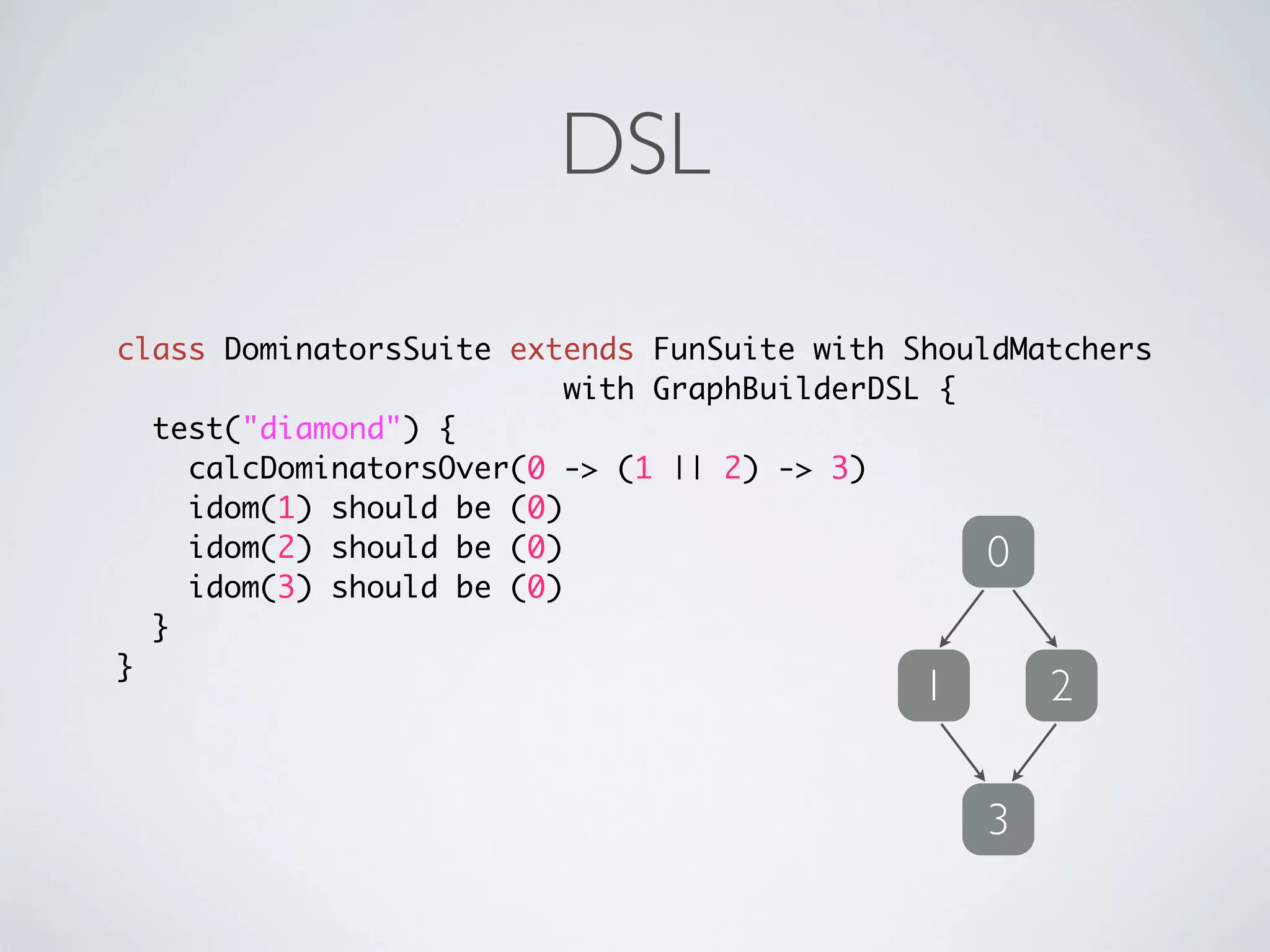
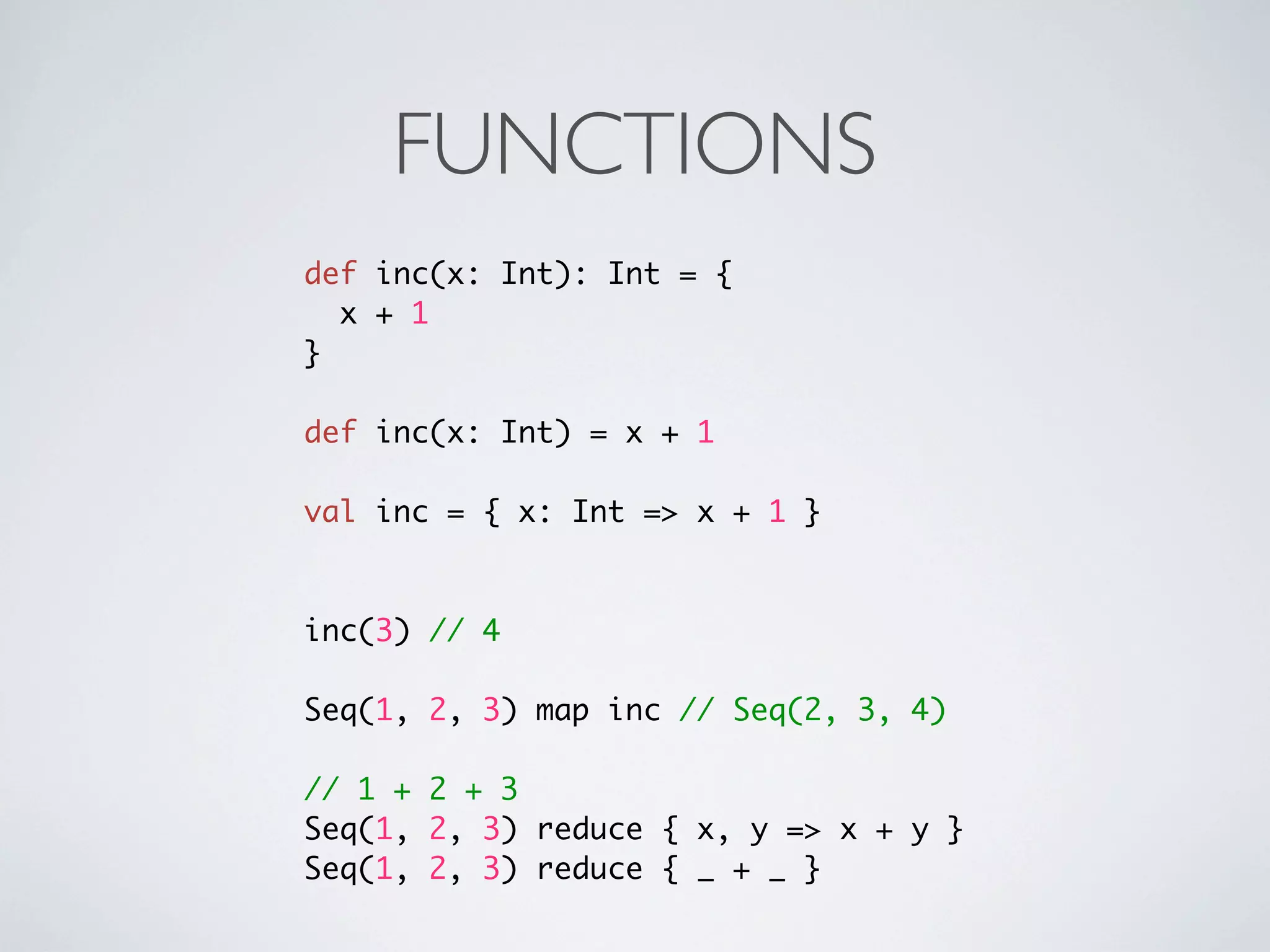
The document provides an overview of Scala, its history, and features such as safety, efficiency, object-oriented and functional programming capabilities. It includes examples of Scala syntax and usage, showcasing its flexibility through various constructs like classes, traits, and functions, as well as collection manipulations. Additionally, it references resources for further learning and libraries for development.













![OOP: TRAITS
trait Ordered[A] {
def compare(that: A): Int
def < (that: A): Boolean = (this compare that) < 0
def > (that: A): Boolean = (this compare that) > 0
def <= (that: A): Boolean = (this compare that) <= 0
def >= (that: A): Boolean = (this compare that) >= 0
def compareTo(that: A): Int = compare(that)
}
class Money extends Ordered[Money] with SomeOtherTrait {
def compare(that: Money) = ...
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-121130090832-phpapp01/75/A-bit-about-Scala-15-2048.jpg)





![DEMO
import java.util.ArrayList;
// ...
Person[] people, minors, adults;
void foo() {
ArrayList<Person> minorsList = new ArrayList<Person>();
Java
ArrayList<Person> adultsList = new ArrayList<Person>();
for (Person person : people)
(person.age < 18 ? minorsList : adultsList).
add(person);
minors = minorsList.toArray(new Person[minorsList.size()]);
adults = adultsList.toArray(new Person[adultsList.size()]);
}
Scala
val people: Array[Person]
val (minors, adults) = people partition { _.age < 18 }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-121130090832-phpapp01/75/A-bit-about-Scala-22-2048.jpg)





![BONUS: CONCURRENCY
actor {
receive {
case people: Set[Person] =>
val (minors, adults) = people partition { _.age < 18 }
School ! minors
Work ! adults
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-121130090832-phpapp01/75/A-bit-about-Scala-28-2048.jpg)
![BONUS: PARALLELISM
val people: Array[Person]
val (minors, adults) = people partition { _.age < 18 }
val (minors, adults) = people.par partition { _.age < 18 }
ag ic!
M](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-121130090832-phpapp01/75/A-bit-about-Scala-29-2048.jpg)
![BONUS: FUTURES
val f: Future[List[String]] = future {
session.getRecentPosts
}
f onFailure {
case t => println("An error has occured: " + t.getMessage)
}
f onSuccess {
case posts => posts foreach println
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scala-121130090832-phpapp01/75/A-bit-about-Scala-30-2048.jpg)

