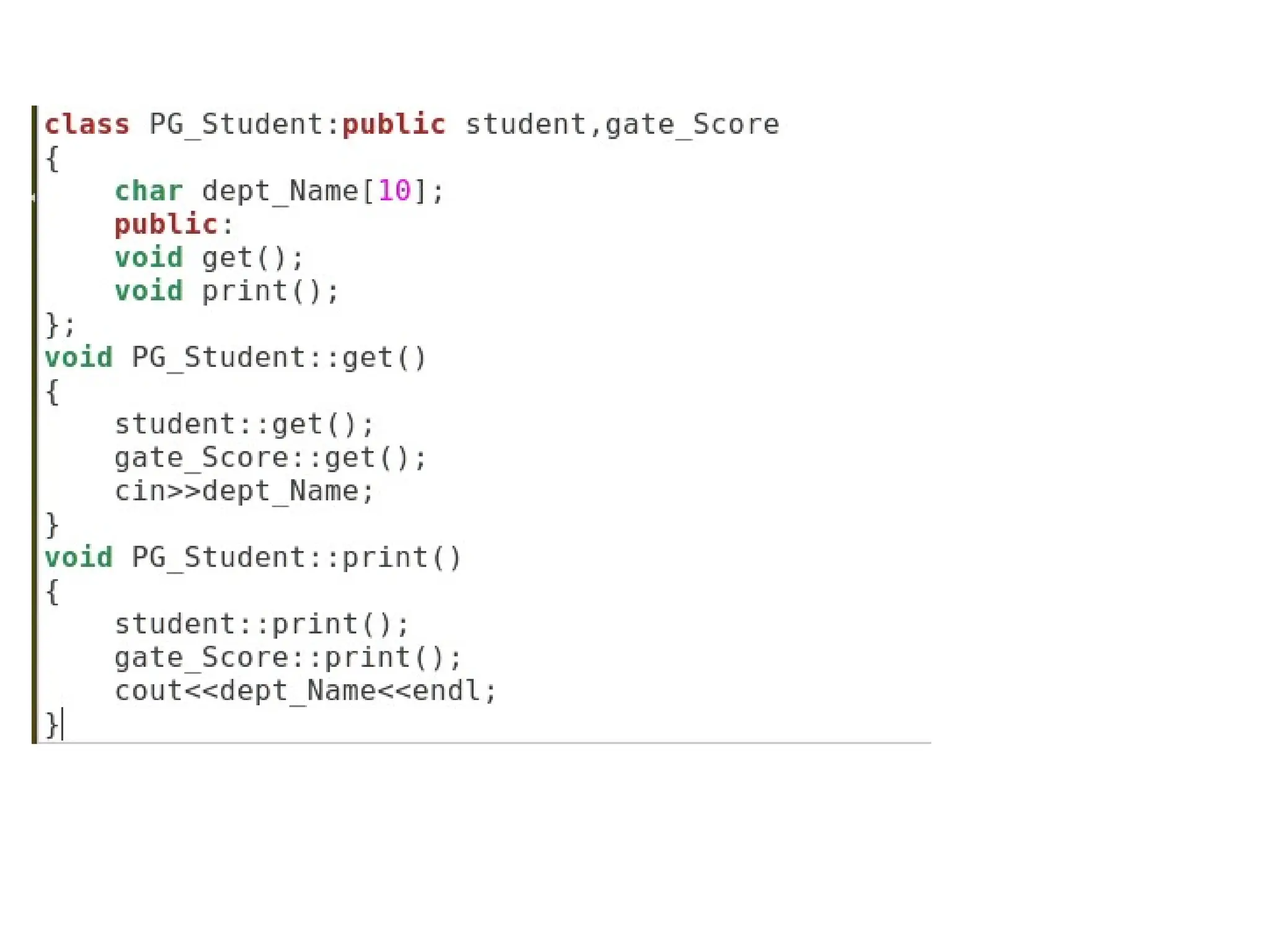
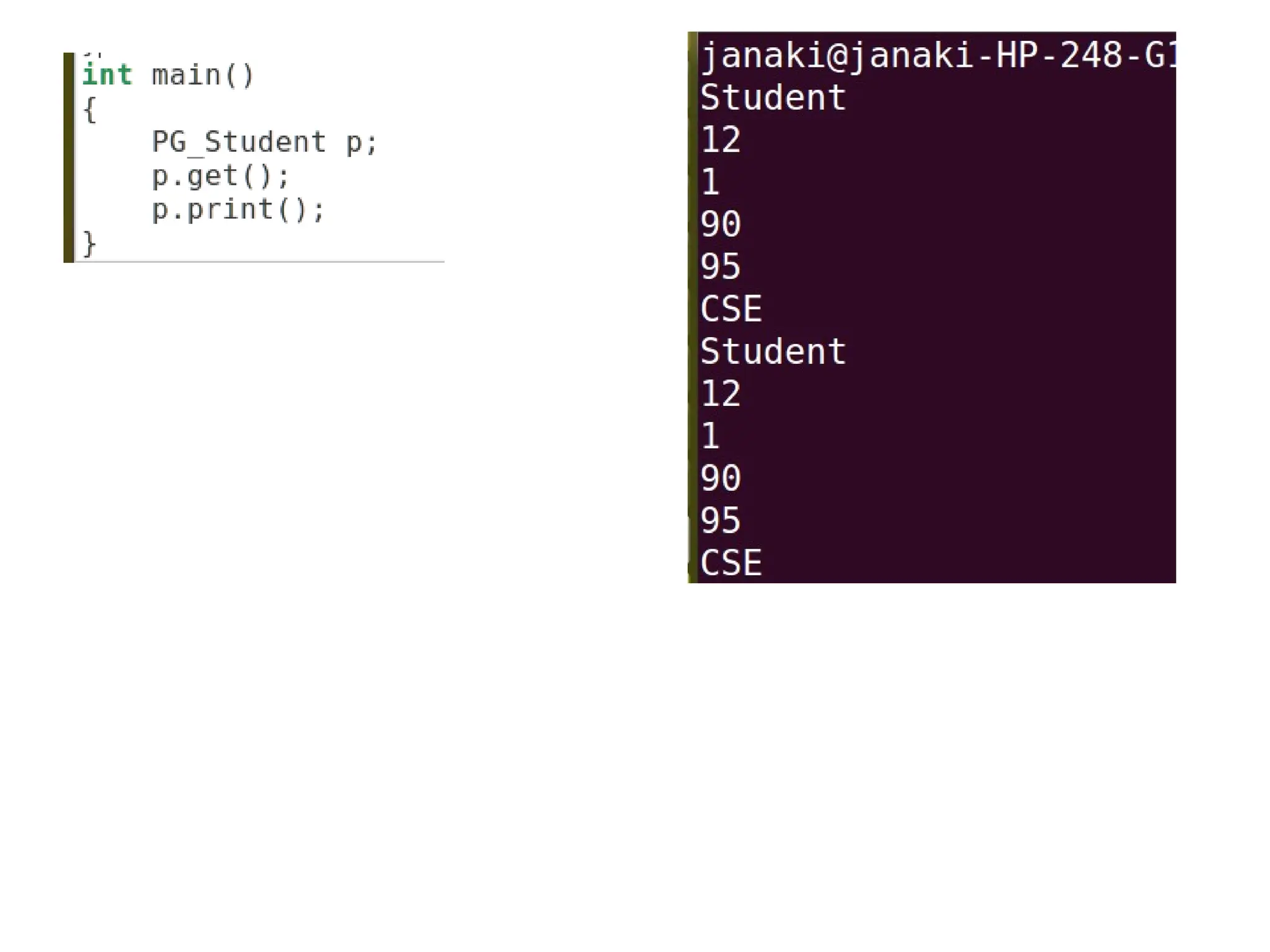
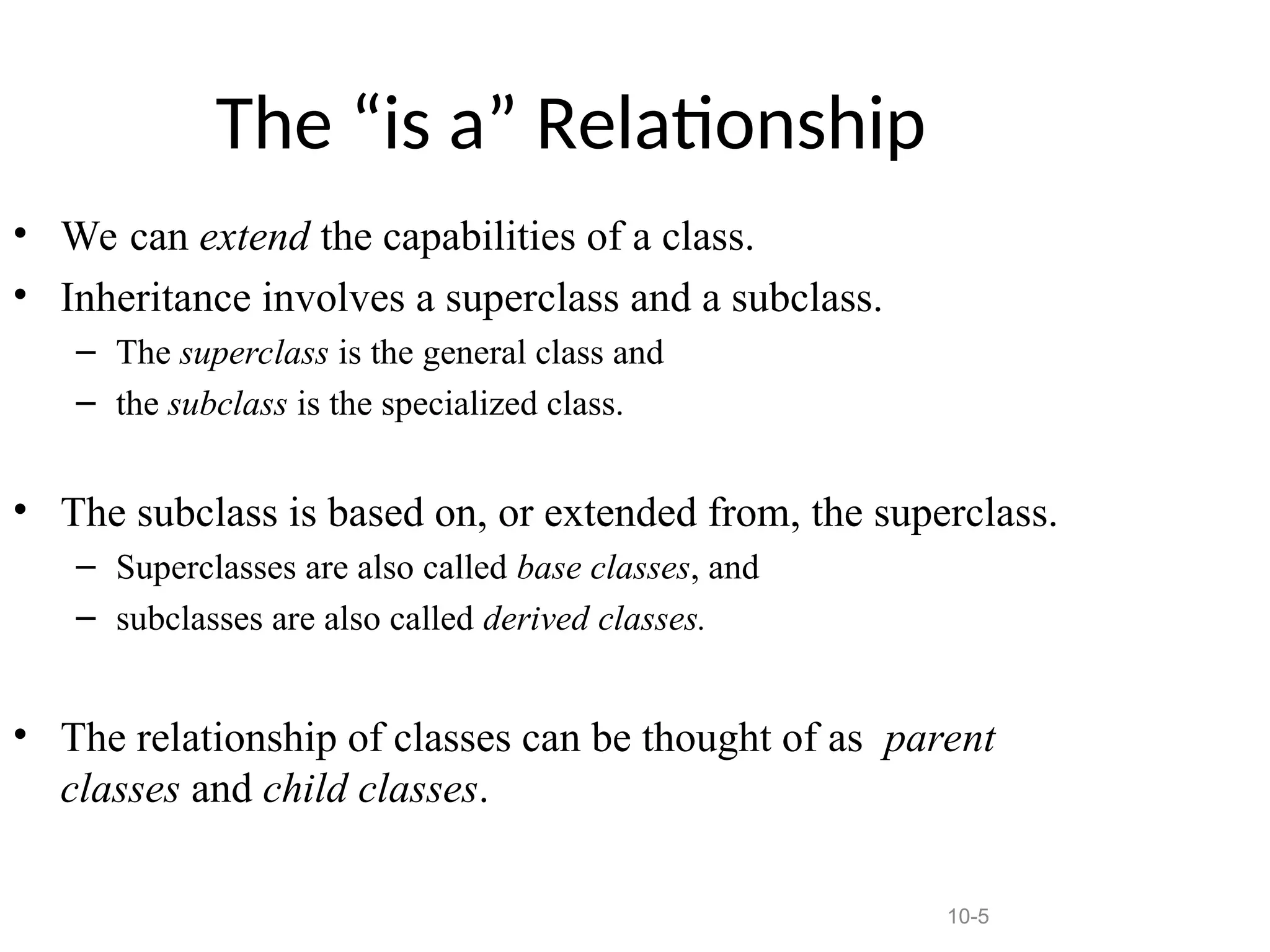
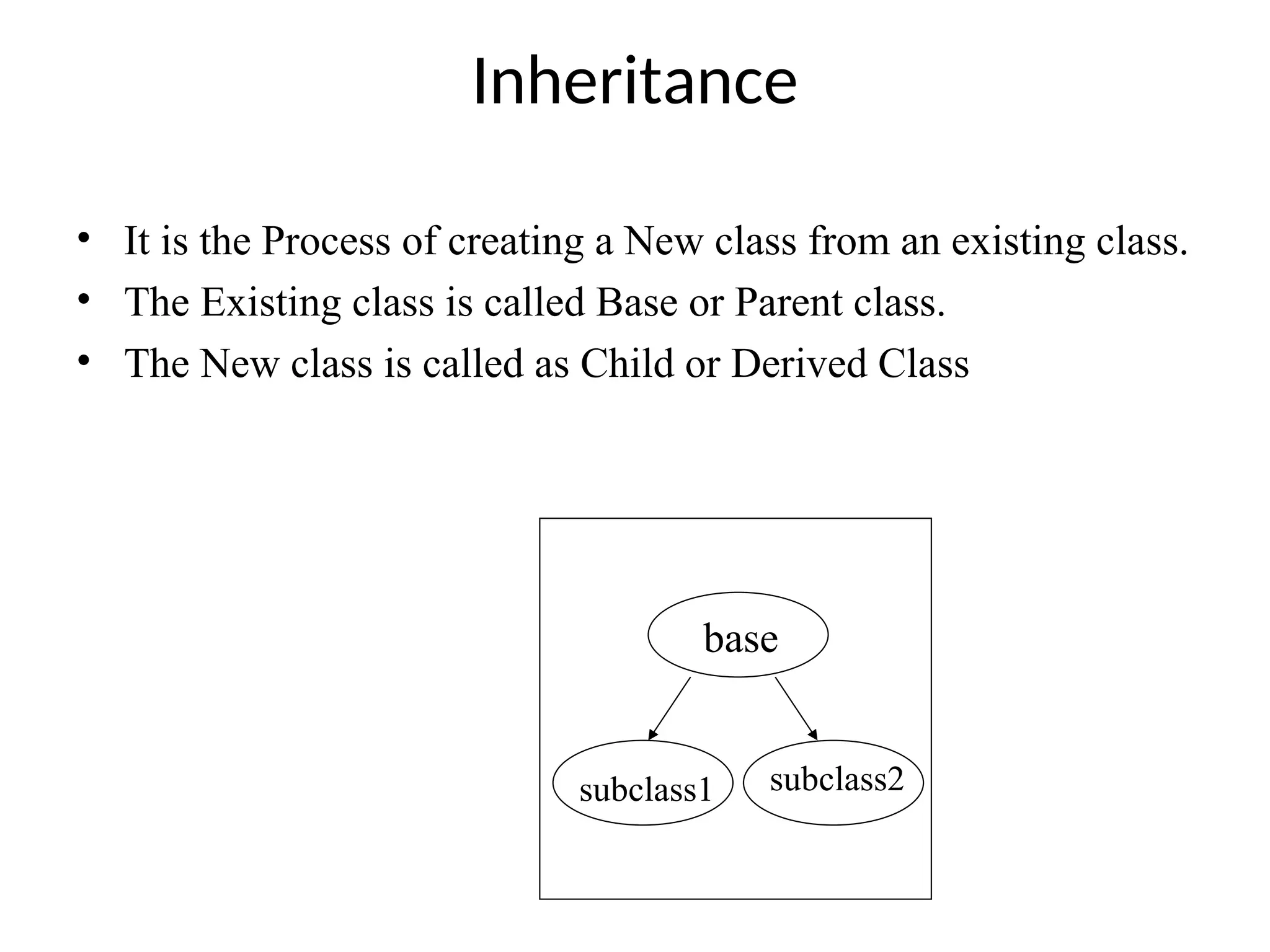
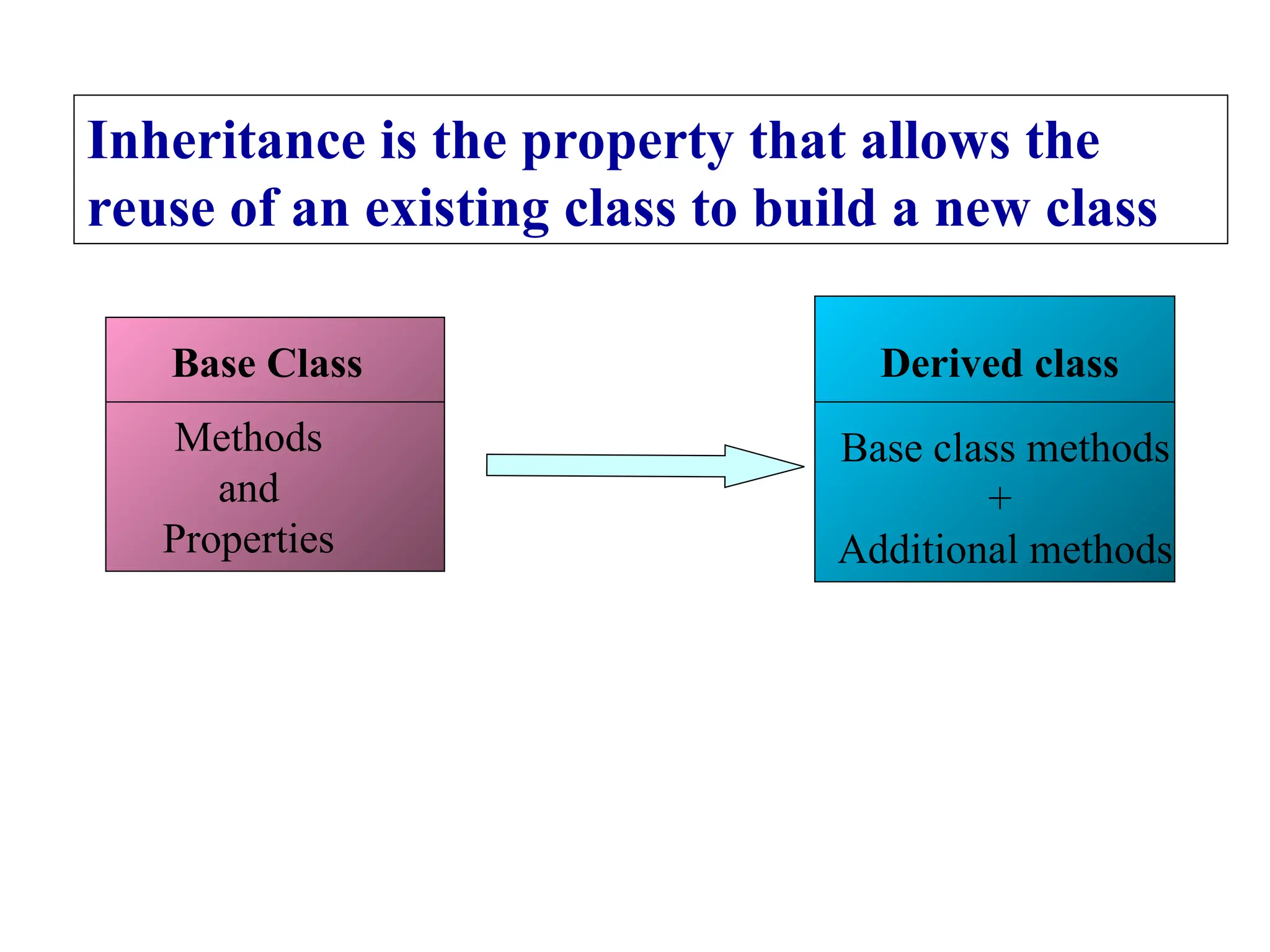
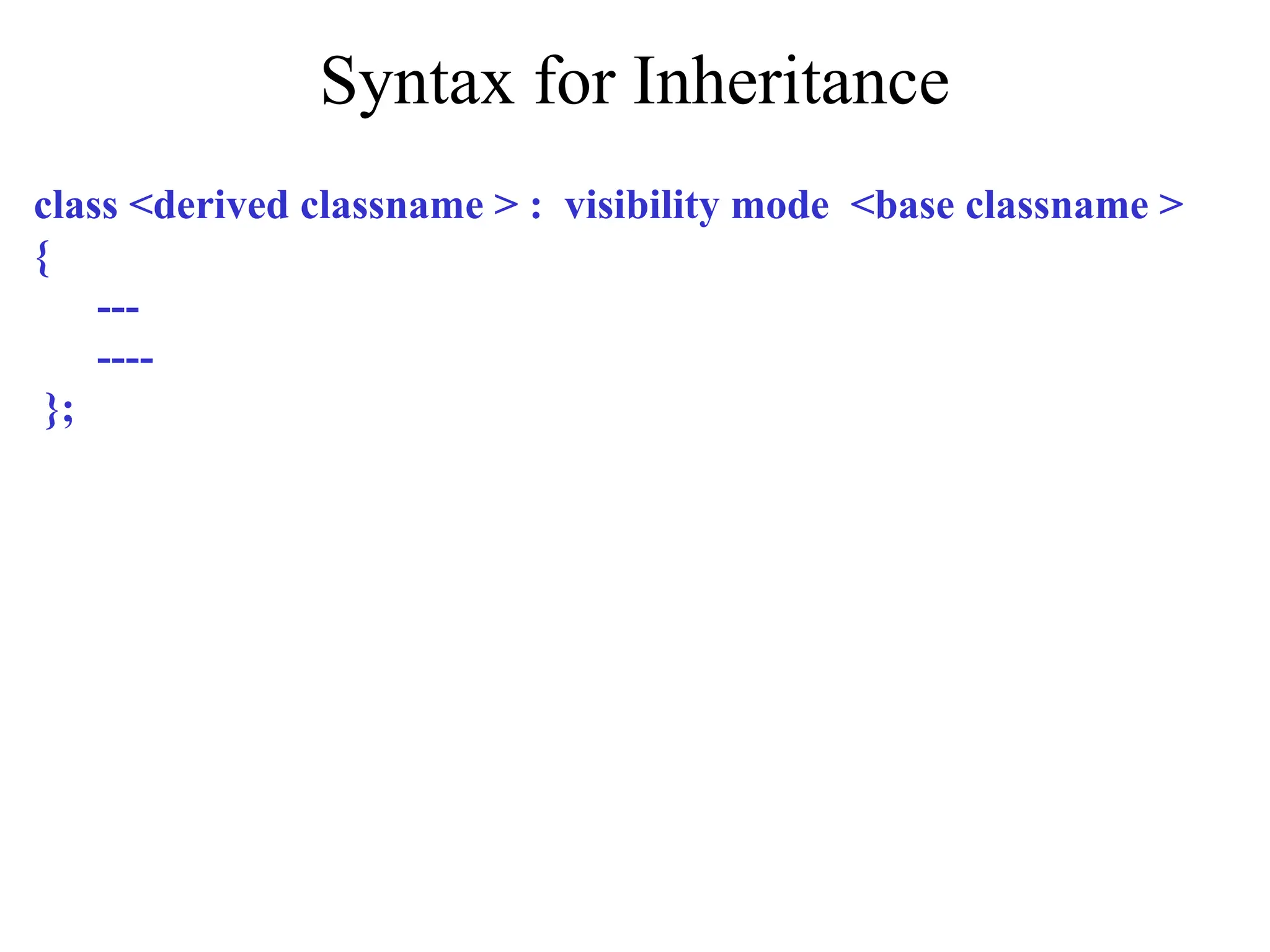
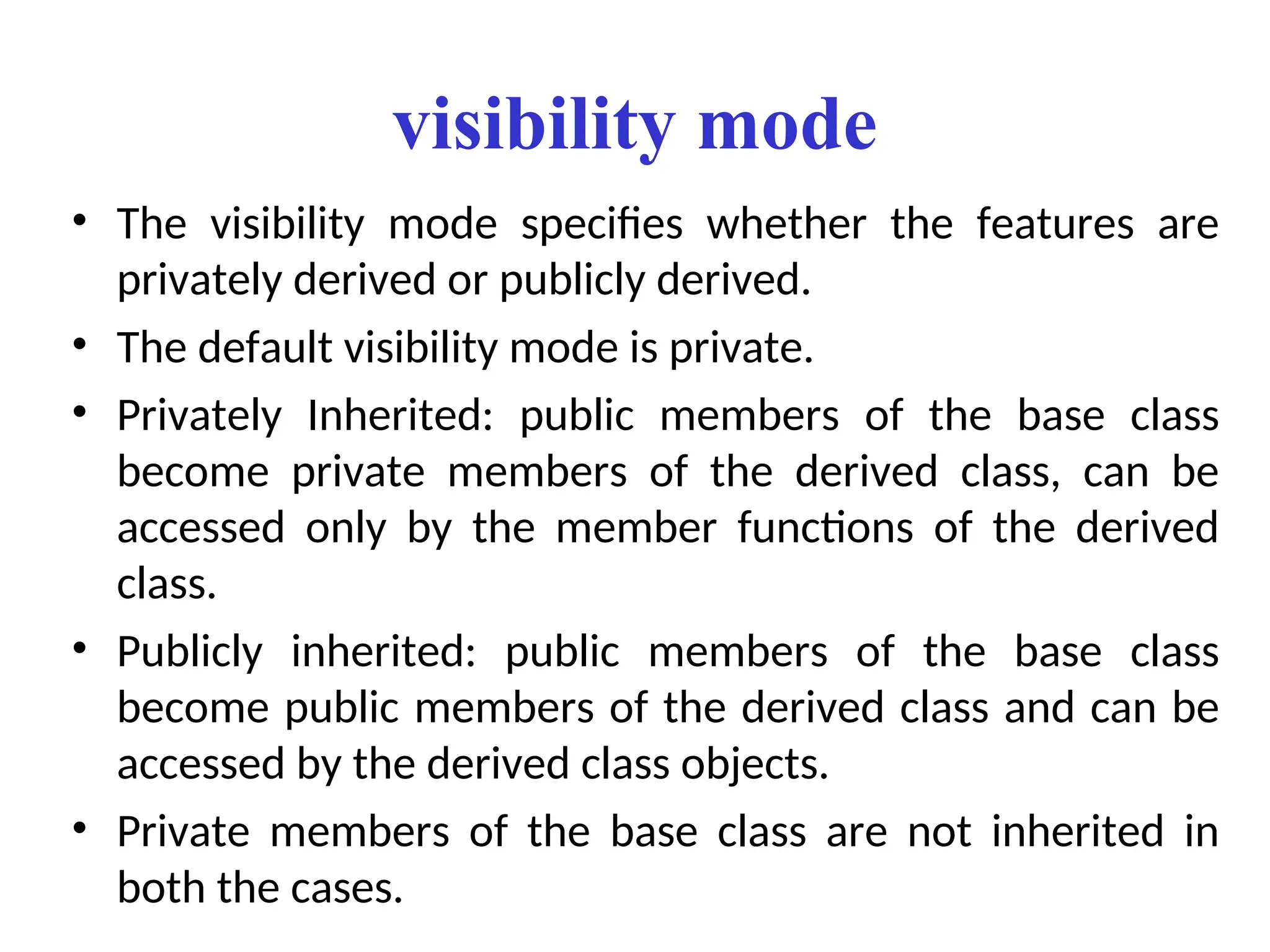
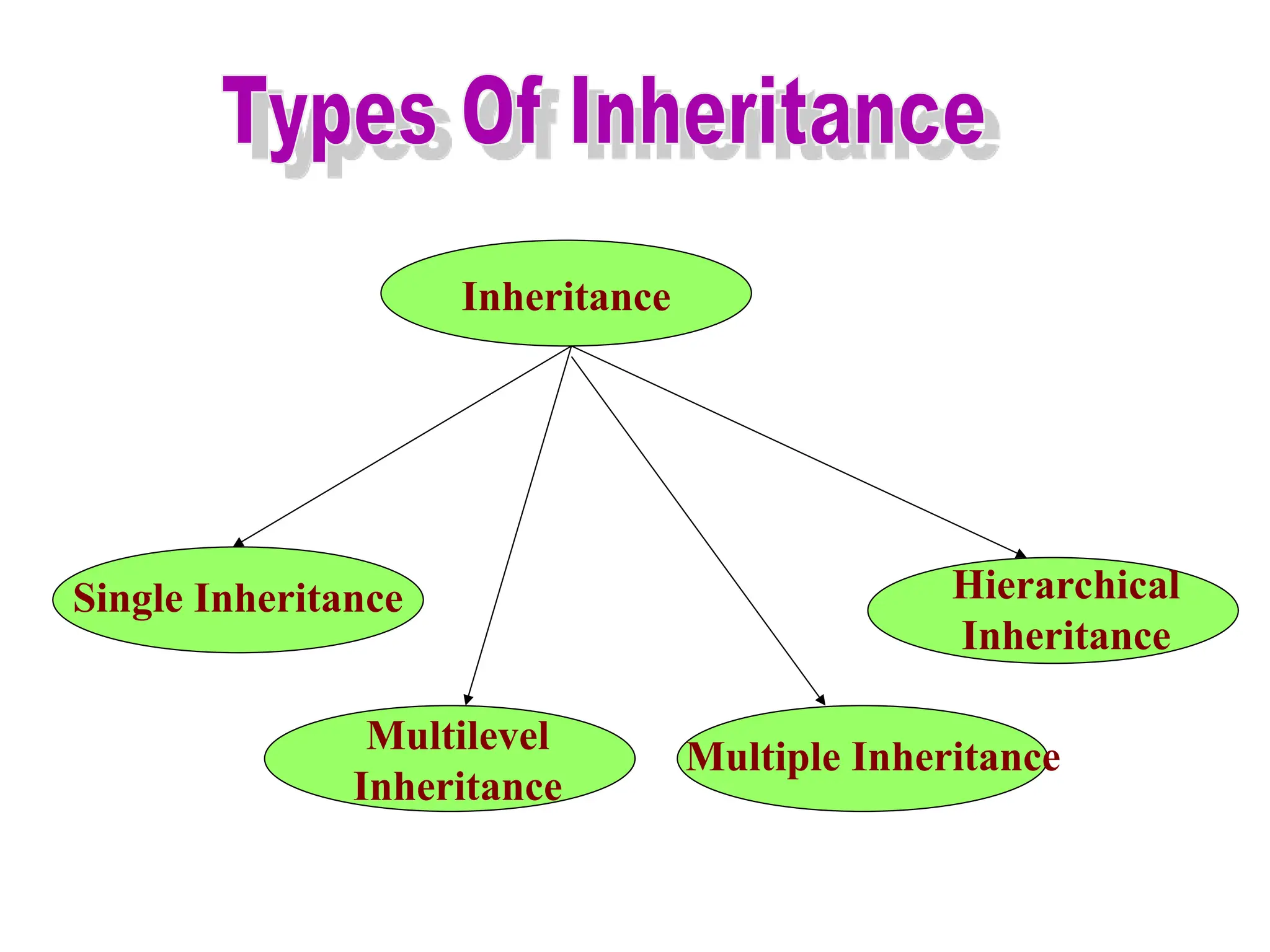
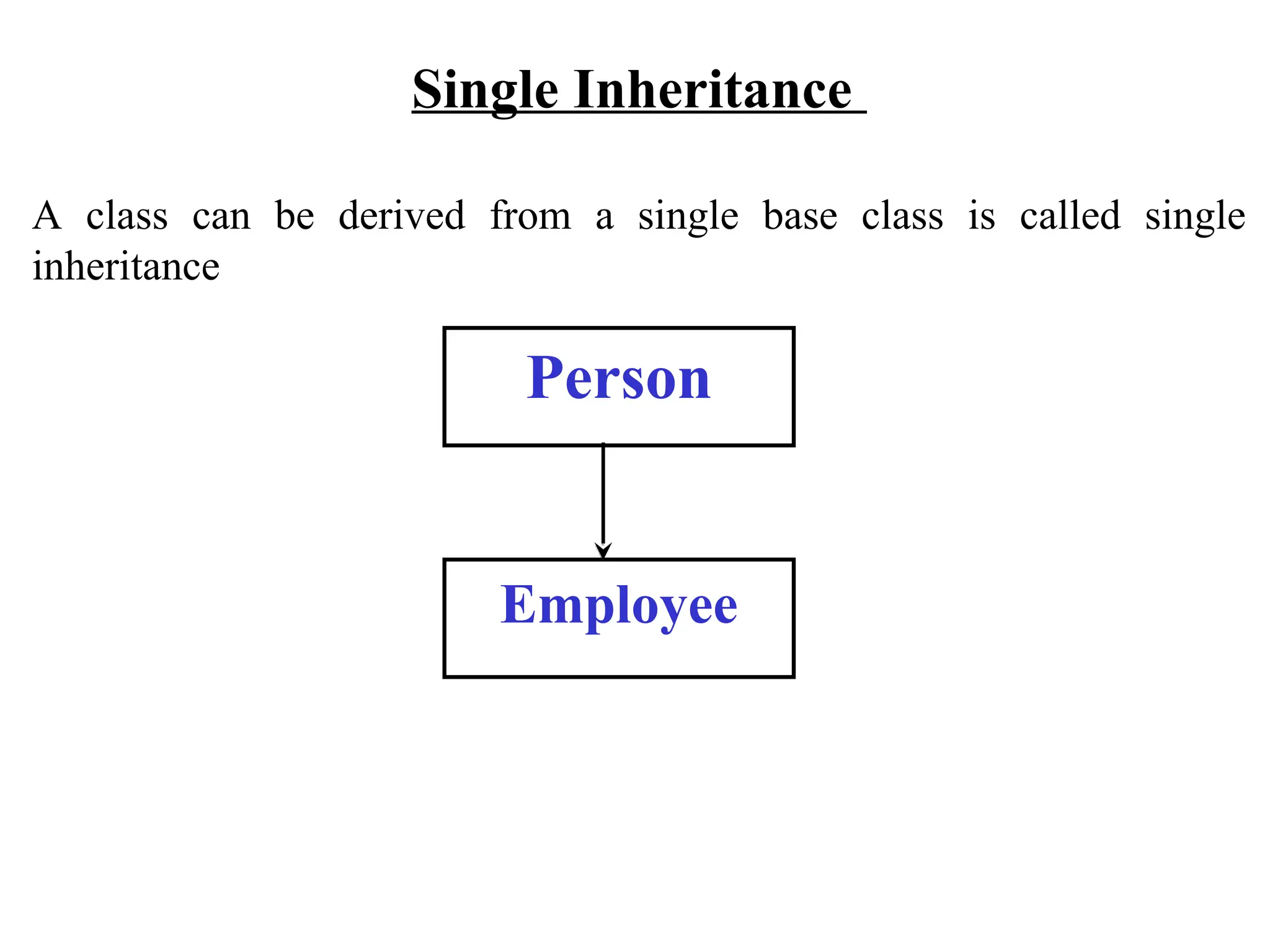
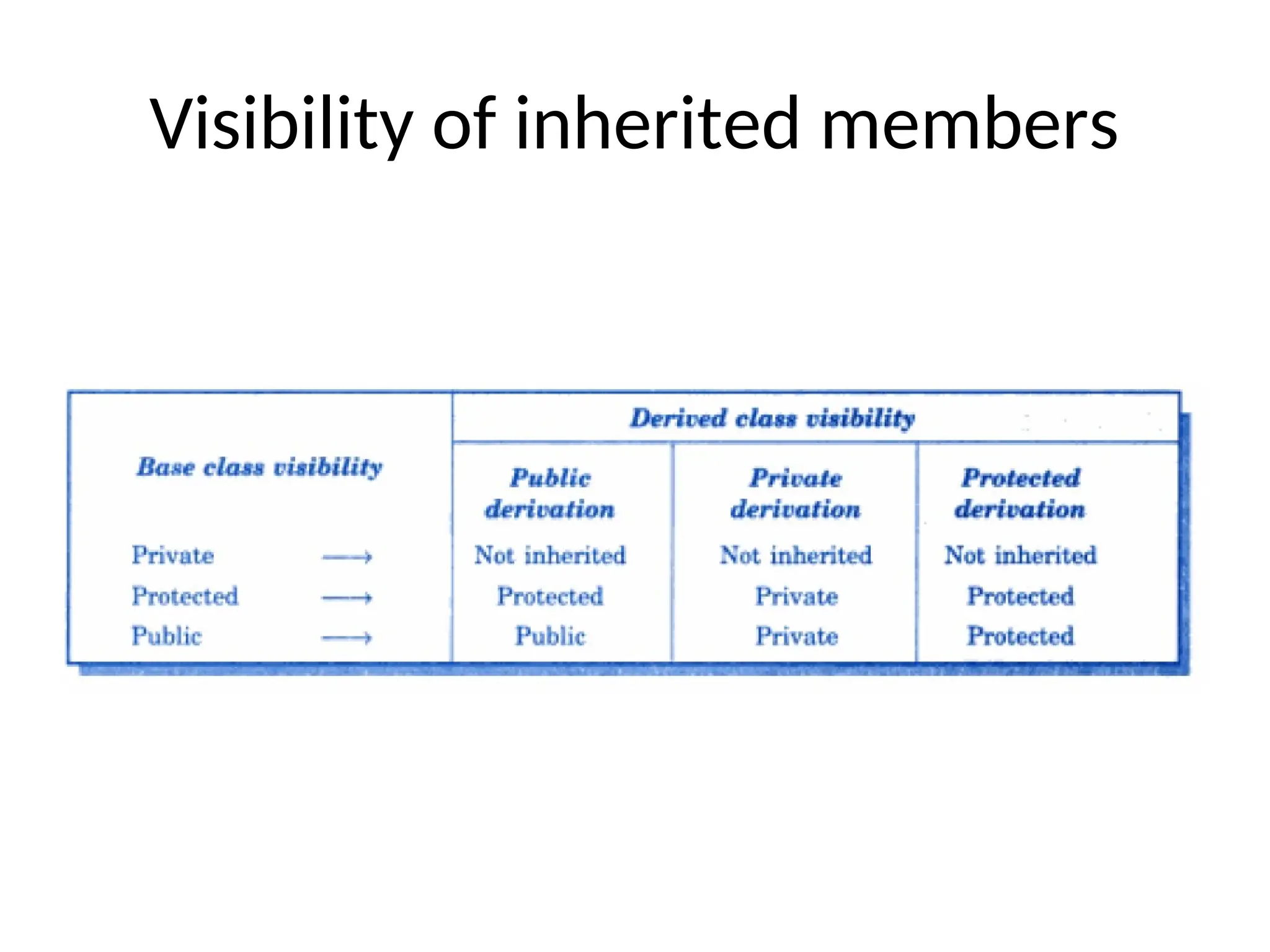
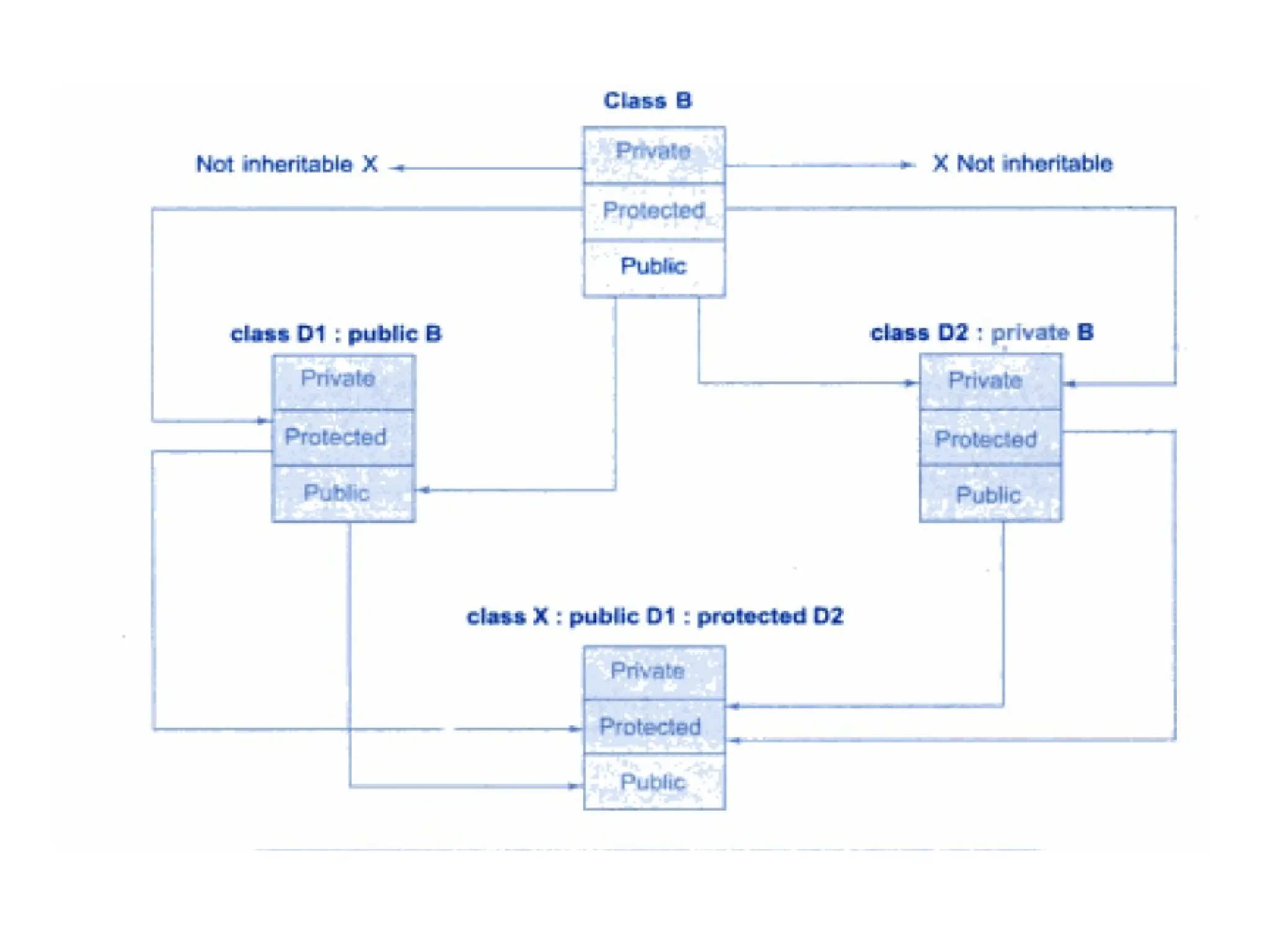
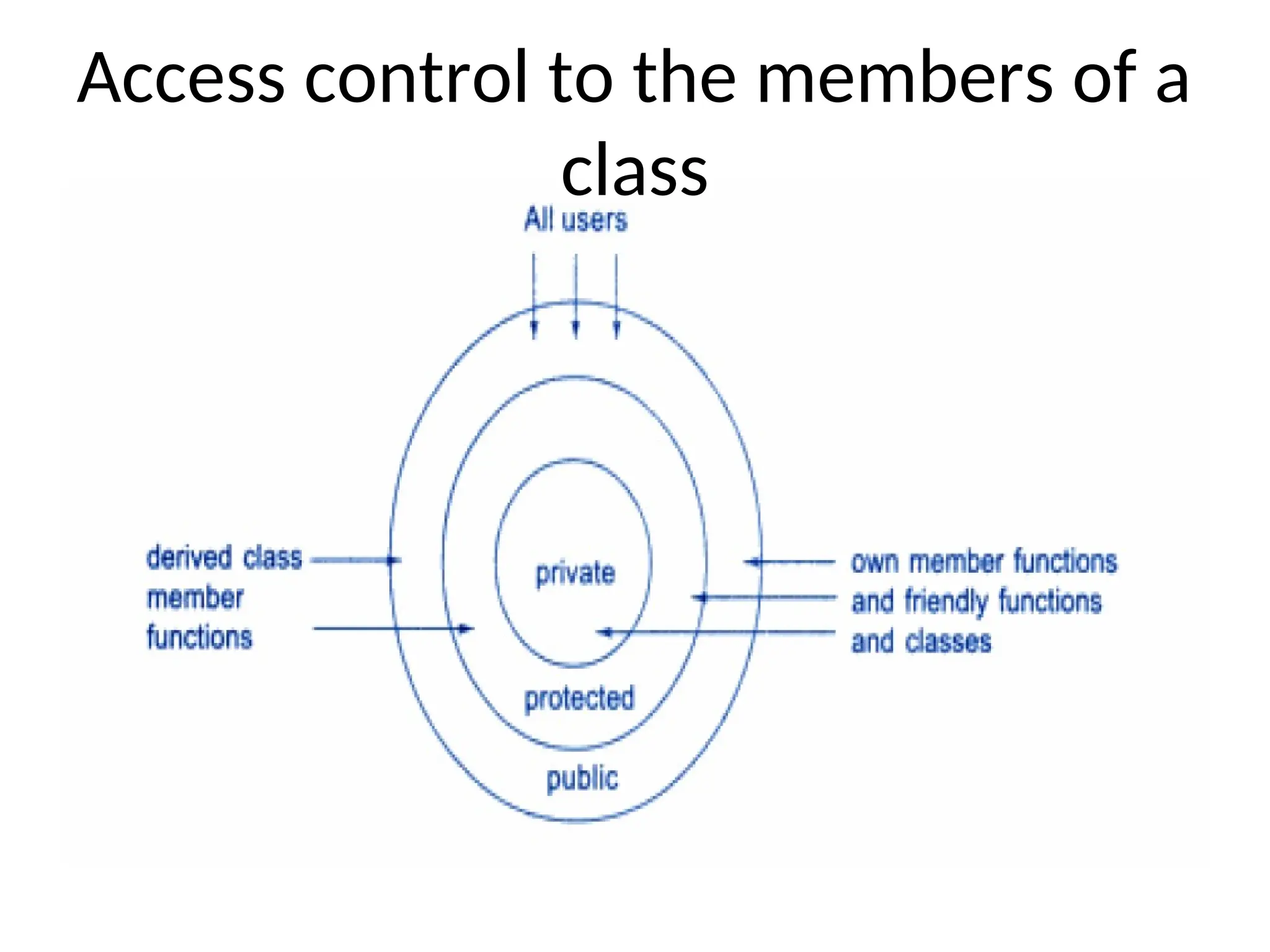
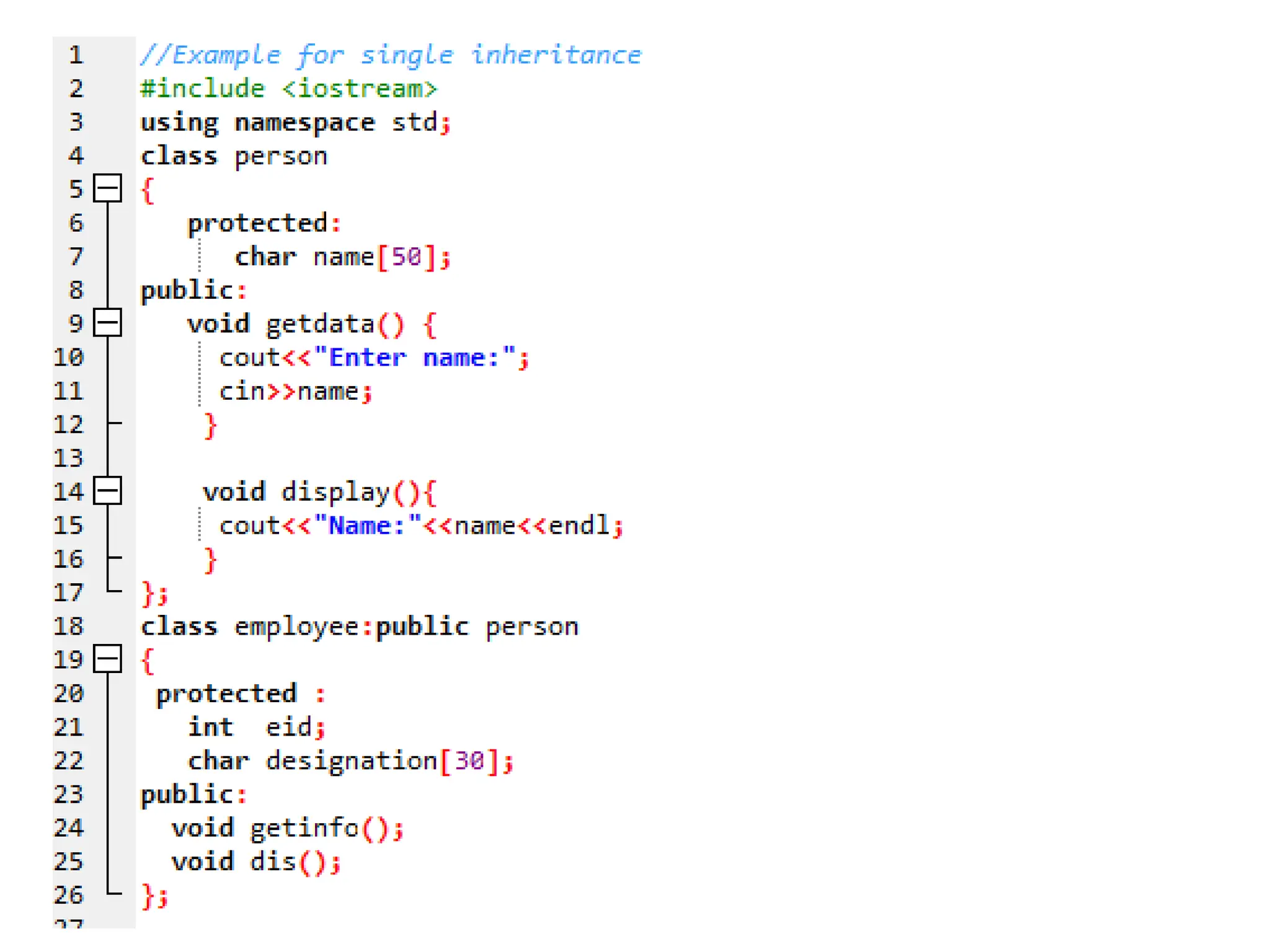
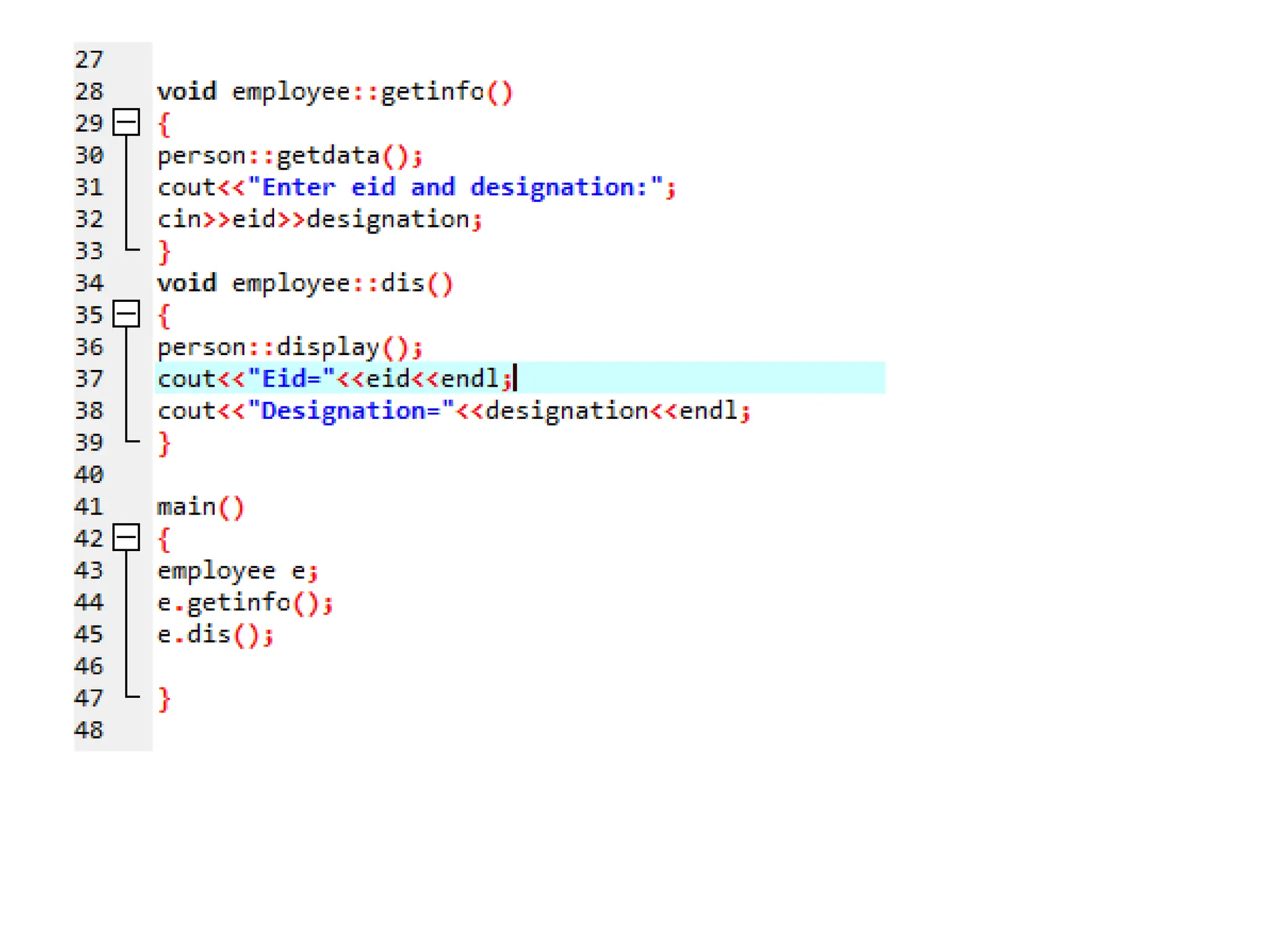
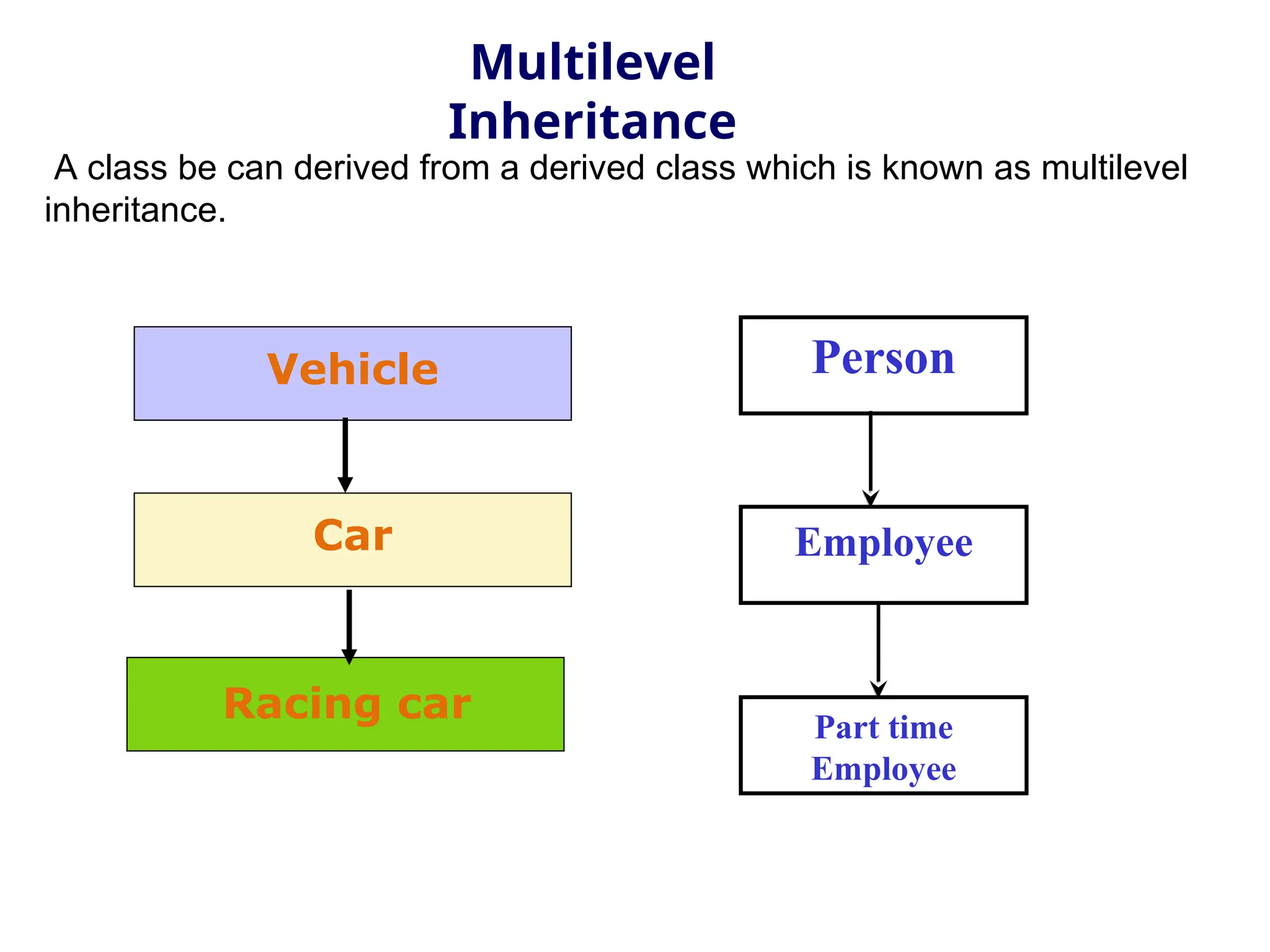
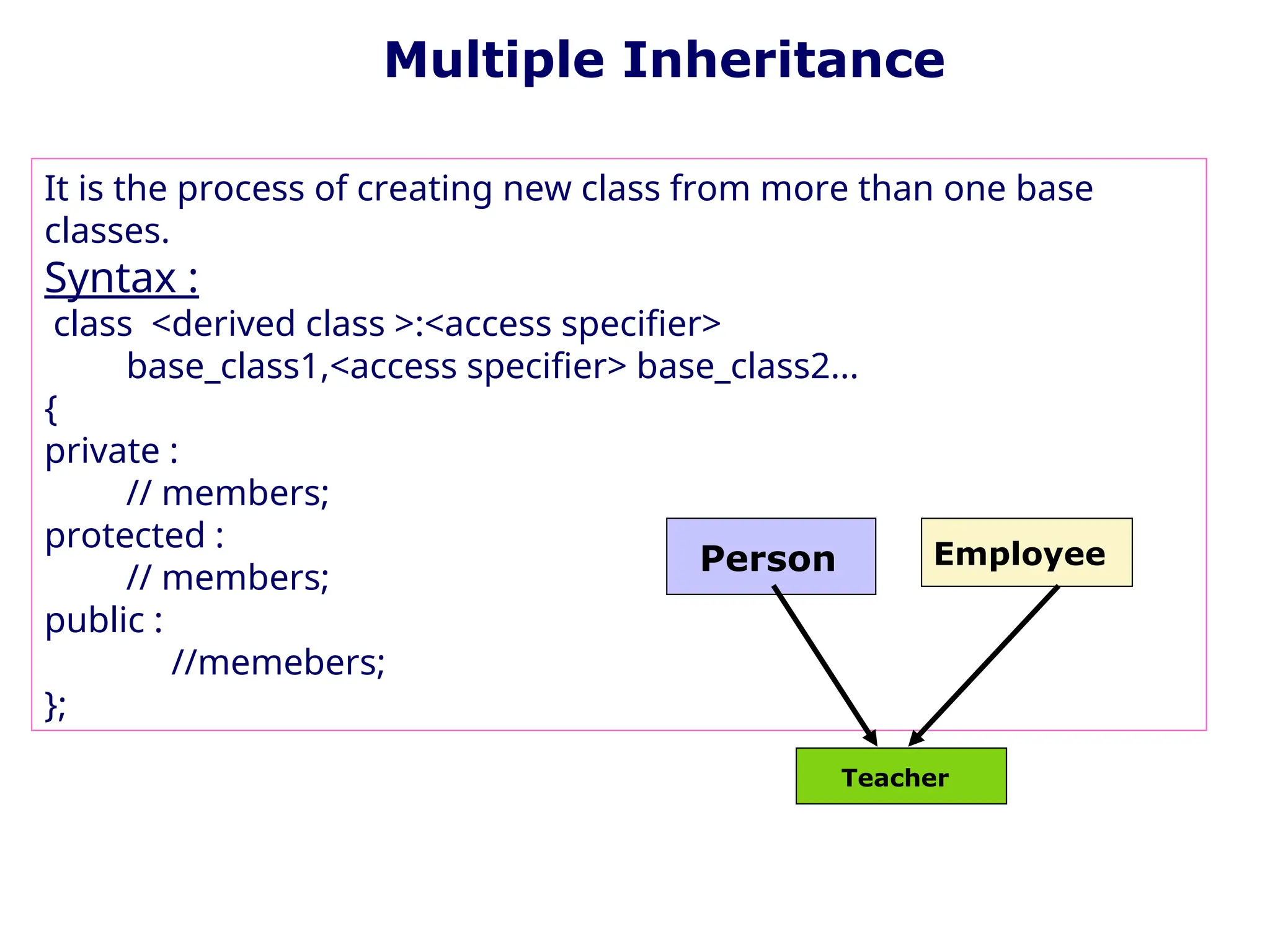
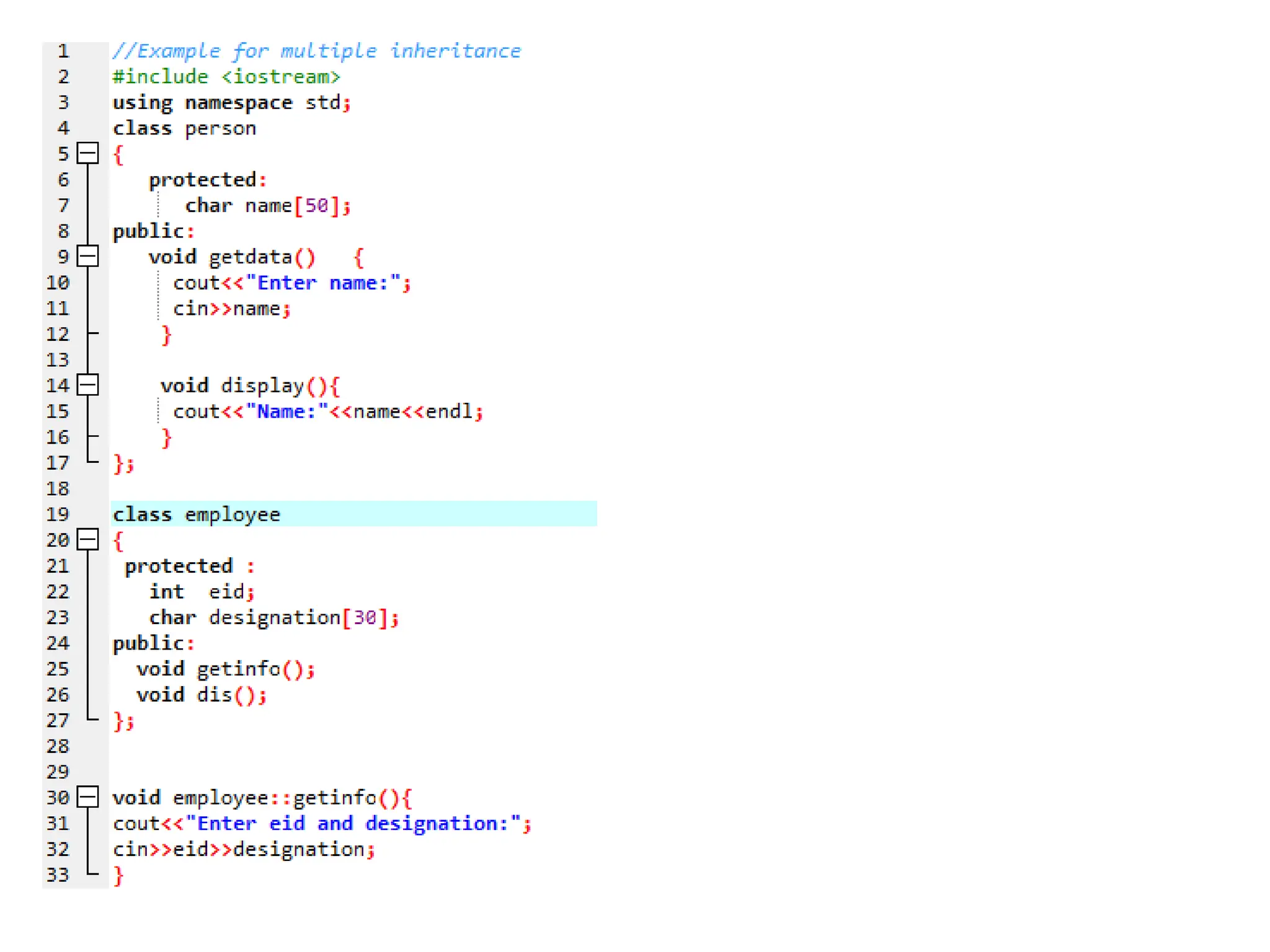
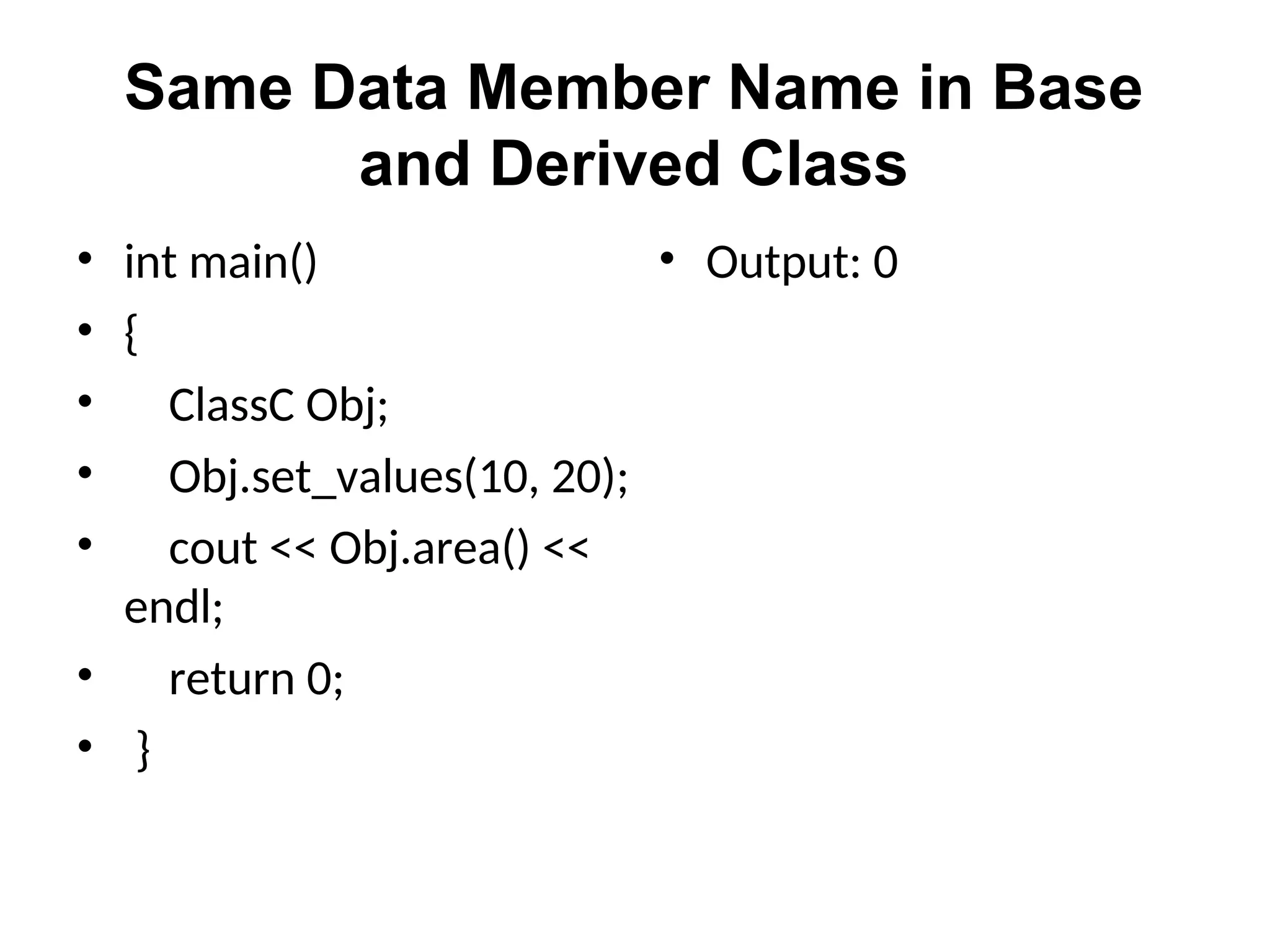
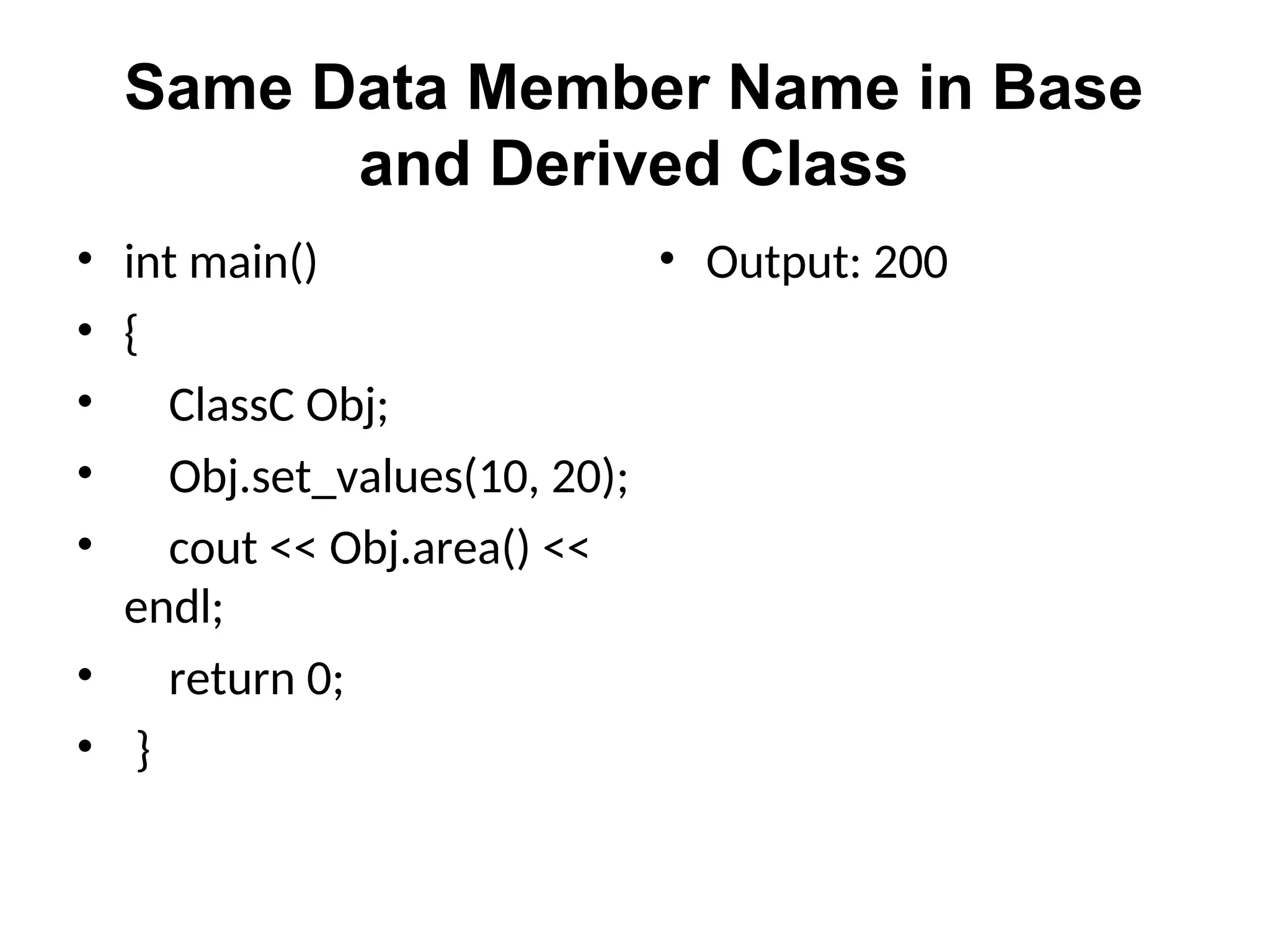
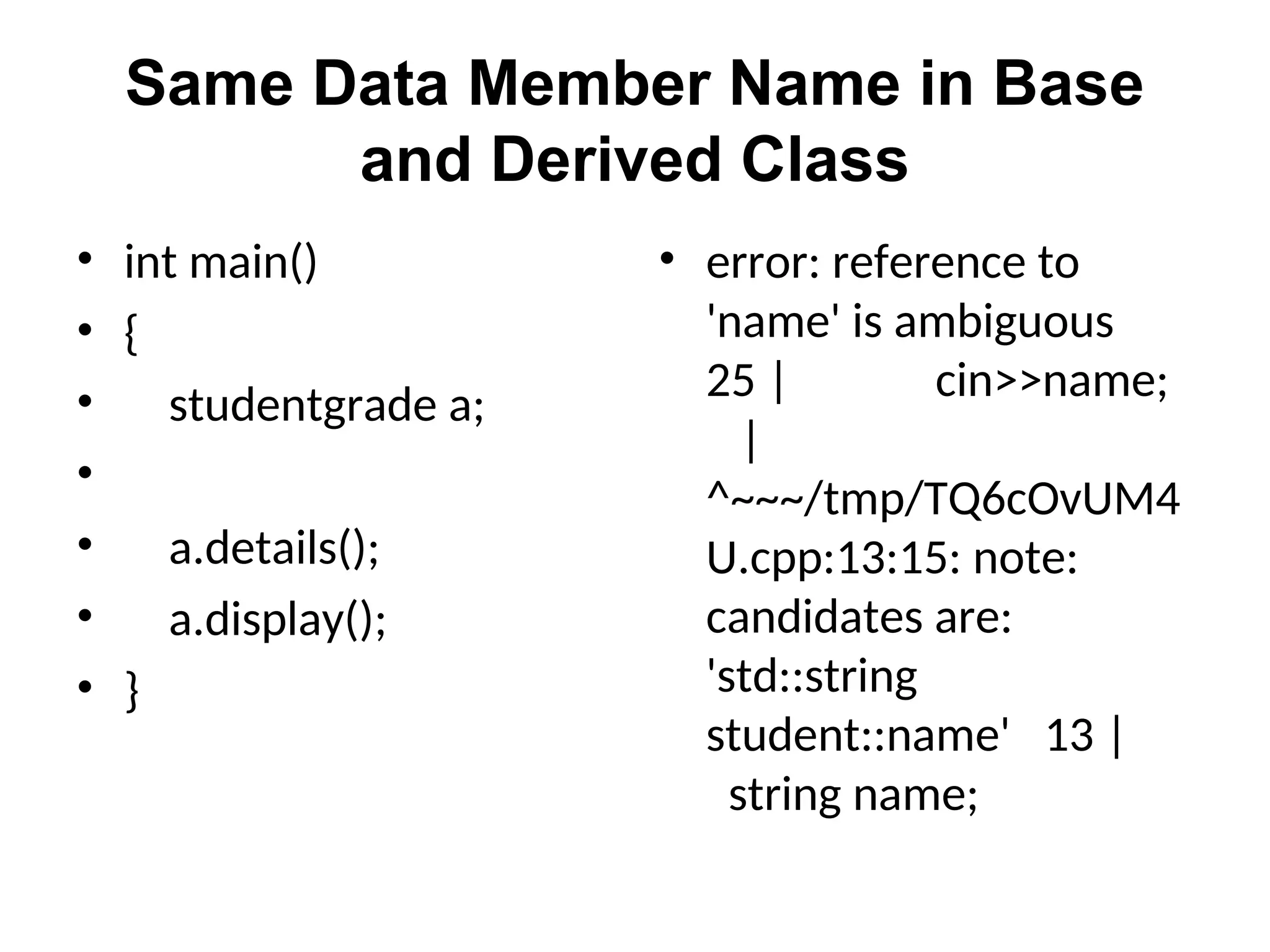
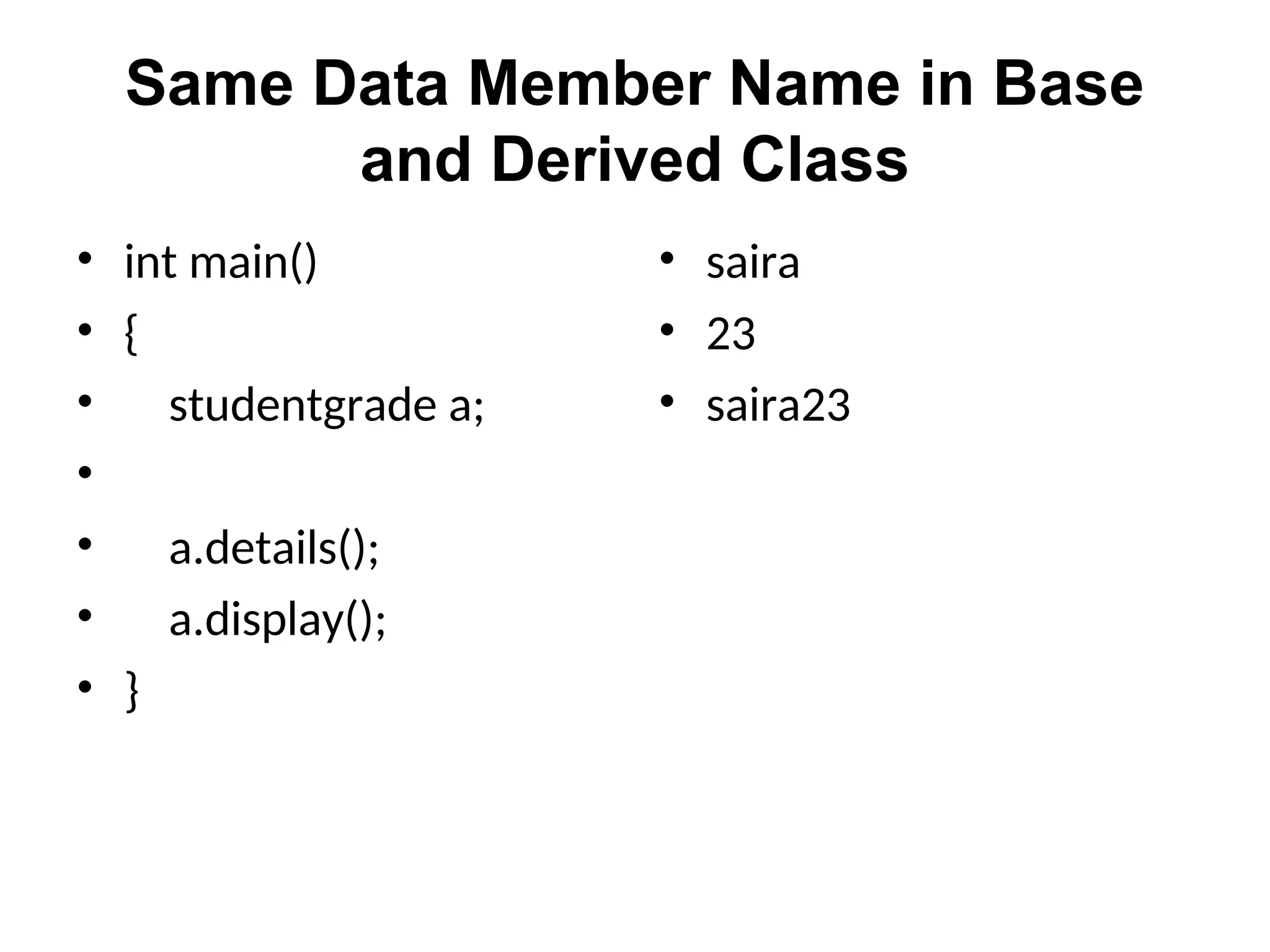
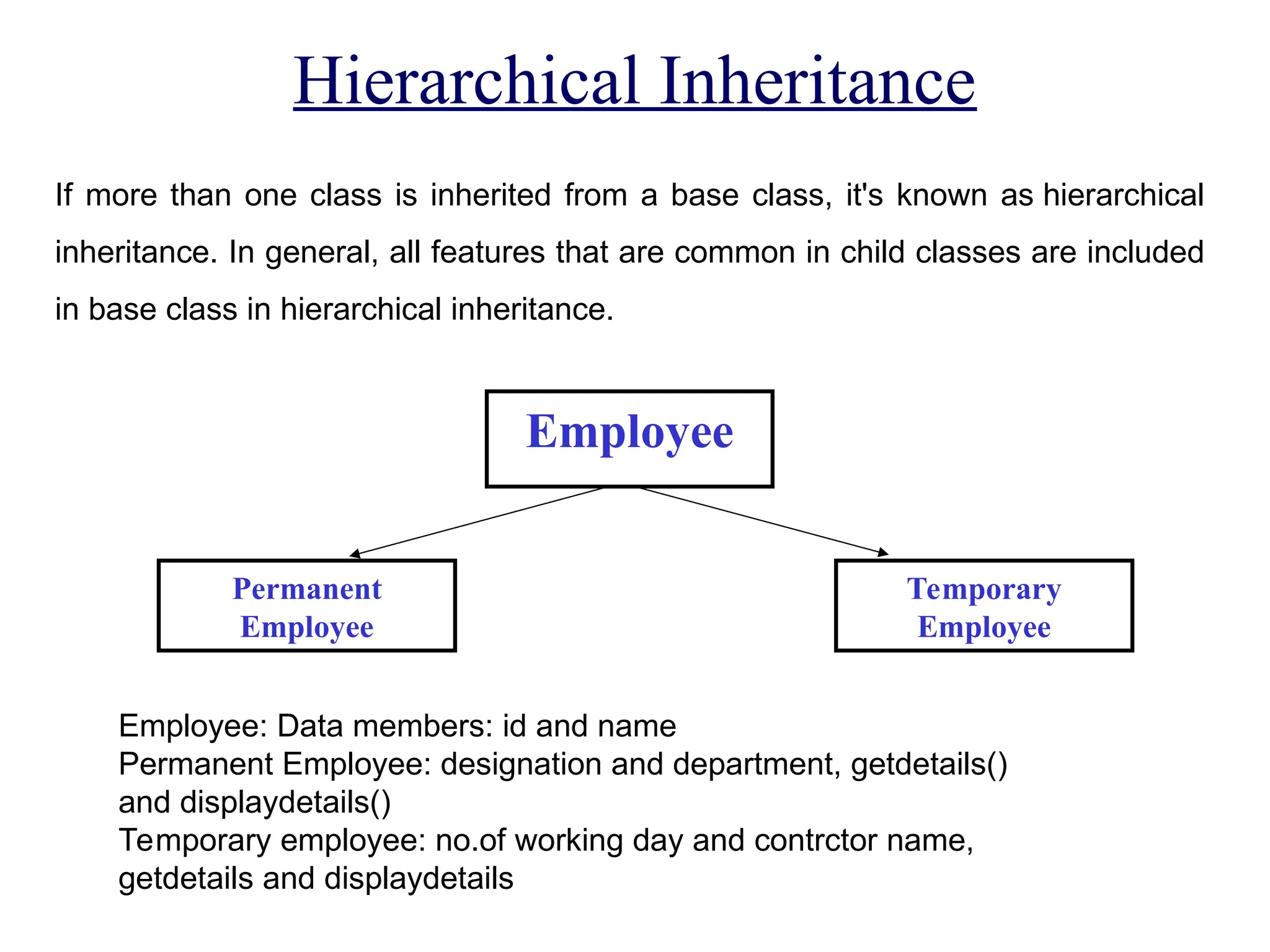
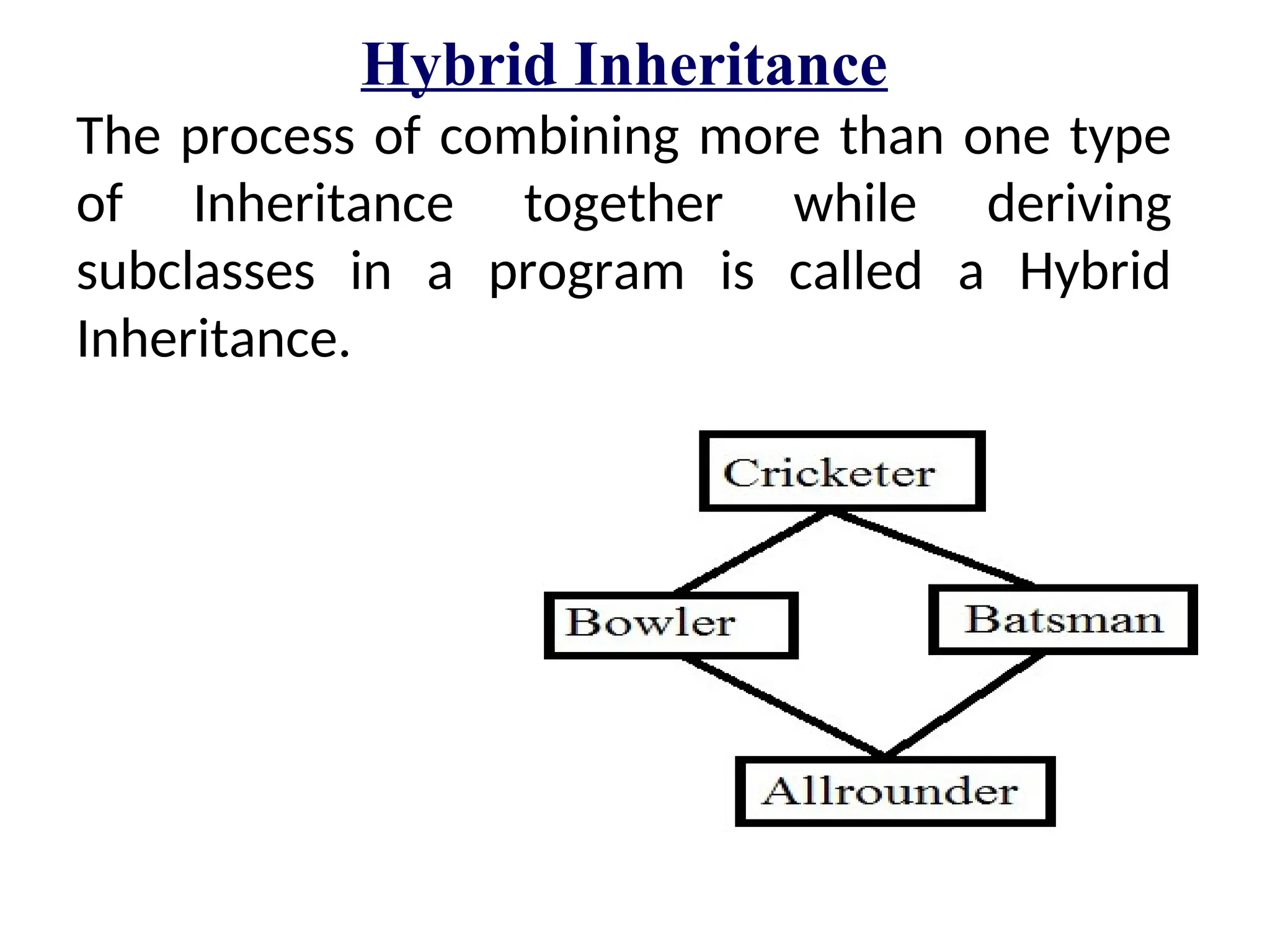
The document discusses inheritance in object-oriented programming, highlighting the concepts of generalization vs. specialization, the 'is a' relationship between classes, and the advantages of inheritance such as code reusability. It explains different types of inheritance including single, multilevel, multiple, hierarchical, and hybrid inheritance, along with access control mechanisms for inherited members. Various examples and syntax for implementing these inheritance types in C++ are provided for clarification.


















![Person: name and age[protected], get() and print()
Student: rollno and marks[private], get() and print()
Gate Score: gatescore[private], get() and print()
PG-Student :dept_name[private]. get() and print()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10-250210092827-e027e33b/75/10-Inheritance-ppt-for-oops-programinggg-43-2048.jpg)