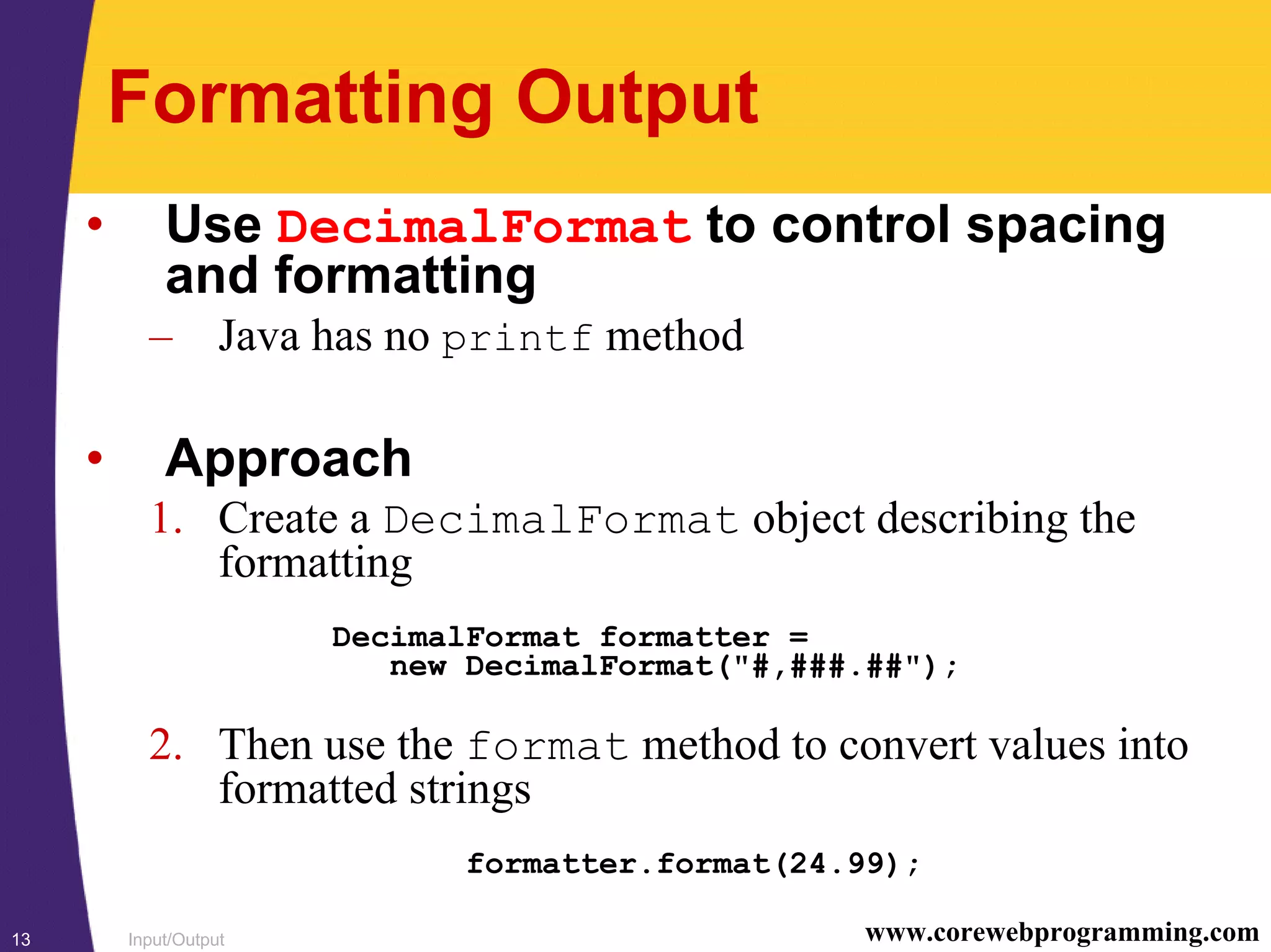
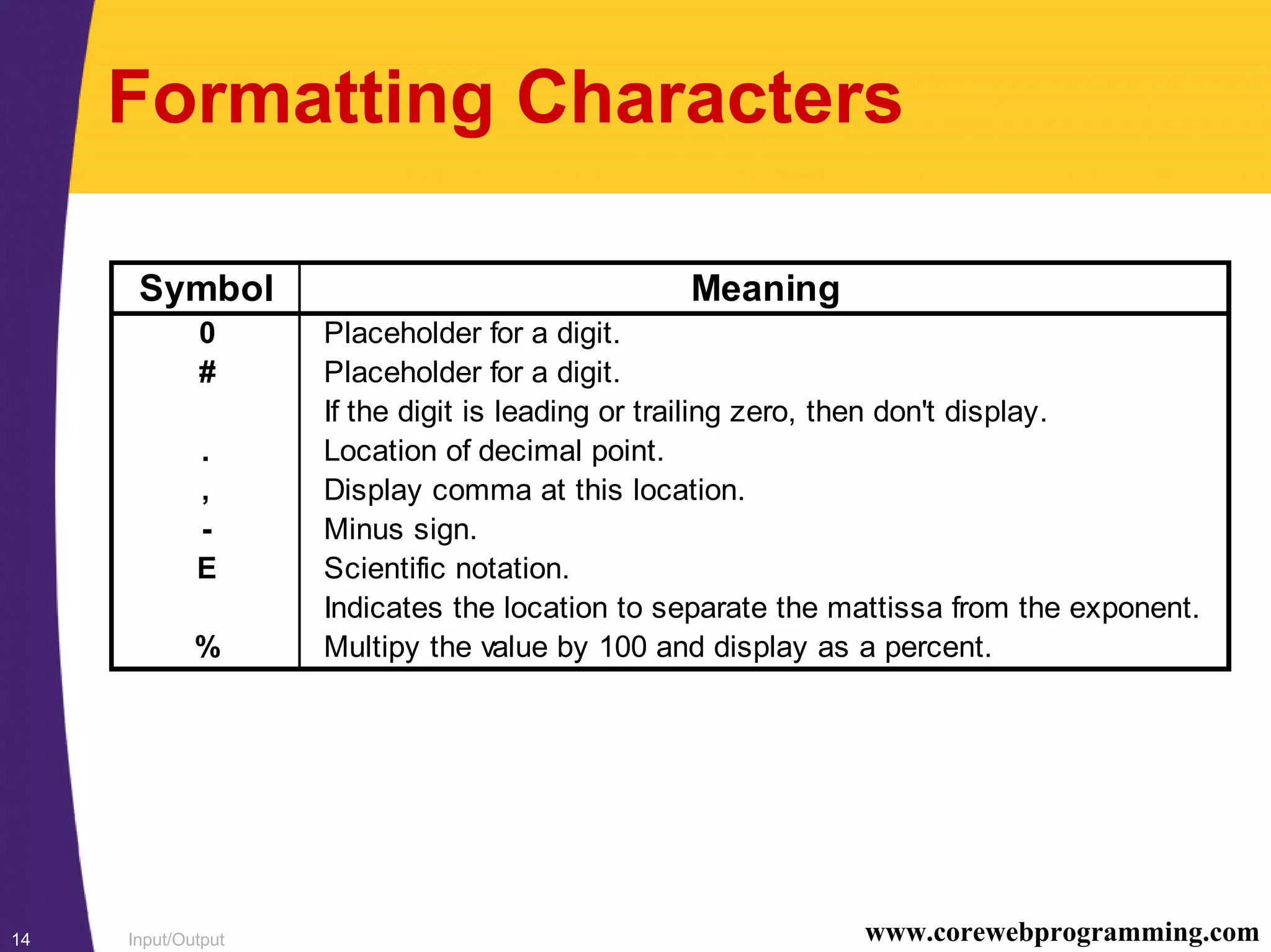
This document discusses input/output (I/O) in Java. It covers handling files and directories using the File class, understanding character-based and byte-based streams, and examples of character and binary file input/output. Character I/O uses Readers and Writers, while binary I/O uses DataStreams. A BufferedReader is required to read full lines of text from a file. Formatting output is handled using DecimalFormat since Java has no printf method. Streams can be chained together, such as a FileOutputStream chained to a DataOutputStream for binary file output.

![Input/Output5 www.corewebprogramming.com
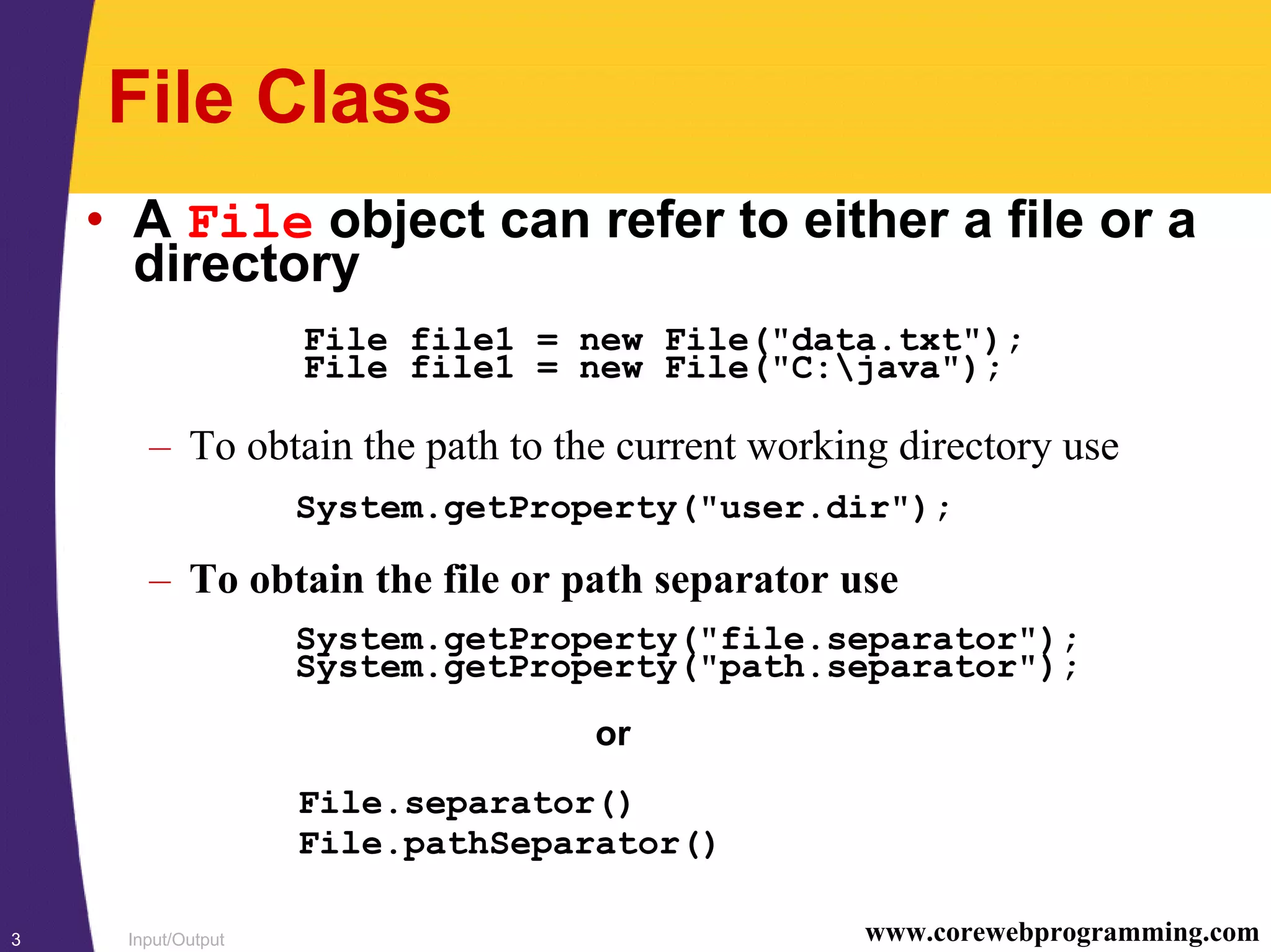
Directory Listing, Example
import java.io.*;
public class DirListing {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File dir = new File(System.getProperty("user.dir"));
if(dir.isDirectory()){
System.out.println("Directory of " + dir);
String[] listing = dir.list();
for(int i=0; i<listing.length; i++) {
System.out.println("t" + listing[i]);
}
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5javaio-1229589834627837-2/75/5java-Io-5-2048.jpg)

![Input/Output8 www.corewebprogramming.com
Character File Output
Desired … Methods Construction
Character File Ouput FileWriter File file = new File("filename");
write(int char) FileWriter fout = new FileWriter(file);
write(byte[] buffer) or
write(String str) FileWriter fout = new FileWriter("filename");
Buffered Character BufferedWriter File file = new File("filename");
File Output write(int char) FileWriter fout = new FileWriter(file);
write(char[] buffer) BufferedWriter bout = new BufferedWriter(fout);
write(String str) or
newLine() BufferedWriter bout = new BufferedWriter(
new FileWriter(
new File("filename")));](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5javaio-1229589834627837-2/75/5java-Io-8-2048.jpg)
![Input/Output9 www.corewebprogramming.com
Character File Output, cont.
Desired … Methods Construction
Character Output PrintWriter FileWriter fout = new FileWriter("filename");
write(int char) PrintWriter pout = new PrintWriter(fout);
write(char[] buffer) or
writer(String str) PrintWriter pout = new PrintWriter(
print( … ) new FileWriter("filename"));
println( … ) or
PrintWriter pout = new PrintWriter(
new BufferedWriter(
new FileWriter("filename")));](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5javaio-1229589834627837-2/75/5java-Io-9-2048.jpg)
![Input/Output10 www.corewebprogramming.com
FileWriter
• Constructors
– FileWriter(String filename)/FileWriter(File file)
• Creates a output stream using the default encoding
– FileWriter(String filename, boolean append)
• Creates a new output stream or appends to the existing output
stream (append = true)
• Useful Methods
– write(String str)/write(char[] buffer)
• Writes string or array of chars to the file
– write(int char)
• Writes a character (int) to the file
– flush
• Writes any buffered characters to the file
– close
• Closes the file stream after performing a flush
– getEncoding
• Returns the character encoding used by the file stream](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5javaio-1229589834627837-2/75/5java-Io-10-2048.jpg)
![Input/Output11 www.corewebprogramming.com
CharacterFileOutput, Example
import java.io.*;
public class CharacterFileOutput {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileWriter out = null;
try {
out = new FileWriter("book.txt");
System.out.println("Encoding: " + out.getEncoding());
out.write("Core Web Programming");
out.close();
out = null;
} catch(IOException ioe) {
System.out.println("IO problem: " + ioe);
ioe.printStackTrace();
try {
if (out != null) {
out.close();
}
} catch(IOException ioe2) { }
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5javaio-1229589834627837-2/75/5java-Io-11-2048.jpg)

![Input/Output15 www.corewebprogramming.com
NumFormat, Example
import java.text.*;
public class NumFormat {
public static void main (String[] args) {
DecimalFormat science = new DecimalFormat("0.000E0");
DecimalFormat plain = new DecimalFormat("0.0000");
for(double d=100.0; d<140.0; d*=1.10) {
System.out.println("Scientific: " + science.format(d) +
" and Plain: " + plain.format(d));
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5javaio-1229589834627837-2/75/5java-Io-15-2048.jpg)

![Input/Output17 www.corewebprogramming.com
Character File Input
Desired … Methods Construction
Character File Input FileReader File file = new File("filename");
read() FileReader fin = new FileReader(file);
read(char[] buffer) or
FileReader fin = new FileReader("filename");
Buffered Character BufferedReader File file = new File("filename");
File Input read() FileReader fin = new FileReader(file);
read(char[] buffer) BufferedReader bin = new BufferedReader(fin);
readLine() or
BufferedReader bin = new BufferedReader(
new FileReader(
new File("filename")));](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5javaio-1229589834627837-2/75/5java-Io-17-2048.jpg)
![Input/Output18 www.corewebprogramming.com
FileReader
• Constructors
– FileReader(String filename)/FileReader(File file)
• Creates a input stream using the default encoding
• Useful Methods
– read/read(char[] buffer)
• Reads a single character or array of characters
• Returns –1 if the end of the steam is reached
– reset
• Moves to beginning of stream (file)
– skip
• Advances the number of characters
• Note: Wrap a BufferedReader around the FileReader to
read full lines of text using readLine](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5javaio-1229589834627837-2/75/5java-Io-18-2048.jpg)
![Input/Output19 www.corewebprogramming.com
CharacterFileInput, Example
import java.io.*;
public class CharacterFileInput {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("book.txt");
FileReader in = null;
if(file.exists()) {
try {
in = new FileReader(file);
System.out.println("Encoding: " + in.getEncoding());
char[] buffer = new char[(int)file.length()];
in.read(buffer);
System.out.println(buffer);
in.close();
} catch(IOException ioe) {
System.out.println("IO problem: " + ioe);
ioe.printStackTrace();
...
}
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5javaio-1229589834627837-2/75/5java-Io-19-2048.jpg)

![Input/Output21 www.corewebprogramming.com
Console Input
• To read input from the console, a stream
must be associated with the standard input,
System.in
import java.io.*;
public class IOInput{
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedReader keyboard;
String line;
try {
System.out.print("Enter value: ");
System.out.flush();
keyboard = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(System.in));
line = keyboard.readLine();
} catch(IOException e) {
System.out.println("Error reading input!"); }
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5javaio-1229589834627837-2/75/5java-Io-21-2048.jpg)
![Input/Output22 www.corewebprogramming.com
Binary File Input and Output
• Handle byte-based I/O using a
DataInputStream or DataOutputStream
– The readFully method blocks until all bytes are read or an EOF occurs
– Values are written in big-endian fashion regardless of computer platform
DataType DataInputStream DataOutputStream
byte readByte writeByte
short readShort writeShort
int readInt writeInt
long readLong writeLong
float readFloat writeFloat
double readDouble writeDouble
boolean readBoolean writeBoolean
char readChar writeChar
String readUTF writeUTF
byte[] readFully](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5javaio-1229589834627837-2/75/5java-Io-22-2048.jpg)
![Input/Output24 www.corewebprogramming.com
Binary File Output
Desired … Methods Construction
Binary File Output FileOutputStream File file = new File("filename");
bytes write(byte) FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream(file);
write(byte[] buffer) or
FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream("filename");
Binary File Output DataOutputStream File file = new File("filename");
byte writeByte(byte) FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream(file);
short writeShort(short) DataOutputStream dout = new DataOutputStream(fout);
int writeInt(int)
long writeLong(long) or
float writeFloat(float)
double writeDouble(double) DataOutputStream dout = new DataOutputStream(
char writechar(char) new FileOutputStream(
boolean writeBoolean(boolean) new File("filename")));
writeUTF(string)
writeBytes(string)
writeChars(string)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5javaio-1229589834627837-2/75/5java-Io-24-2048.jpg)
![Input/Output25 www.corewebprogramming.com
Binary File Output, cont.
Desired … Methods Construction
Buffered Binary BufferedOutputStream File file = new File("filename");
File Output flush() FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream(file);
write(byte) BufferedOutputStream bout = new BufferedOutputStream(fout);
write(byte[] buffer, int off, int len) DataOutputStream dout = new DataOutputStream(bout);
or
DataOutputStream dout = new DataOutputStream(
new BufferedOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream(
new File("filename"))));](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5javaio-1229589834627837-2/75/5java-Io-25-2048.jpg)
![Input/Output26 www.corewebprogramming.com
BinaryFileOutput, Example
import java.io.*;
public class BinaryFileOutput {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] primes = { 1, 2, 3, 5, 11, 17, 19, 23 };
DataOutputStream out = null;
try {
out = new DataOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream("primes.bin"));
for(int i=0; i<primes.length; i++) {
out.writeInt(primes[i]);
}
out.close();
} catch(IOException ioe) {
System.out.println("IO problem: " + ioe);
ioe.printStackTrace();
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5javaio-1229589834627837-2/75/5java-Io-26-2048.jpg)
![Input/Output27 www.corewebprogramming.com
Binary File Input
Desired … Methods Construction
Binary File Input FileInputStream File file = new File("filename");
bytes read() FileInputStream fin = new FileInputStream(file);
read(byte[] buffer) or
FileInputStream fin = new FileInputStream("filename");
Binary File Input DataInputStream File file = new File("filename");
byte readByte() FileInputStream fin = new FileInputStream(file);
short readShort() DataInputStream din = new DataInputStream(fin);
int readInt()
long readLong() or
float readFloat()
double readDouble() DataInputStream din = new DataInputStream(
char readchar() new FileInputStream(
boolean readBoolean() new File("filename")));
readUTF()
readFully(byte[] buffer)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5javaio-1229589834627837-2/75/5java-Io-27-2048.jpg)
![Input/Output28 www.corewebprogramming.com
Binary File Input, cont.
Desired … Methods Construction
Bufferred Binary BufferedInputStream File file = new File("filename");
File Input read() FileInputStream fin = new FileInputStream(file);
read(byte[] buffer, int off, int len) BufferedInputStream bin = new BufferedInputStream(fin);
skip(long) DataInputStream din = new DataInputStream(bin);
or
DataInputStream din = new DataInputStream(
new BufferedInputStream(
new FileInputStream(
new File("filename"))));](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5javaio-1229589834627837-2/75/5java-Io-28-2048.jpg)
![Input/Output29 www.corewebprogramming.com
BinaryFileInput, Example
import java.io.*;
public class BinaryFileInput {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DataInputStream in = null;
File file = new File("primes.bin");
try {
in = new DataInputStream(
new FileInputStream(file));
int prime;
long size = file.length()/4; // 4 bytes per int
for(long i=0; i<size; i++) {
prime = in.readInt();
System.out.println(prime);
}
in.close();
} catch(IOException ioe) {
System.out.println("IO problem: " + ioe);
ioe.printStackTrace();
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5javaio-1229589834627837-2/75/5java-Io-29-2048.jpg)

