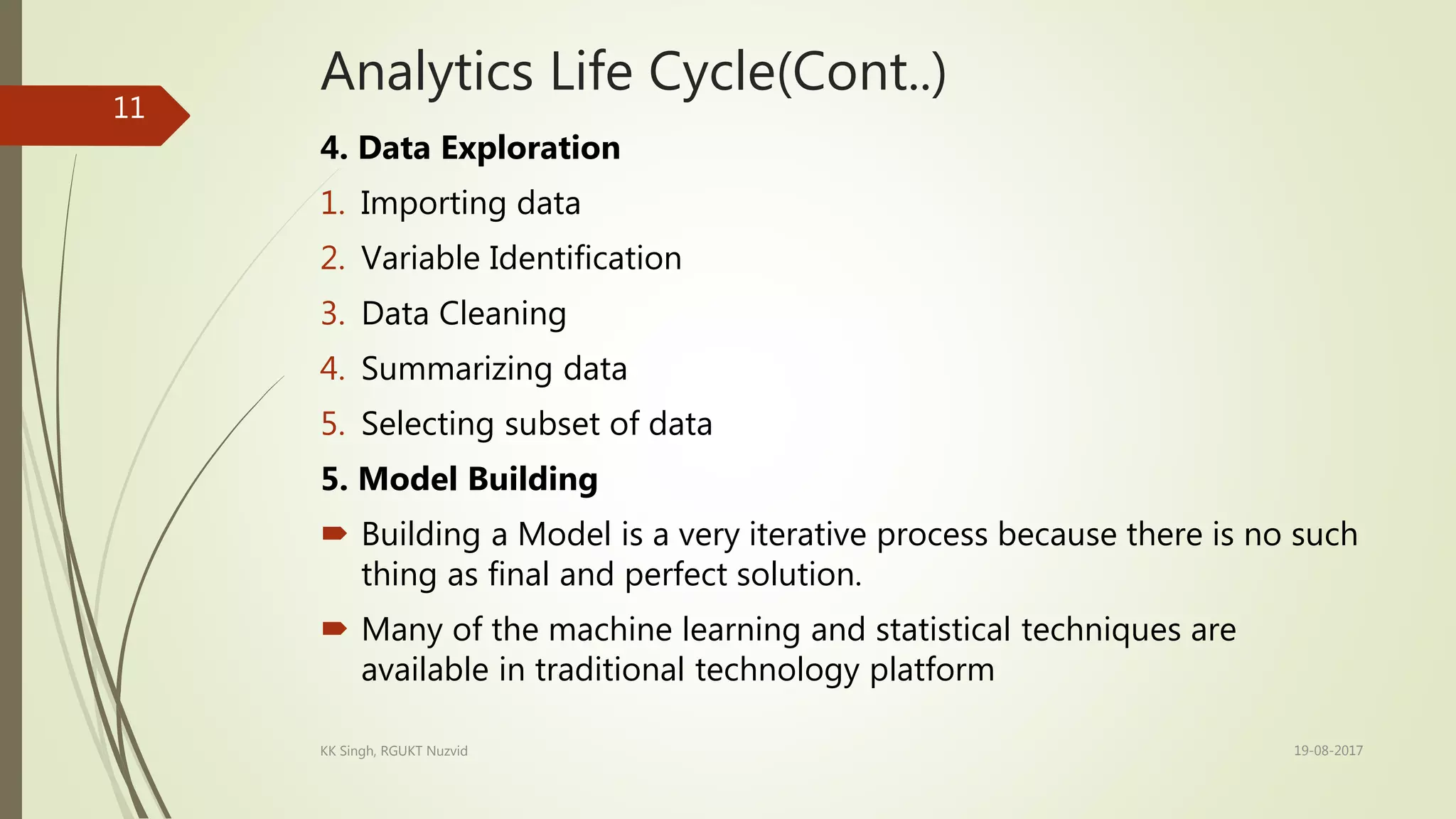
The document provides an introduction to data analytics, including defining key terms like data, information, and analytics. It outlines the learning outcomes which are the basic definition of data analytics concepts, different variable types, types of analytics, and the analytics life cycle. The analytics life cycle is described in detail and involves problem identification, hypothesis formulation, data collection, data exploration, model building, and model validation/evaluation. Different variable types like numerical, categorical, and ordinal variables are also defined.