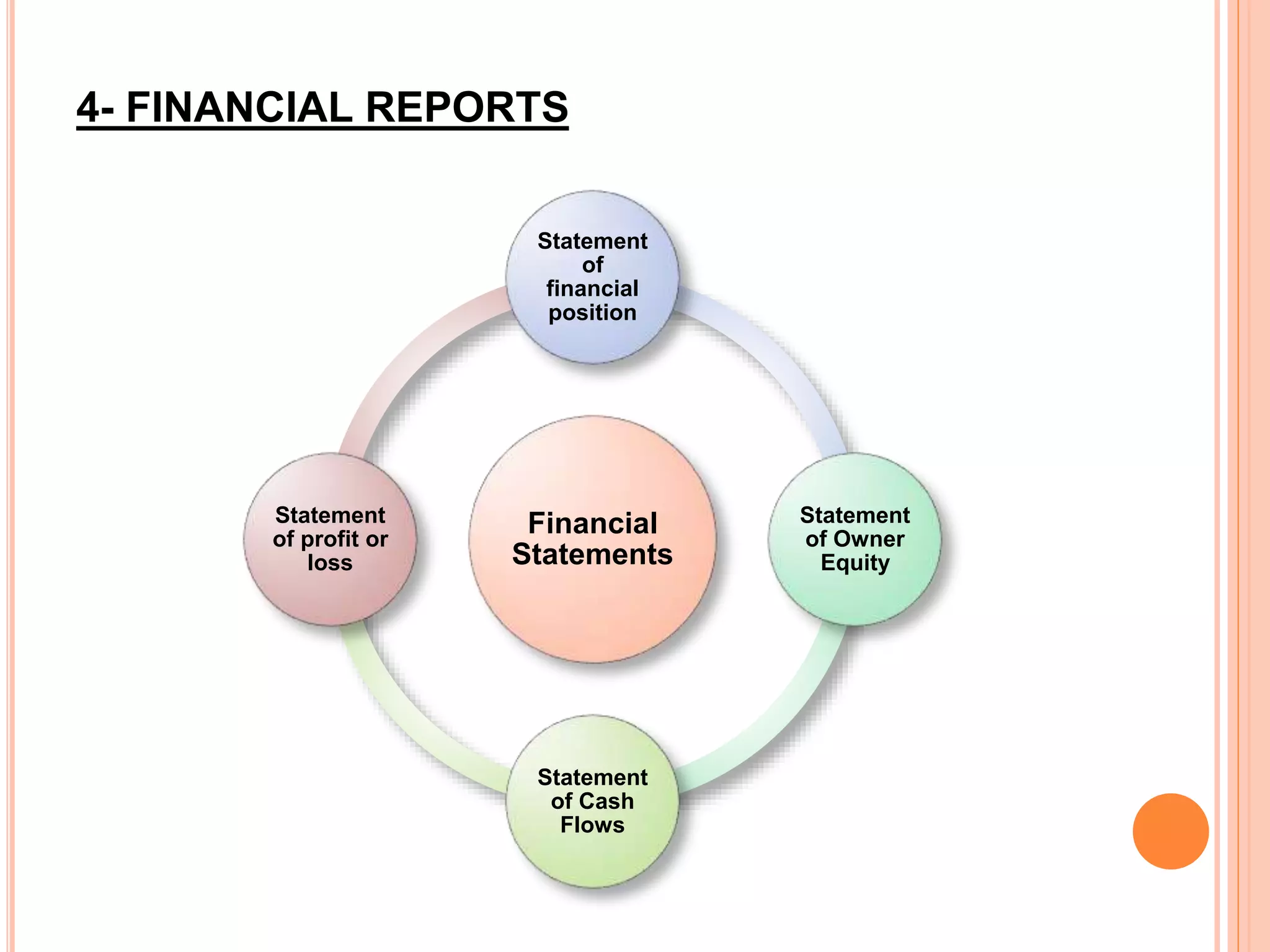
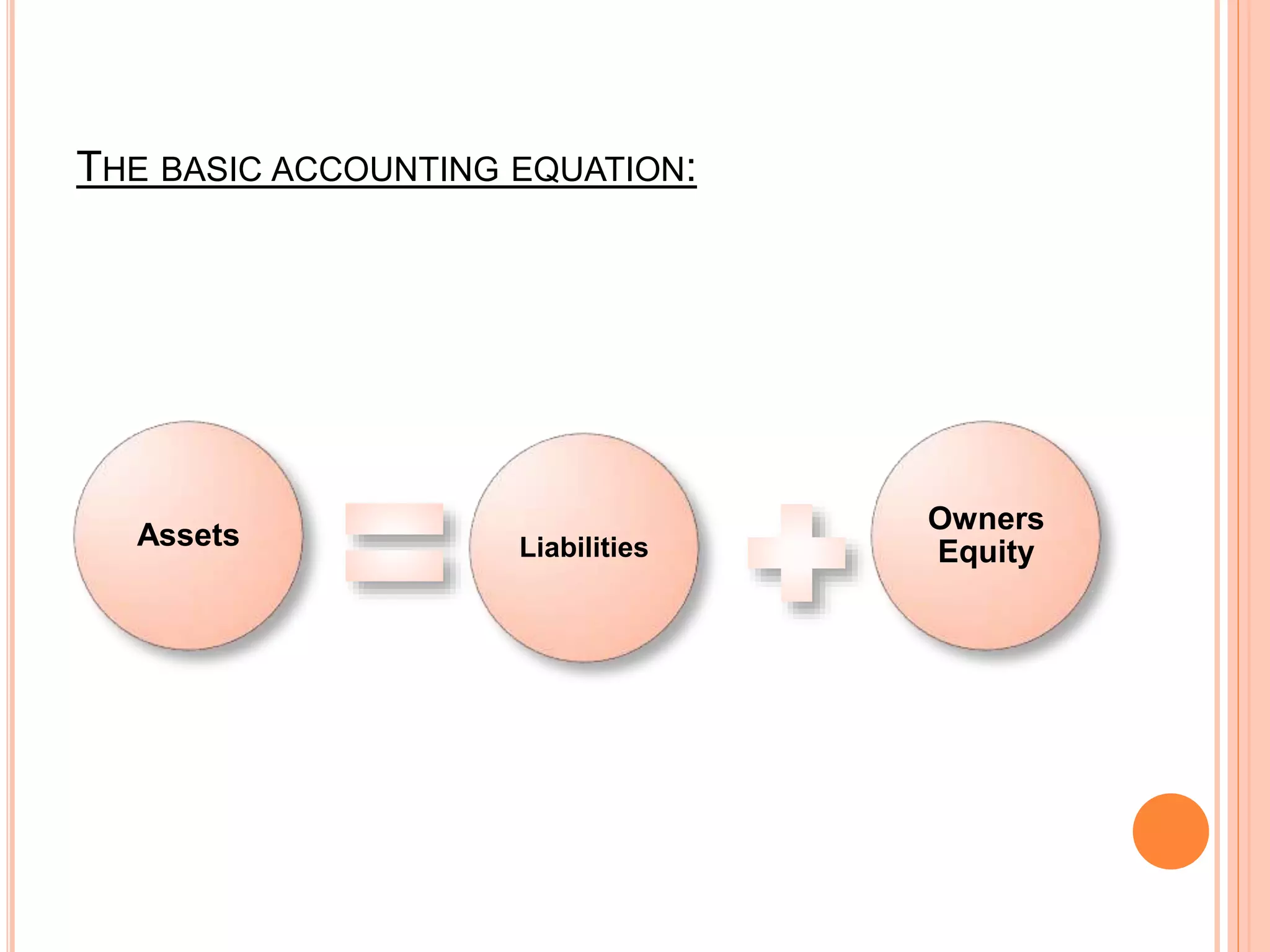
This document provides an overview of accounting basics and principles. It defines accounting as the process of identifying, recording, and communicating financial information. The objectives of accounting are to provide useful information to decision makers through relevance, reliability, and other qualitative characteristics. The document outlines key accounting principles like the business entity, accrual basis, and matching principles. It also describes the main financial statements - the balance sheet, income statement, statement of cash flows, and statement of owners' equity - and their purpose in communicating financial information to both internal and external users of accounting data.