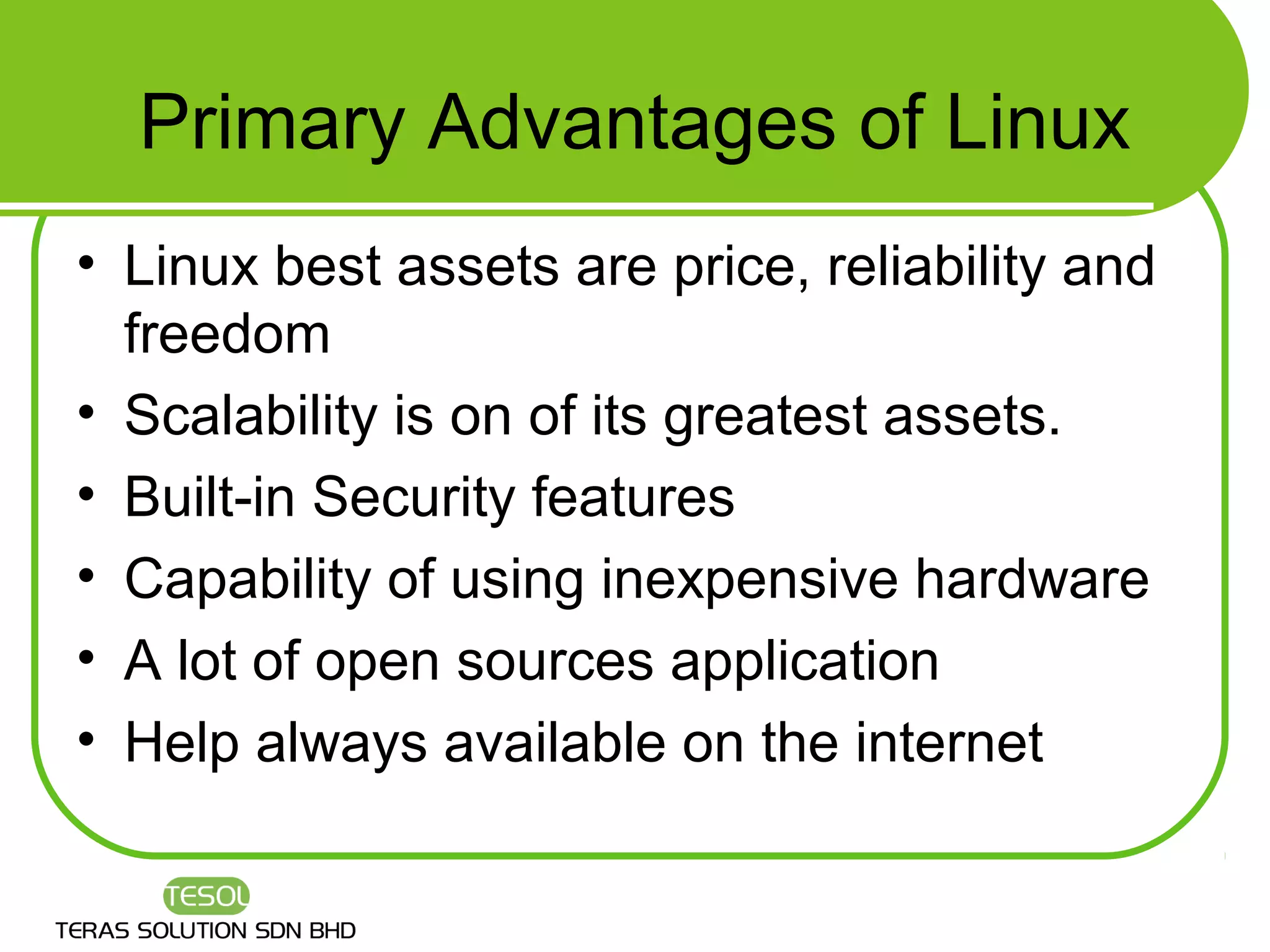
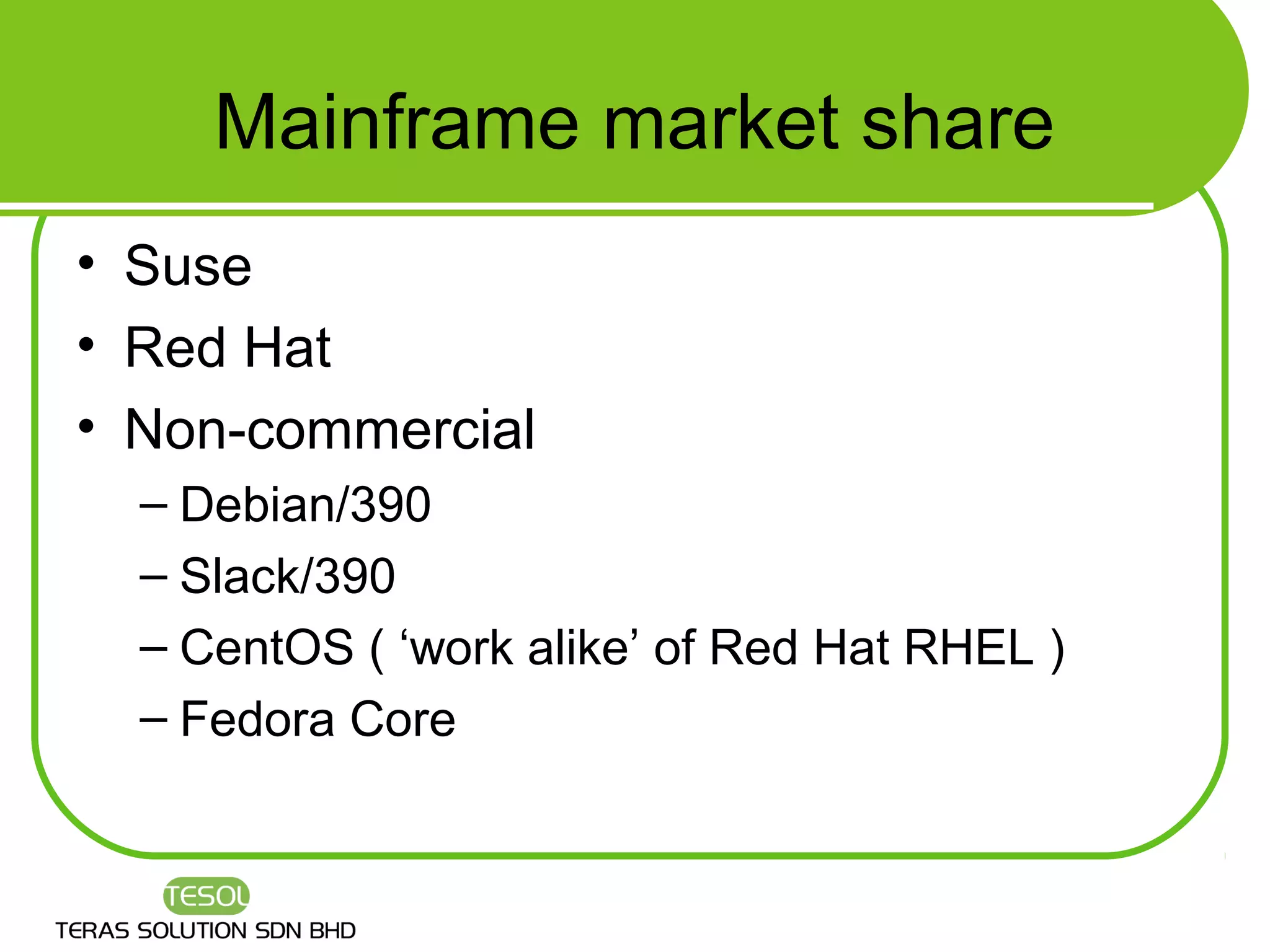
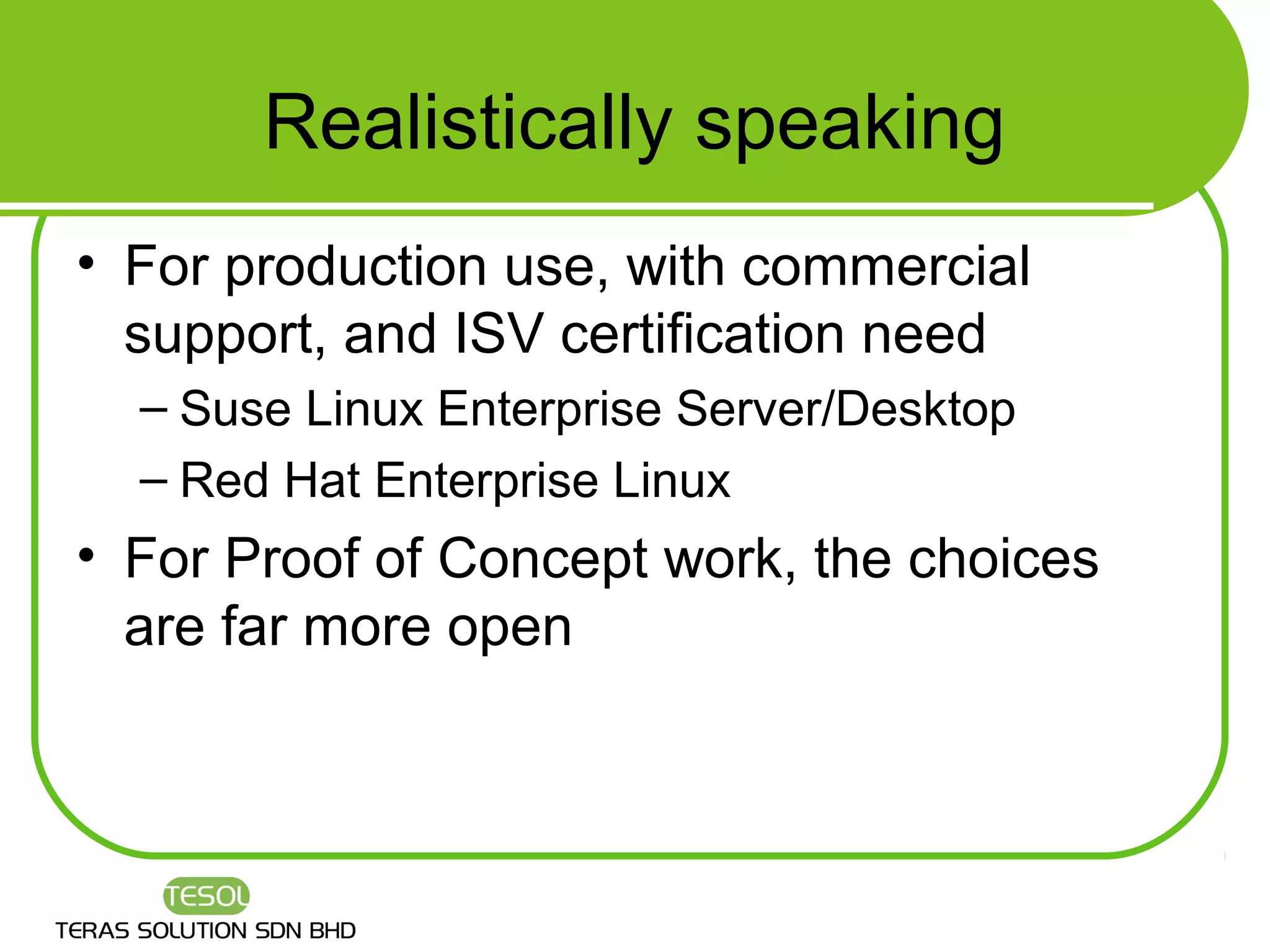
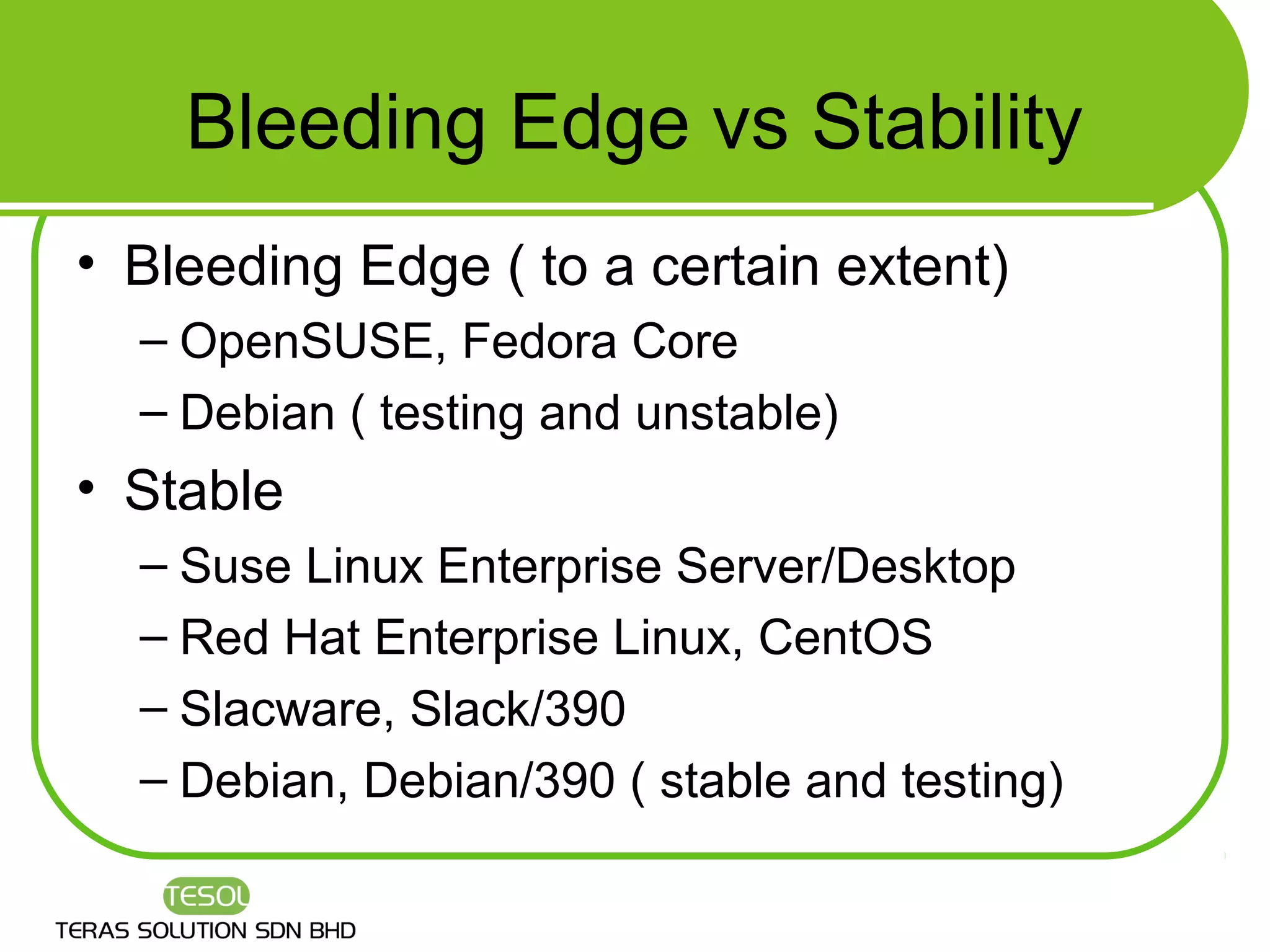
This document provides an introduction to Linux, including what Linux is, what an operating system is, common Linux features, advantages of Linux, how to select a Linux distribution, and additional resources for learning more. It discusses that Linux is an open source operating system created by Linus Torvalds in 1991 and is now developed by thousands of contributors. Key features covered include multi-user access, multi-tasking, hardware support, networking, and graphical user interfaces.