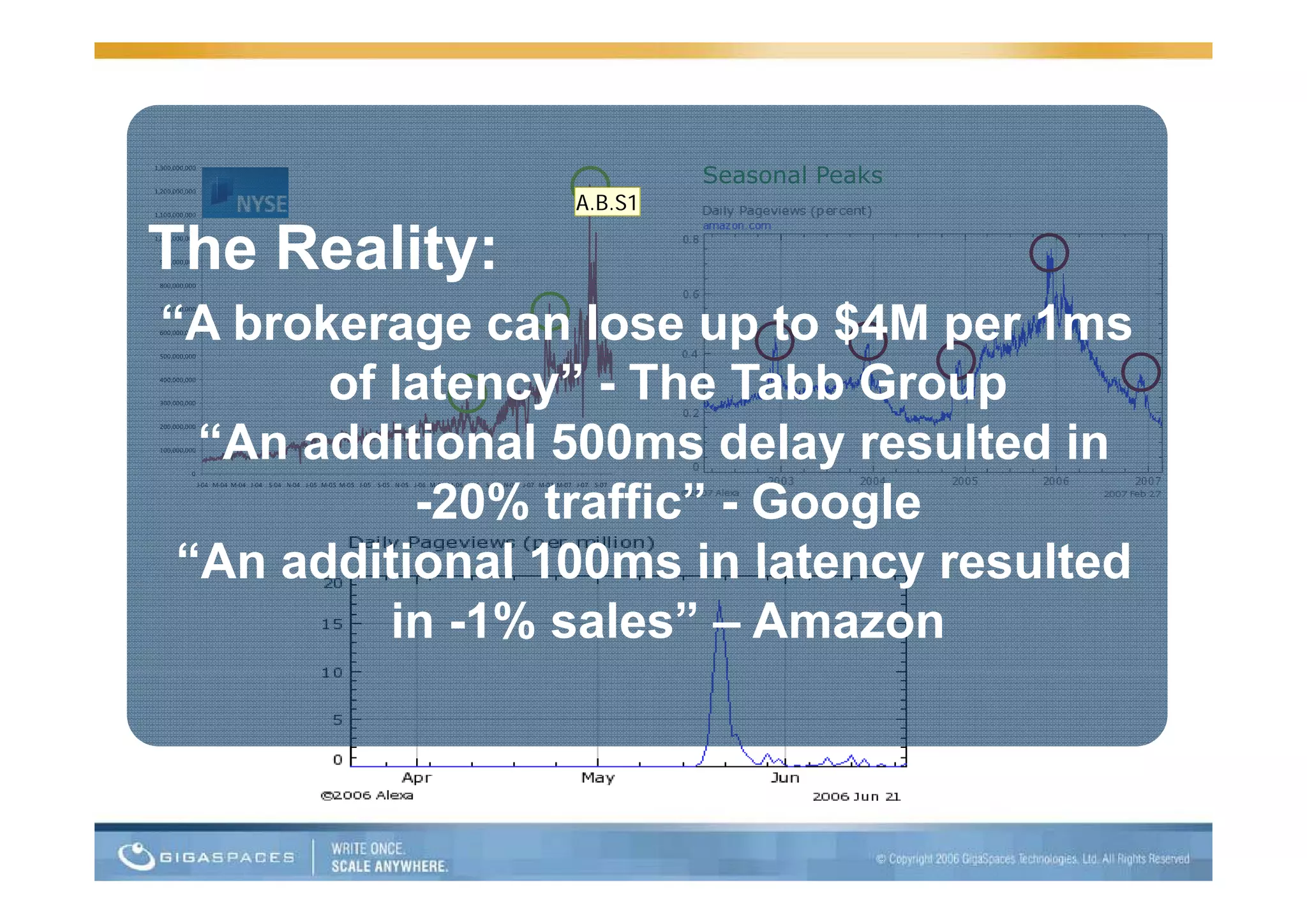
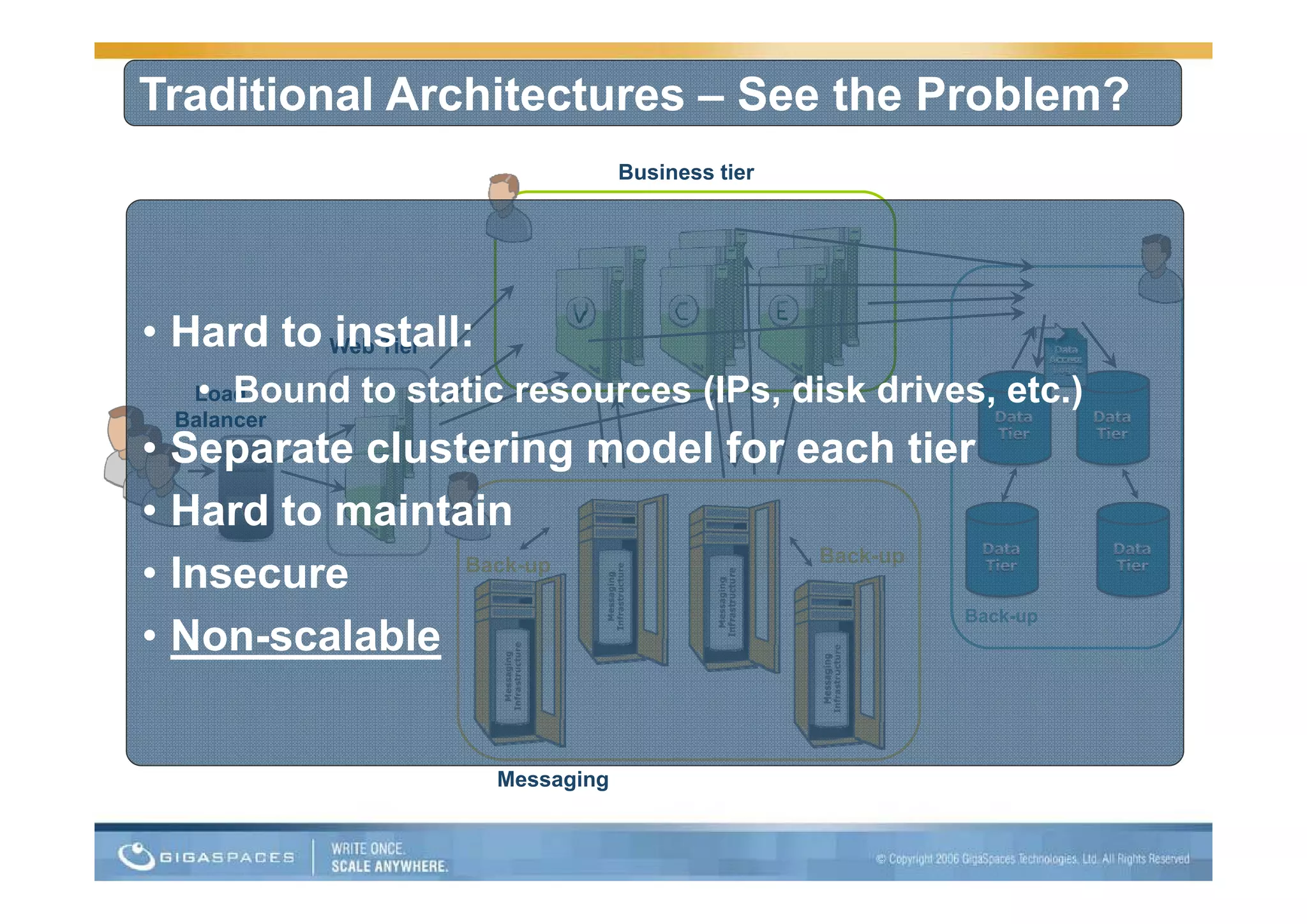
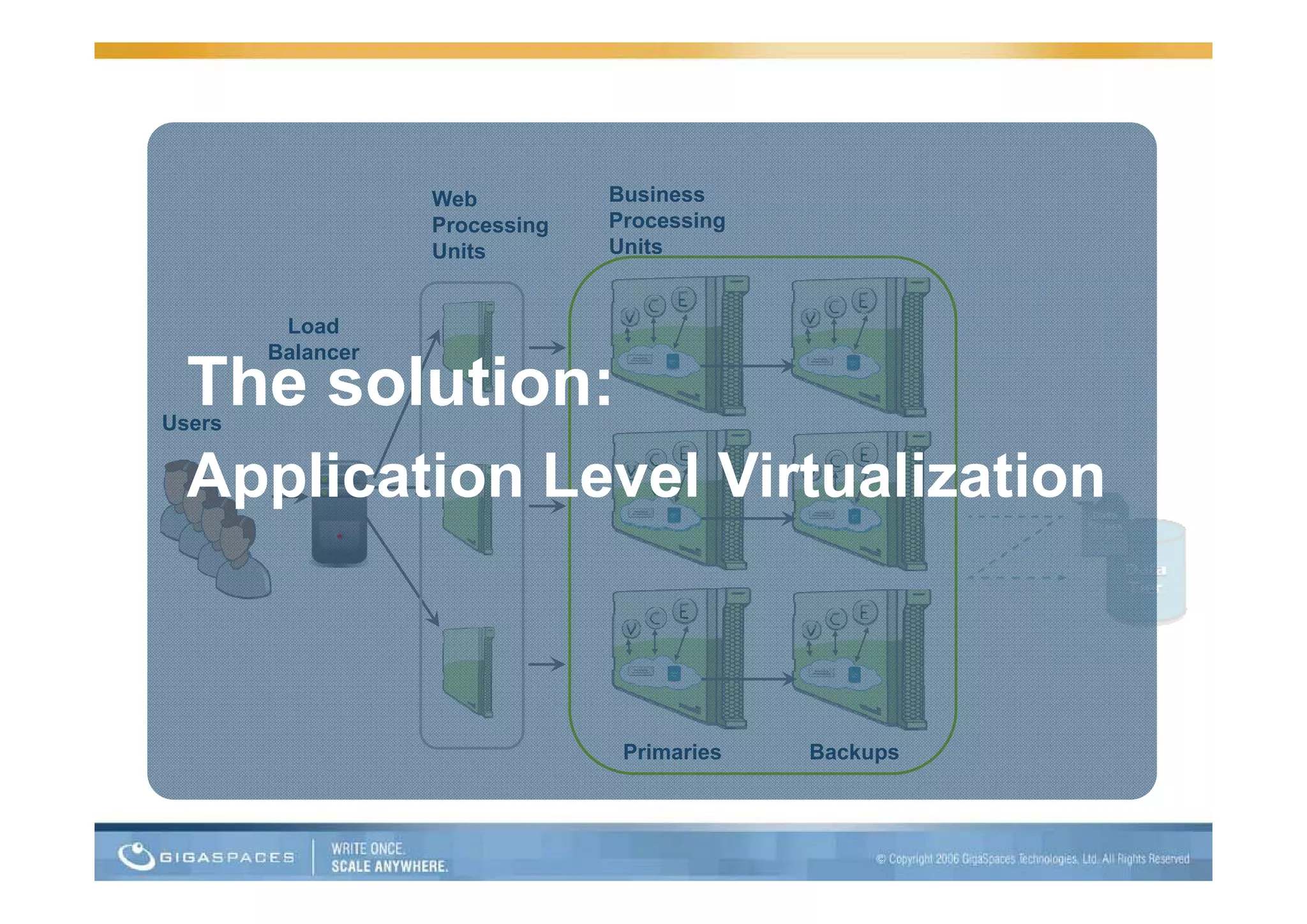
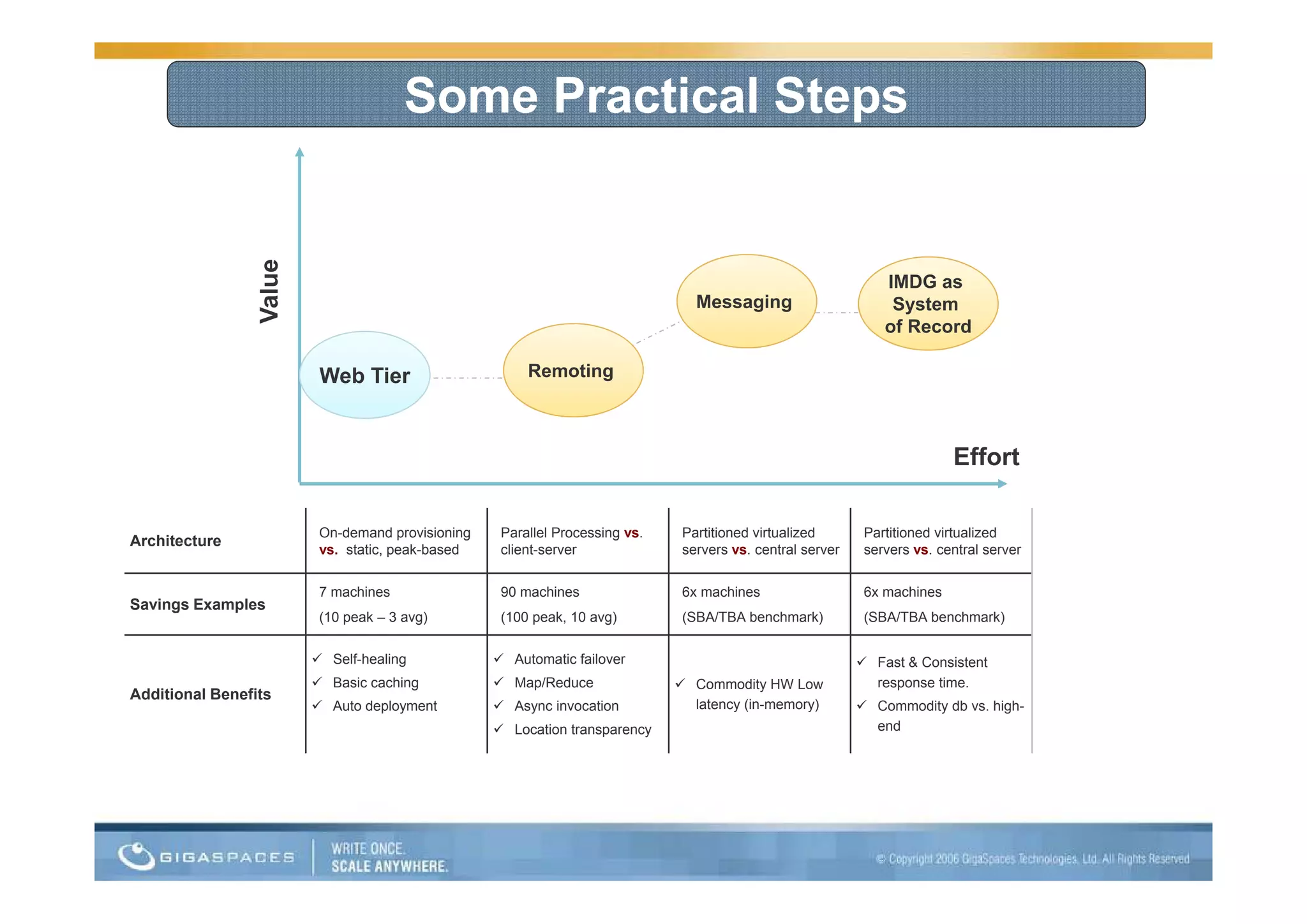
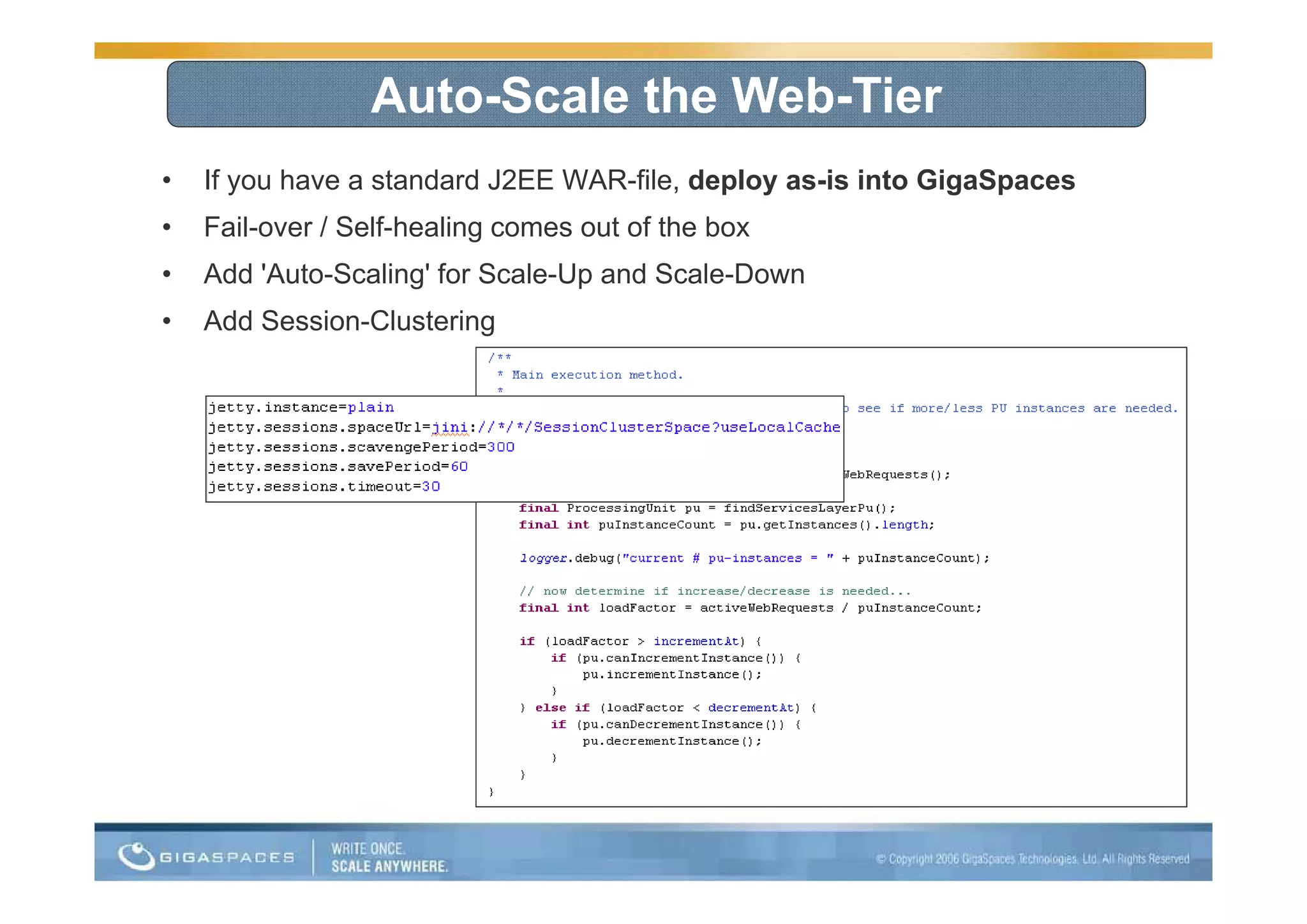
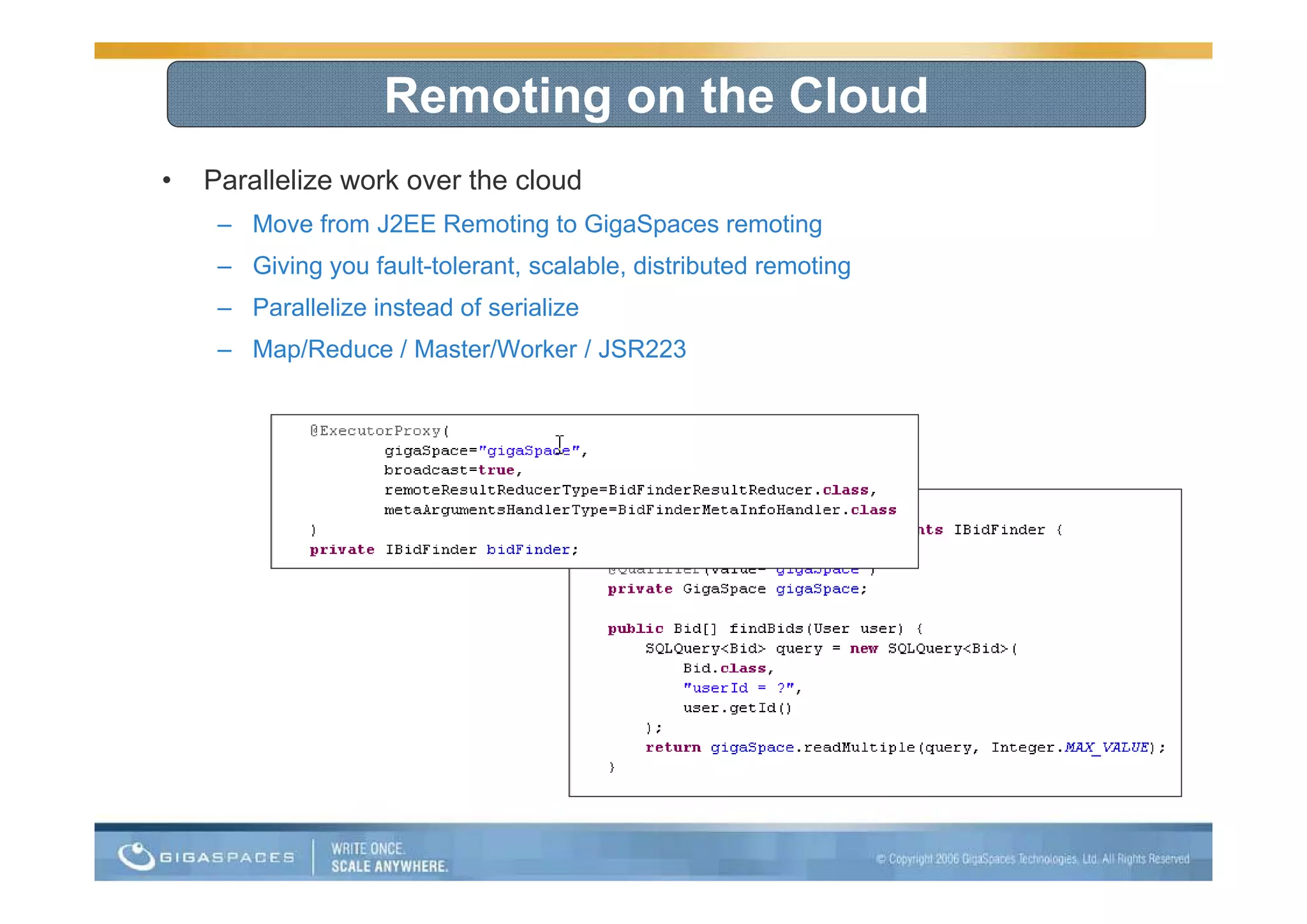
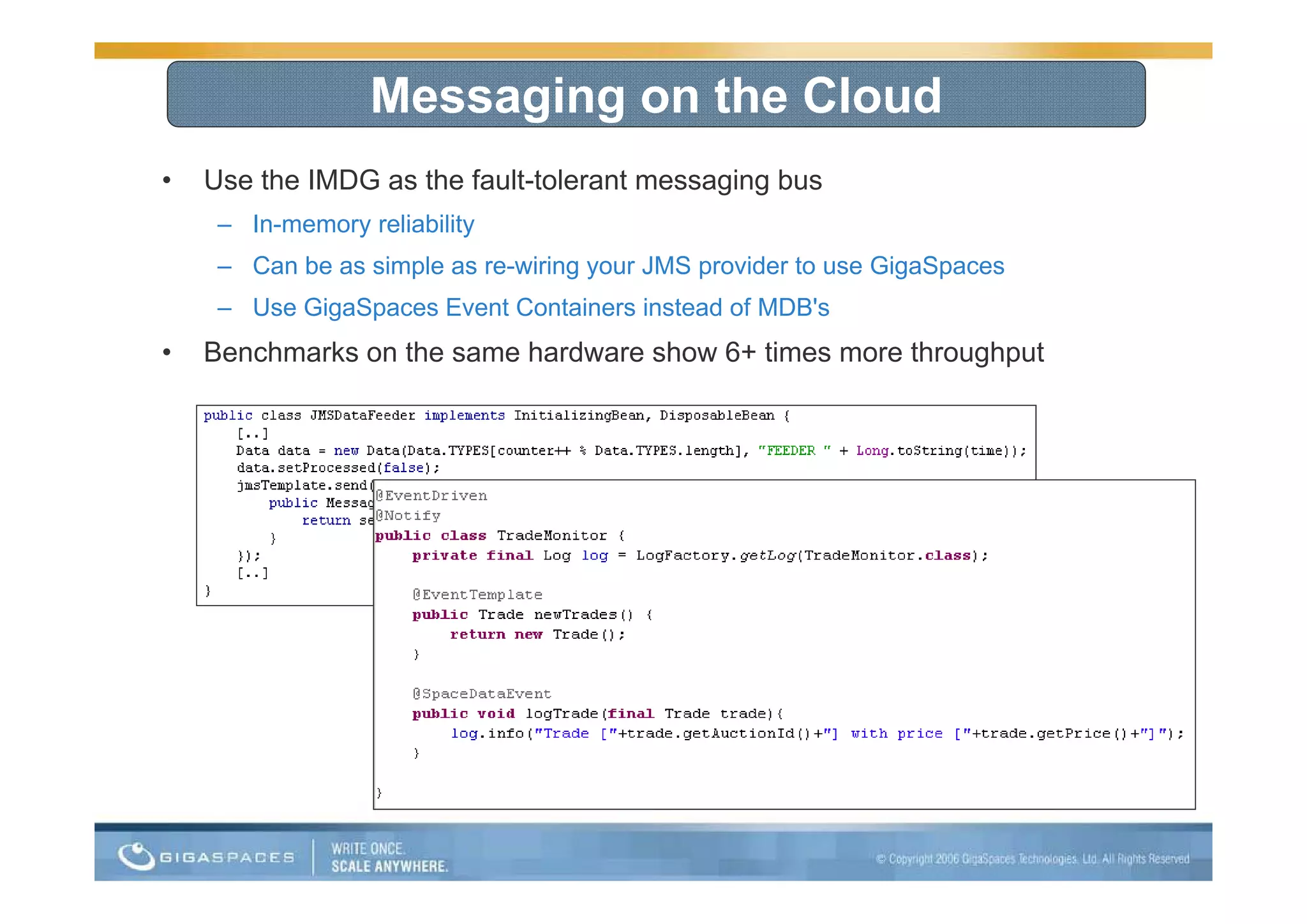
This document discusses building applications for the cloud and provides best practices. It notes that deploying applications on the cloud introduces challenges related to scalability, reliability, security, and management. It recommends that applications be designed to be elastic, memory-based, and easy to operate in order to fully take advantage of the cloud. Specific steps are outlined, such as using in-memory data grids for messaging and as the system of record, and auto-scaling the web tier.